Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests


[Zelensky Says Security Service Planning New Actions Against Russia] Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy Stated On January 28 That The Security Service Of Ukraine (SBU) Is Continuously Planning New Actions Against Russia That Would Alter The Course Of The Russia-Ukraine Conflict. On The Same Day, Zelenskyy Received A Briefing From The SBU On Operational Plans, Including Frontline Combat, Particularly The Operations Of The SBU's Alpha Group Special Forces, And Actions Taken By The SBU Within Russian Territory In Response To Russian Attacks
Kathy Jones, Chief Fixed-income Strategist At Charles Schwab: The Fed's Policy Statement Is Expected To Make A Judgment On U.S. Inflation
USA Natural Gas Inventories Seen Down 232 Billion Cubic Feet Last Week In Thursday's EIA Report, Reuters Poll Shows
Torsten Slok, Chief Economist At Apollo: The Fed Is Expected To Say They Are Staying On The Sidelines
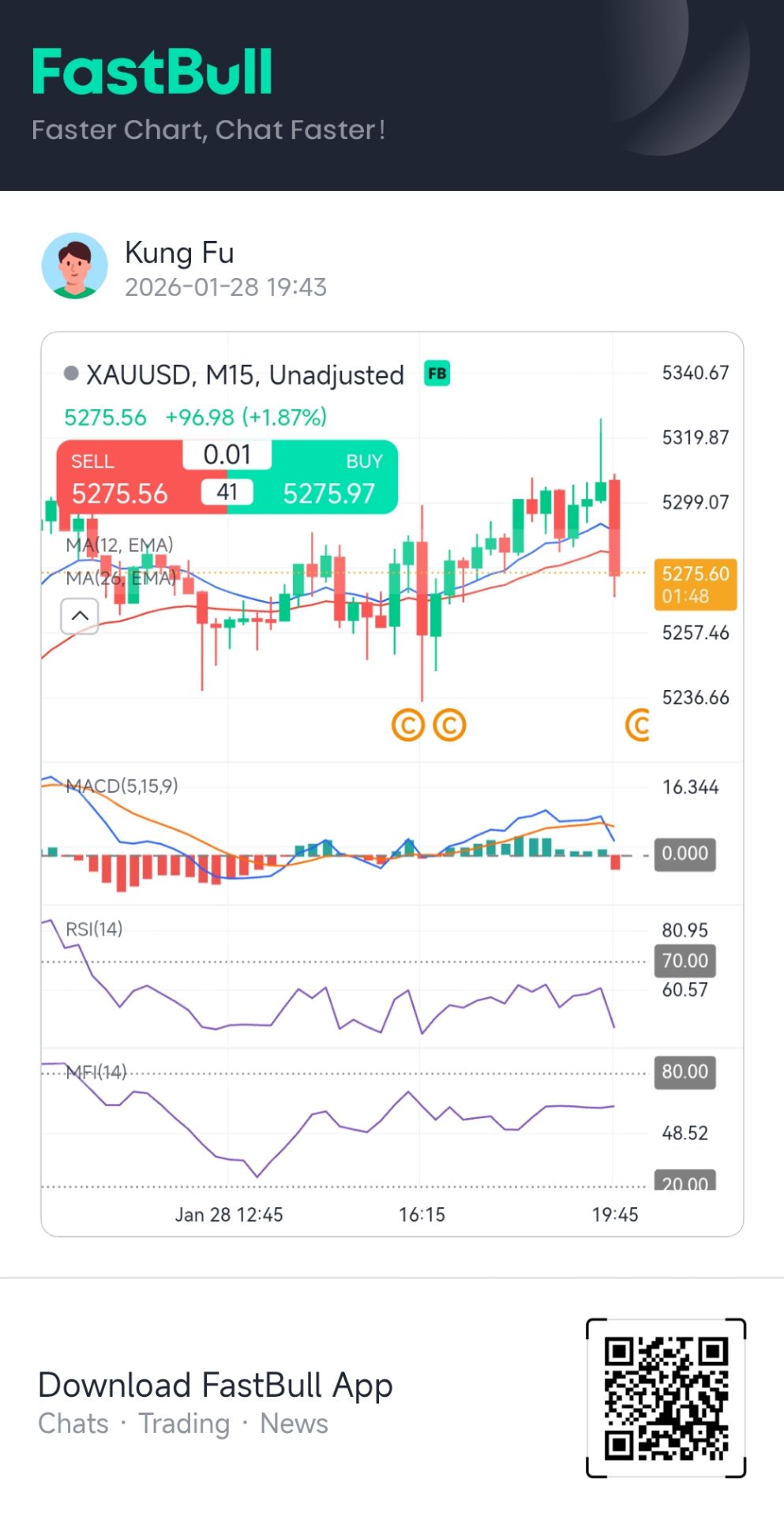
[Market Update] Spot Gold Fell More Than $20 In The Short Term, Currently Trading At $5280.94 Per Ounce
U.S. Senate Majority Leader John Thune: Democrats Must Work With President Trump’s White House To Address The Budget Issues (related To The Department Of Homeland Security/Dhs)
[Market Update] Ahead Of The Fed's Decision, Spot Gold Rose Above $5,320 Per Ounce, Hitting A New High, Up 2.71% On The Day
New York Fed Accepts $1.103 Billion Of $1.103 Billion Submitted To Reverse Repo Facility On Jan 28
Petrobras Says Sales Potential Up To 60 Million Barrels, With A Total Value That May Exceed $ 3.1 Billion
Canada, South Korea Sign Memorandum Of Understanding Intending To Bring South Korean Auto Manufacturing And Investment To Canada -The Globe And Mail, Citing Document
European Central Bank Executive Board Member Schnabel: European Central Bank Rates In A Good Place And Expected To Remain At Current Levels For Extended Period
USTR: Talks On Stronger Rules Of Origin For Key Industrial Goods, Enhanced Collaboration On Critical Minerals, And Increased External Trade Policy Alignment
LME Copper Rose $80 To $13,086 Per Tonne. LME Aluminum Rose $50 To $3,257 Per Tonne. LME Zinc Rose $13 To $3,364 Per Tonne. LME Lead Fell $3 To $2,017 Per Tonne. LME Nickel Rose $101 To $18,270 Per Tonne. LME Tin Rose $1,075 To $55,953 Per Tonne. LME Cobalt Was Unchanged At $56,290 Per Tonne
Iran's Araqchi: Tehran Has Always Welcomed A Fair Nuclear Deal Which Ensures Iran's Rights And Guarantees No Nuclear Weapons
Rubio: There Might Be A USA Presence In The Ukraine Talks In Abu Dhabi This Weekend But It Won't Be Witkoff And Kushner

 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
 U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Gasoline StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)
Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)
Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. Yield
Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)
India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)
India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW
U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoWA:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Overnight Target Rate
Canada Overnight Target RateA:--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Monetary Policy Report
BOC Monetary Policy Report U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks ChangeA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks ChangeA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by ProductionA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports ChangesA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock ChangesA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks ChangeA:--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Press Conference
