Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Prices Received Index (Jan)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Prices Received Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing New Orders Index (Jan)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing New Orders Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Export Price Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. Export Price Index YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Jan)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)
U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Export Price Index MoM (Nov)
U.S. Export Price Index MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Nov)
Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Nov)
Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)
U.S. Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Nov)
Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Nov)
Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Philadelphia Fed Business Activity Index (SA) (Jan)
U.S. Philadelphia Fed Business Activity Index (SA) (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks ChangeA:--
F: --
P: --
 Richmond Federal Reserve President Barkin delivered a speech.
Richmond Federal Reserve President Barkin delivered a speech. U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central Banks
U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central BanksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany CPI Final MoM (Dec)
Germany CPI Final MoM (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany CPI Final YoY (Dec)
Germany CPI Final YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany HICP Final MoM (Dec)
Germany HICP Final MoM (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany HICP Final YoY (Dec)
Germany HICP Final YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil PPI MoM (Nov)
Brazil PPI MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada New Housing Starts (Dec)
Canada New Housing Starts (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Capacity Utilization MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Capacity Utilization MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Industrial Output YoY (Dec)
U.S. Industrial Output YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Manufacturing Capacity Utilization (Dec)
U.S. Manufacturing Capacity Utilization (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Manufacturing Output MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Manufacturing Output MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. NAHB Housing Market Index (Jan)
U.S. NAHB Housing Market Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia CPI YoY (Dec)
Russia CPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Core Machinery Orders YoY (Nov)
Japan Core Machinery Orders YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Core Machinery Orders MoM (Nov)
Japan Core Machinery Orders MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Jan)
U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland GDP YoY (YTD) (Q4)
China, Mainland GDP YoY (YTD) (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Dec)
China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Industrial Output Final MoM (Nov)
Japan Industrial Output Final MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Industrial Output Final YoY (Nov)
Japan Industrial Output Final YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Core HICP Final MoM (Dec)
Euro Zone Core HICP Final MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone HICP Final MoM (Dec)
Euro Zone HICP Final MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone HICP Final YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone HICP Final YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone HICP MoM (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)
Euro Zone HICP MoM (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Core CPI Final YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone Core CPI Final YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Core HICP Final YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone Core HICP Final YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone CPI YoY (Excl. Tobacco) (Dec)
Euro Zone CPI YoY (Excl. Tobacco) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Core CPI Final MoM (Dec)
Euro Zone Core CPI Final MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Dec)
Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Trimmed CPI YoY (SA) (Dec)
Canada Trimmed CPI YoY (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (Dec)
Canada CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (Dec)
Canada CPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI YoY (Dec)
Canada Core CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (Dec)
Canada Core CPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea PPI MoM (Dec)
South Korea PPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland 1-Year Loan Prime Rate (LPR)
China, Mainland 1-Year Loan Prime Rate (LPR)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland 5-Year Loan Prime Rate
China, Mainland 5-Year Loan Prime Rate--
F: --
P: --
 Germany PPI YoY (Dec)
Germany PPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany PPI MoM (Dec)
Germany PPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --













































No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
Canada and China dramatically cut tariffs on EVs and canola, signaling a major reset and strategic trade recalibration.
Canada and China have forged a new trade agreement that dramatically lowers tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles (EVs) and Canadian canola, signaling a major reset in relations between the two countries. The deal was announced during Prime Minister Mark Carney’s visit to Beijing, the first by a Canadian prime minister since 2017.