BOC Press Conference Russia PPI MoM (Dec)
Russia PPI MoM (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia PPI YoY (Dec)
Russia PPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances
U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target
U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)--
F: --
P: --
 FOMC Statement
FOMC Statement FOMC Press Conference
FOMC Press Conference Brazil Selic Interest Rate
Brazil Selic Interest Rate--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)
Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)
Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone 3-Month M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone 3-Month M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 South Africa PPI YoY (Dec)
South Africa PPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Consumer Confidence Index Final (Jan)
Euro Zone Consumer Confidence Index Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Selling Price Expectations (Jan)
Euro Zone Selling Price Expectations (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Climate Index (Jan)
Euro Zone Industrial Climate Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Services Sentiment Index (Jan)
Euro Zone Services Sentiment Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)
Euro Zone Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Consumer Inflation Expectations (Jan)
Euro Zone Consumer Inflation Expectations (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Italy 5-Year BTP Bond Auction Avg. Yield
Italy 5-Year BTP Bond Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 Italy 10-Year BTP Bond Auction Avg. Yield
Italy 10-Year BTP Bond Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 France Unemployment Class-A (Dec)
France Unemployment Class-A (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 South Africa Repo Rate (Jan)
South Africa Repo Rate (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Nonfarm Unit Labor Cost Final (Q3)
U.S. Nonfarm Unit Labor Cost Final (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)
U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Trade Balance (Nov)
U.S. Trade Balance (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Trade Balance (SA) (Nov)
Canada Trade Balance (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --














































No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
Trump's China rapprochement faced bipartisan congressional pushback, limiting his power and securing Taiwan.
Upon returning to office in January 2025, Donald Trump began to reshape U.S. policy in Asia with unprecedented authority, sidelining Congress and installing a loyalist administration. This second term saw Trump exert extraordinary control over the federal government, the Republican-led Congress, and a Supreme Court dominated by Republican appointees, including three of his own. Unlike his first term, dissent within the White House was virtually nonexistent, giving him a free hand to pursue his agenda with China and Taiwan.
The year began with friction. The Trump administration engaged in two brief but intense standoffs with Beijing in April and October, with both sides threatening massive tariffs and severe export controls. However, the confrontations quickly gave way to compromise, culminating in an amicable in-person summit between Trump and President Xi Jinping on October 28.