The agreement aims to mend diplomatic and economic ties that have frayed in recent years, positioning Canada to navigate a complex global trade environment.
The centerpiece of the deal is a significant rollback of tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles. Under the new terms, Canada will permit an initial quota of 49,000 Chinese EVs to enter the country at a 6.1% tariff.
This marks a stark reversal from the 100% tariff imposed in 2024 under former Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, a policy that mirrored similar penalties from the United States. For context, China exported 41,678 EVs to Canada in 2023.
"This is a return to levels prior to recent trade frictions, but under an agreement that promises much more for Canadians," Carney told reporters after meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping.
The EV quota is set to expand, reaching approximately 70,000 vehicles within five years. Carney justified the policy shift as a strategic move to bolster Canada's own EV industry.
"For Canada to build its own competitive EV sector, we will need to learn from innovative partners, access their supply chains, and increase local demand," he explained. This new rationale moves away from the previous government's argument that high tariffs were necessary to shield domestic manufacturers from subsidized competition.
In exchange for the EV concessions, China has agreed to adjust its own trade measures:
• Canola Seed: Tariffs will be reduced from 84% to a combined rate of about 15% by March 1.
• Other Agricultural Goods: Anti-discrimination tariffs on Canadian canola meal, lobsters, crabs, and peas are expected to be removed from March 1 through the end of the year.
China’s Commerce Ministry confirmed it was adjusting anti-dumping and anti-discrimination measures on Canadian agricultural and aquatic products in response to Canada’s move on EV tariffs. Carney estimated the deal would unlock nearly $3 billion in new export orders for Canadian farmers and fish harvesters.
The deal immediately drew criticism at home. Doug Ford, Premier of Ontario—Canada’s automotive manufacturing hub—condemned the agreement.
"The federal government is inviting a flood of cheap made-in-China electric vehicles without any real guarantee of equal or immediate investments in Canada's economy, auto sector or supply chain," he posted on X.
The policy also represents a departure from Washington's approach. While some members of U.S. President Donald Trump’s cabinet criticized the move ahead of a review of the U.S.-Canada-Mexico trade deal, Trump himself offered his support.
"That's what he should be doing," Trump told reporters. "It's a good thing for him to sign a trade deal. If you can get a deal with China, you should do that."
Beyond the tariff adjustments, the two nations pledged to restart high-level economic and financial dialogues and strengthen cooperation in several key sectors, including agriculture, oil, gas, and green energy.
Carney highlighted Canada's ambitious energy plans, noting that the country will double its energy grid over the next 15 years and sees opportunities for Chinese investment in areas like offshore wind. He also stated that Canada is scaling up its liquified natural gas (LNG) exports, aiming to produce 50 million tonnes annually for Asian markets by 2030.
Additionally, Carney said President Xi committed to providing visa-free access for Canadians traveling to China, though further details were not provided.
Analysts suggest the move is a pragmatic response to Canada's increasingly strained trade relationship with the United States under President Trump, who has imposed tariffs on some Canadian goods.
"Given current complexities in Canada's trade relationship with the U.S., it's no surprise that Carney's government is keen to improve the bilateral trade and investment relationship with Beijing," said Even Rogers Pay of Trivium China.
When asked if China was now a more reliable partner than the U.S., Carney responded, "In terms of the way our relationship has progressed in recent months with China, it is more predictable, and you see results coming from that." He also mentioned having "much alignment of views" with Xi on the topic of Greenland.
While the Canada-China rapprochement could reshape the context of the broader Sino-U.S. rivalry, experts do not expect a dramatic strategic shift away from Washington.
"Canada is a core U.S. ally and deeply embedded in American security and intelligence frameworks," said Sun Chenghao, a fellow at Tsinghua University's Centre for International Security and Strategy. "It is therefore very unlikely to realign strategically away from Washington."
Following weeks of disruptive protests across Iran—met with internet blackouts and a severe security crackdown—US President Donald Trump has kept the region on edge with repeated threats of military action if the violence escalates.
These demonstrations represent one of the most serious challenges the Islamic Republic has faced in years. They have spread across numerous cities, involved diverse social groups, and triggered a level of state force that reveals how threatened the country's leadership feels. By warning Iran against killing protestors, Trump has signaled that internal repression will now have external consequences.
Although the White House pulled back from military action on one occasion, the threat of force remains a key part of the president's strategy. This approach keeps the possibility of escalation alive, preserving the element of surprise and his freedom to act.
While the protests have subsided under heavy repression, many observers believe sustained external pressure from the US is necessary to prevent the Iranian regime from returning to business as usual.
Trump's warnings come at a time when Iran is strategically exposed. Since October 7, 2023, sustained Israeli strikes against its "axis of resistance" and a direct war between the two nations—which included US strikes on Iranian nuclear facilities last summer—have weakened Iran's deterrence and revealed the limits of its defensive capabilities.
The domestic protests add another layer of vulnerability, combining regional setbacks with internal political and economic strain. This creates an opportunity that Washington is now actively seeking to leverage. Understanding Trump's Iran strategy requires looking beyond individual statements and tactical moves to see how his administration is working to turn Iran's accumulated weaknesses into a lasting strategic advantage for the US.
In his second term, President Trump’s Iran policy is a mix of strategic calculation and his belief in pressure and unpredictability. This approach is not improvised; it is rooted in the core principles of his administration's National Security Strategy, which prioritizes strategic competition and deterrence through strength.
The ultimate objective is not classic regime change but "strategic submission." The goal is to force Iran's leadership to accept permanent limits on its nuclear ambitions, scale back its regional influence, and understand that the US is prepared to escalate swiftly if its red lines are crossed.
Iran's future now seems increasingly dependent on how the United States chooses to apply or withhold pressure in the coming months.
Washington's strategy relies on several coordinated efforts designed to constrain Tehran from multiple angles.
Tying Domestic Repression to Global Consequences
A significant policy shift has been the explicit link between Iran's internal conduct and external consequences. Since the protests started, Trump has repeatedly stated that mass killings or executions would provoke a US response, potentially including military force. These threats are designed to attach an international cost to domestic repression at a time when the regime is already stretched thin by regional and economic pressures.
Neutralizing the Nuclear Threat
Iran's nuclear program remains a central focus of Trump's strategy. On June 22 of last year, the US conducted direct military strikes on Iranian nuclear facilities in Operation Midnight Hammer. This marked a major escalation in the effort to deny Tehran a path to a nuclear weapon.
Following the operation, Trump declared that Iran's nuclear program had been "effectively buried." This reflects the administration's view that a combination of US pressure, Israeli military action, covert operations, and cyberattacks has placed Tehran in a strategically weakened position.
Expanding Economic Warfare
Economic pressure, a long-standing tool of Trump's Iran policy, has become broader and more punitive. Beyond the "maximum pressure" sanctions implemented after the US left the Iran nuclear deal in 2018, the administration has proposed a 25% tariff on any country or company doing business with Tehran.
This move from financial sanctions to trade punishment aims to deter third parties from serving as an economic lifeline for Iran. By threatening access to the massive US market, Washington seeks to compound the regime's regional losses with severe domestic economic strain.
Maintaining Military Ambiguity
Military signaling remains a core component of the strategy. Reports indicate that a US aircraft carrier, the USS Lincoln, is en route to the region, though the timing and scope of any future military action remain intentionally ambiguous.
This posture is guided by Trump's belief that Iran has consistently underestimated American resolve. Examples include Tehran's assumption that Washington would not leave the nuclear deal in 2018, its miscalculation before the US killed Qassem Suleimani in 2020, and its actions during the war last summer. Current US force adjustments are intended to prevent Tehran from believing the situation has stabilized.
Even as pressure mounts, President Trump has deliberately left an opening for a negotiated settlement. His references to wanting a deal and "making Iran great again" are transactional signals directed at the leadership, not the Iranian people.
The message is that economic relief and reintegration into the global community are possible, but only after Iran accepts permanent, verifiable limits on its nuclear and ballistic missile programs and alters its regional behavior. The key question is whether Tehran has fully grasped this reality after a series of shocks and warnings.
If Iran has, it is more likely to respond with greater restraint at home and abroad. If not, further miscalculation appears inevitable. Trump's strategy is less about engineering internal change and more about forcing Iran's leaders to recognize the limits of their resistance, with major implications for the regime's durability and the future of US-Iran relations.
China appears to be accelerating its "derisking" strategy by systematically reducing its exposure to U.S. government debt while increasing its gold reserves. This financial pivot reflects a broader policy of diversifying assets amid ongoing geopolitical tensions.
According to data from the U.S. Treasury, China sold another $6.1 billion in U.S. Treasuries in November. This sale brought its total holdings down to $682.6 billion, the lowest level recorded since 2008.
This trend of selling U.S. debt is not new but has intensified since the beginning of the trade conflict with the United States. The move is a core component of China's long-term goal to diversify its massive foreign reserves.
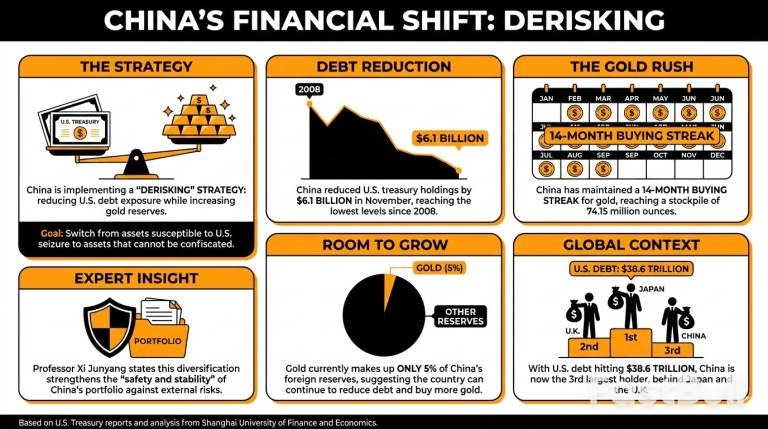
Xi Junyang, a professor at the Shanghai University of Finance and Economics, stated that the reduction is a direct result of a multi-year effort to optimize and diversify foreign asset holdings. This strategy, he explained, is designed to improve the overall safety and stability of the country's financial portfolio.
While China divests from U.S. debt, it is simultaneously accumulating gold. The country is now in the midst of a 14-month gold buying streak. This shift is driven by a desire to move from assets controlled by the U.S. government—and thus susceptible to potential seizure—to hard assets that cannot be controlled or confiscated by third parties.
Currently, China's gold stockpile stands at 74.15 million ounces. However, this impressive figure still only accounts for about 5% of the nation's total foreign reserves. This suggests China has significant capacity to continue selling U.S. debt and converting the proceeds into gold.
Professor Junyang believes this trend will continue, noting that allocating more reserves to gold can enhance the "stability of reserve assets" and strengthen the country's "ability to withstand external risks."
China's strategic asset reallocation is also happening as it voices criticism over the growth of U.S. national debt, which recently surpassed $38.6 trillion with no signs of slowing down.
Despite the consistent selling, China remains the third-largest international holder of U.S. debt, trailing only Japan and the United Kingdom. This indicates that its "derisking" is a gradual and calculated process rather than a sudden exit from the market.