This meeting set a new tone. In the months that followed, both Washington and Beijing focused on maintaining stability and securing positive outcomes for Trump's planned visit to China in April and a reciprocal visit by Xi to the U.S. later in the year.
The summit with Xi was the capstone of a successful week-long tour of East Asia. Despite his general unpopularity in the region, Trump's meetings with ASEAN leaders in Malaysia and summits with Japanese and South Korean counterparts were positive. An earlier meeting in Washington with Australia's prime minister also went smoothly.
This trend of rapprochement left officials in Taiwan concerned. The Taiwanese government struggled to secure a tariff-reduction agreement with the United States. Adding to the anxiety, the Trump administration reportedly took several actions in deference to Beijing ahead of the October summit:
• A planned U.S. visit by Taiwan's defense minister was halted.
• A U.S. stopover by Taiwan's President Lai Ching-te was blocked.
• Public announcements of U.S. warships transiting the Taiwan Strait ceased.
• Key arms sales to Taiwan were delayed.
After the summit, Trump stated that Taiwan was not discussed. However, the administration later sent reassuring signals. In November, two arms sales packages worth over $1 billion were confirmed. On December 2, Trump signed the Taiwan Assurance Implementation Act into law. This was followed by a December 17 announcement of an $11 billion sale of sophisticated arms to Taiwan. By January 15, 2026, the U.S. and Taiwan announced a trade deal that lowered tariffs to 15% and promised $250 billion in Taiwanese investment in American semiconductor and technology manufacturing.
Despite these positive developments, the mixed signals fueled fears in Taiwan that Trump's focus on deal-making could lead to a compromise with Beijing at Taiwan's expense. The administration's November 30 National Security Strategy did little to clarify matters, notably omitting China as a specific danger. The National Defense Strategy, released on January 23, prioritized the Western Hemisphere over the Indo-Pacific but emphasized a "strong denial defense along the first Island Chain," a strategic area where Taiwan is central.
While Trump pursued diplomacy with Beijing, Congress operated on a different track. Despite Trump's influence over Republicans, a strong bipartisan consensus remained to counter Chinese government actions and support Taiwan. This congressional activism, a consistent feature since 2018, continued unabated.
Led by Republicans and the House Select Committee on the CCP, Congress focused primarily on defending U.S. interests from Chinese challenges. By August 2025, 564 pieces of legislation mentioning China had been introduced, with 247 containing substantive provisions on issues including:
• Technology decoupling
• Rare earth supply chains
• Higher education oversight
• Strengthening U.S. commitments to Taiwan
Bipartisan Pushback on Trump's Overtures
Though some Democrats criticized Trump's tariffs and sought to open communication with Beijing—as seen in a September visit to China by a delegation led by Representative Adam Smith—this did not signal a collapse of the "Washington Consensus." In practice, bipartisanship consistently prevailed in hardening U.S. policy.
Often, Democratic criticism was that the administration's policies were not tough enough on China. For example, Democrats opposed the end of U.S. support for Voice of America and international climate change measures, arguing these moves weakened U.S. resolve.
A sharp, bipartisan rebuke came in December after Trump allowed the sale of advanced Nvidia AI chips to China. Ahead of the decision, Senate Intelligence Committee Chair Tom Cotton introduced a bill with bipartisan support to block such sales. In January, the House Foreign Affairs Committee voted 42-2 for a bill to give Congress greater control over AI chip exports to China, directly challenging White House AI czar David Sacks.
Trump's tight grip on the Republican party showed its limits. He failed to convince Senate Republicans to eliminate the filibuster or end the practice allowing home-state senators to block judicial nominees.
By early 2026, congressional resistance was growing. Bipartisan majorities began to push back on several of Trump's initiatives, including a military attack in Venezuela and threats against Greenland. Seventeen House Republicans joined Democrats to extend Affordable Care Act subsidies. Furthermore, Congress passed several spending bills that explicitly rejected the president's proposed budget cuts, wording them to limit the administration's ability to make unilateral funding decisions.
These developments underscore a critical reality: a powerful, bipartisan congressional majority focused on countering China serves as a significant check on the Trump administration. This dynamic acts as a crucial brake, restricting any potential compromises with Beijing that might come at Taiwan's expense.
U.S. private employers recorded a weekly average addition of 7,750 jobs for four weeks ending January 3, 2026, per the latest ADP Nonfarm Employment report released January 27.
The report's lower figures suggest potential impacts on U.S. economic sentiment and may influence cryptocurrency markets if macro trends adjust monetary policy outlooks.
The latest ADP Nonfarm Employment data highlights a reduction in U.S. job growth. The average of +7,750 jobs per week reflects a consistent decline from previous weeks' figures.