Commodity

Political

Remarks of Officials

Economic

Central Bank

Russia-Ukraine Conflict

Middle East Situation

Daily News
Gold prices edged lower on Friday, pulling back as geopolitical fears surrounding Iran subsided and the U.S. dollar gained strength. The move caps a week of significant gains for the precious metal, which had benefited from safe-haven demand.
Front-month Comex gold for January delivery fell $27.90, or 0.60%, to settle at $4,588.40 per troy ounce. Despite the daily loss, gold still finished the week up by $98.10, a 2.18% increase.
Silver also saw a sharp decline Friday, with the January contract dropping $3.785, or 4.12%, to $88.091 per ounce. However, it recorded a powerful weekly surge of $9.2070, or 11.67%.
The primary driver for gold's decline was a de-escalation of tensions between the United States and Iran. Earlier threats from U.S. President Donald Trump to launch military strikes have been replaced by a "wait-and-watch" approach.
The initial warnings came after reports that Iran used violent measures to suppress a civil uprising that began in December 2025. Iran, in turn, advised its neighbors not to harbor U.S. troops and warned of retaliation if an offensive began.
However, President Trump has since stated he was informed the killings have stopped. He cautioned that the U.S. is still monitoring the situation and that there will be "grave consequences" if they resume. This shift in tone eased investor concerns about an imminent military conflict in the Middle East.
Adding to the pressure on gold was robust U.S. economic data that bolstered the dollar. The Department of Labor reported that initial jobless claims for the week ending January 10 fell by 9,000 to 198,000, well below market expectations of 215,000.
Other key labor metrics also showed strength:
• Continuing jobless claims for the week ending January 3 decreased to 1,884,000 from 1,903,000.
• The four-week average of jobless claims fell to 205,000 from 211,500.
These strong labor market figures have dampened expectations for a near-term interest rate cut from the Federal Reserve, making the dollar more attractive to investors and weighing on dollar-denominated assets like gold.
Several other global events are shaping market sentiment.
Conflict in Ukraine Continues
In Europe, the war in Ukraine remains a key focus. Ukrainian drones reportedly targeted the Russian-occupied Zaporizhia region. Meanwhile, Russian overnight attacks on Zhytomyr and Kharkiv caused fresh power outages, leaving thousands without heat.
On the diplomatic front, President Trump stated that Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy was blocking a peace deal with Russia. Zelenskyy refuted the claim, asserting that Ukraine "has never been and will never be a stumbling block."
US Pursues Taiwan Trade Deal and Greenland Interests
On the trade front, the U.S. finalized a deal with Taiwan that will see Taiwanese technology companies invest at least $250 billion in American production capacity. In exchange, the U.S. will lower tariffs on Taiwanese semiconductor exports.
Separately, Trump suggested he could impose new tariffs on countries that do not support U.S. interests in controlling Greenland.
The Federal Reserve is also in the spotlight ahead of its January 27-28 policy meeting. According to the CME Group's FedWatch Tool, traders are pricing in a 95.0% probability that the central bank will hold interest rates steady.
The Fed is also dealing with an internal issue, as it was announced earlier this week that Fed Chair Jerome Powell was served with grand jury subpoenas related to financial overruns in the renovation of the Fed's building last year. President Trump has distanced himself from the matter.

International oil companies are lobbying the U.S. and Venezuelan governments to overhaul Venezuela's hydrocarbon law, seeking direct control over the oil they produce and the right to export it freely. This push comes as potential investors navigate how to engage with Venezuela's struggling oil industry without waiting years for comprehensive legal reforms to protect their capital.
The proposal aims to fast-track investment into a sector devastated by years of underinvestment and sanctions, aligning with a U.S. vision for a $100 billion reconstruction plan.
Under current Venezuelan law, state-run oil giant PDVSA must control and sell all oil produced through its joint ventures with foreign partners. PDVSA is then supposed to deposit the proceeds into joint accounts to cover expenses, fund new investments, and pay dividends.
However, U.S. sanctions imposed on Venezuela’s oil industry since 2019 have rendered this system unworkable. The restrictions have prevented PDVSA from effectively managing sales and payments, causing it to accumulate billions of dollars in debt to its international partners, including major players like Chevron, Italy's ENI, and Spain's Repsol.
To resolve this impasse, representatives for international oil firms are proposing specific modifications to the existing legal framework. Their key demands include:
• Control over Production: Granting foreign partners direct control over their share of the oil produced in joint ventures.
• Export Infrastructure Access: Allowing these companies to use PDVSA's oil terminals and export facilities to manage their own shipments.
• Simplified Tax Structure: Eliminating extra taxes introduced after 2021, leaving only royalties and income tax.
This tax reform would significantly reduce the government's share of revenue from oil production. Under current law, Venezuela's government take is among the highest in Latin America, securing at least 50% of the oil's value. The proposed changes would still leave PDVSA as the majority stakeholder in all oil joint ventures.
The Venezuelan government is also signaling a move toward reform. Delcy Rodriguez, the country's interim president and oil minister, recently announced that a government proposal to change the hydrocarbon law would be submitted to Congress.
According to Rodriguez, the reform aims to attract "investment flows to be incorporated into new fields, fields where no investment has ever been made and into fields where there is no infrastructure."
However, the government's plan includes a controversial element: it intends to formally incorporate a series of undisclosed oil contracts approved under President Nicolas Maduro into the new legislation.
The Controversy of Secret Deals
These contracts, which were never made public, are a major point of concern for many oil companies and Venezuela's political opposition. Their legality is ambiguous because their terms were not covered by the existing oil law.
Furthermore, the deals were negotiated with little-known companies and signed during a period of U.S. sanctions that explicitly forbade new investment in Venezuela's oil sector. The opaque nature of these agreements, which lacked any public oversight, has been a target of criticism for over a decade and adds another layer of risk for any company considering future investment.

The U.S. State Department has unveiled its strategic vision for 2026-2030, a comprehensive plan that pushes allies to increase defense spending while forging a "pro-American" economic bloc to counter global rivals.
Released on Thursday, the "Agency Strategic Plan Fiscal Years 2026-2030" details a diplomatic roadmap focused on strengthening economic and military ties, particularly in the Indo-Pacific. The core principle is to build partnerships that directly benefit U.S. strength, rather than those that come at its expense.
A central pillar of the new strategy involves deepening military relationships. The State Department plans to actively encourage allies to increase their own defense budgets, invest more in deterrence measures, and grant the U.S. military greater access to their critical infrastructure and resources.
In return, the United States will offer its partners increased access to its revitalized Defense Industrial Base. This push for allies to shoulder more of the security burden is designed to allow the U.S. to focus its resources on deterring its primary geopolitical rival, China.
An Integrated Defense Industrial Base
The plan emphasizes the importance of creating an integrated defense industry that includes reliable partners in both the Indo-Pacific and Europe. The document states that the U.S. will champion American defense companies and support industry-wide interoperability and collaboration.
According to the plan, this integration is crucial for ensuring defense supply chain stability and maintaining U.S. military readiness for potential conflicts far from American shores. An integrated base would provide the U.S. and its allies with "strategic productive depth" in the event of a conflict.
Alongside military objectives, the strategy outlines a renewed focus on commercial diplomacy. The State Department aims to prevent foreign powers from gaining global market dominance by leveraging commerce as a critical tool for forging alliances.
The plan details a push to create a "strong economic bloc of pro-American countries." This will be achieved by mobilizing U.S. businesses to become the "preferred choice" for allies and partners through commercial deals pursued in all bilateral relationships. This bloc is intended to:
• Leverage American businesses and exports.
• Establish a new economic security consensus.
• Unlock new industries through flagship infrastructure projects.
• Finance U.S. reindustrialization.
• Ensure American economic and technological leadership throughout the 21st century.
An early example of this initiative is the "Pax Silica" coalition, a U.S.-led effort for supply chain cooperation on artificial intelligence and critical minerals. This growing coalition, which includes South Korea and Japan, is seen as a direct move to counter China's influence in vital technologies and resources.
While the strategy is clearly designed to strengthen the U.S. position relative to its rivals, it also addresses direct engagement with China. The State Department confirmed it will consistently seek open lines of communication with the Asian superpower to reduce misunderstandings and mitigate risks.
The plan states that the United States has a strong interest in a peaceful and prosperous Indo-Pacific and desires neither war nor regime change, a message it intends to communicate clearly to allies, partners, and adversaries alike.
French Prime Minister Sebastien Lecornu has proposed a sweeping overhaul of his budget plans in a high-stakes bid to secure a deal with opposition parties and prevent the collapse of his government.
After halting a parliamentary debate on the 2026 finances that he admitted was heading for failure, Lecornu presented a revised strategy aimed at winning crucial support.
"This budget will be different from the initial one—it's better, it can bring people together, and I believe it's responsible," he announced in a televised address on Friday.
The government's survival hinges on its ability to navigate a fragmented National Assembly. While Lecornu can use constitutional powers to bypass a direct vote on the budget, he must offer concessions to dissuade opposition lawmakers from ousting him through a subsequent no-confidence motion.
Lecornu's new proposals are clearly designed to appeal to the Socialist Party, whose lawmakers represent a pivotal voting bloc. The prime minister is trying to secure their support, or at least their abstention, to survive any no-confidence challenges.
The key features of the revised budget plan include:
• Tax Protection: A pledge to shield households from tax increases.
• Income Support: Measures to boost the incomes of those earning near the minimum wage.
• Benefit Preservation: A commitment not to cut housing benefits.
• Fairness and Investment: Guarantees that the wealthy will pay a fair share of tax, while funding for students and new jobs in education will be maintained.
"The compromise budget we are proposing protects those who work and produce—this common-sense approach should get support," Lecornu stated.
To pass the budget without a parliamentary majority, Lecornu has two primary constitutional options, though he has not yet specified which he will choose.
The first is Article 49.3, a tool that allows the government to pass legislation without a vote. However, deploying it immediately exposes the prime minister to no-confidence motions. If a motion succeeds, the budget is rejected, and the prime minister is forced to resign.
The second option involves Article 47, which would allow the government to use untested decrees known as ordonnances. While this path would also likely trigger no-confidence votes, any measures implemented by decree would remain in effect even if the government falls, providing a degree of fiscal stability.
Government spokeswoman Maud Bregeon confirmed that discussions with political groups would continue and that "nothing is excluded."
Despite previously opposing the use of Article 49.3, the Socialists now see it as preferable to the use of decrees, which would grant parliament no say in the budget's content. Socialist lawmaker Philippe Brun described the use of decrees as a "kind of creeping coup d'etat" on France Info radio.
The ongoing political standoff is testing investor confidence in France. The country has already experienced market selloffs since snap elections in 2024 resulted in a hung parliament.
In October, the premium on France's 10-year bond yields over their safer German counterparts rose to more than 85 basis points as Lecornu struggled to form a government. That pressure eased toward the end of 2025 when the prime minister made concessions, but it is rising again. On Friday, the spread closed at 68 basis points, its highest level in over a week.
Adding to the pressure, Bank of France Governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau has warned that the country would enter a "danger zone" with markets if it fails to cut its budget deficit to within 5% of economic output this year, down from an expected 5.4% in 2025.
Lecornu insists his new budget will achieve this through "fair" savings. "This year we will be at 5% and if growth supports it—and political stability helps—it will probably be less," he said. "France keeps its commitments, it is governed and must remain credible."
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up