ADP, in collaboration with the Stanford Digital Economy Lab, provides this data, noting that private employers added fewer jobs than anticipated.
"Small establishments recovered from November job losses with positive end-of-year hiring, even as large employers pulled back." — Nela Richardson, Chief Economist, ADP
The decay in employment figures could potentially influence broader economic indicators. The U.S. labor market's performance is central to shaping Federal Reserve decisions.
Soft employment figures, such as this report, often raise expectations of looser monetary policy, which can affect cryptocurrency and broader financial markets.
This report outlines current labor market volatility as seen in recent weeks. It shows fluctuations in job numbers, highlighting potential influences on market sentiment and possible regulatory adjustments.
Historical data suggest that lower employment numbers might correspond with increased speculation in cryptocurrency markets, with assets like BTC and ETH potentially seeing upward trends.
China's natural gas production surged to an all-time high in 2025, reaching 261.9 billion cubic meters. This 6% year-over-year increase was driven by a state-backed campaign to develop complex shale gas fields, allowing the nation to meet 60% of its domestic consumption with homegrown supply.
The new output level, equivalent to 193 million metric tons of liquefied natural gas (LNG), positions China as a major global producer. For perspective, this volume is roughly triple Japan's annual gas demand and brings China nearly on par with Iran, which produced 262.9 billion cubic meters in 2024 to rank third globally behind the U.S. and Russia.
China's 2025 production has now eclipsed the 2024 output of major LNG exporters like Qatar (179.5 billion cubic meters) and Australia (150.1 billion cubic meters). A think tank under the state-owned China National Petroleum Corp. (CNPC) projects this growth will continue, targeting 300 billion cubic meters by 2030.
The engine behind this record output is China's shale gas revolution. In 2024, shale gas production broke the 100 billion cubic meter mark for the first time and now accounts for nearly half of the country's total natural gas supply. Key production gains have come from the Ordos and Sichuan basins.
This success is the result of a deliberate government strategy. Beijing has used subsidies and tax incentives to encourage state-owned energy giants, primarily CNPC and Sinopec, to ramp up production. Their efforts contrast with the mass withdrawal of foreign companies like Shell, which found China's unconventional gas fields too difficult to develop due to their depth and complex geology.
Unlike the U.S. shale boom, which was pioneered by smaller, agile companies through trial and error, China's development has been characterized by strong state leadership. While Chinese firms have invested in American shale projects and likely referenced U.S. technology, the geological differences—notably shallower shale layers in the U.S.—have made direct application difficult.
Despite the technical challenges, Chinese shale gas has proven economically competitive. According to a 2023 analysis by Cinda Securities, the cost to supply shale gas in eastern China was:
• 50% higher than conventional natural gas.
• 50% cheaper than imported LNG.
• 20% cheaper than Russian gas delivered via pipeline.
This cost advantage is reshaping China's energy import landscape. While maintaining a 60% self-sufficiency rate, the country's combined pipeline and LNG imports fell by 3% in volume last year, the first decrease in two years.
The impact was most pronounced in the LNG market, where imports dropped 11% to 68.43 million tons. Geopolitical tensions dramatically altered trade flows:
• United States: Imports of U.S. LNG plummeted 94% to just 250,000 tons and have been near zero since March, crippled by Beijing's tariffs.
• Australia: Shipments from Australia, China's largest LNG supplier, fell 22% to 20.38 million tons.
• Russia: In contrast, LNG imports from Russia rose 18% to 9.79 million tons, making it the third-largest source with a 14% market share. These supplies included gas from the Arctic LNG 2 project, which is under Western sanctions.
Pipeline gas imports from Russia also continued to grow, with Tass reporting a 17% increase by value in 2025.
Even as China's economy slowed, its demand for natural gas remained resilient, dipping just 0.1% in the first eleven months of 2025. This stability is supported by government policies aimed at improving air quality by encouraging factories to switch from coal and heavy oil to natural gas. The number of gas-fired power plants is also on the rise.
Looking ahead, the CNPC think tank forecasts that China's gas consumption will climb to 550 billion cubic meters by 2030—a 30% jump from 2024 levels. This suggests that even with its record-breaking domestic production, China will remain a critical player in the global gas market for years to come.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is launching a major initiative to build a domestic nuclear fuel supply chain, signaling a strategic push to support the growing demand for carbon-free energy. The plan centers on creating "Nuclear Lifecycle Innovation Campuses" across the country.
The DOE will formally invite states to submit proposals for hosting these advanced facilities. The goal is to create hubs that can handle every stage of the nuclear fuel process, a move designed to reduce America's reliance on foreign uranium and pioneer new technologies.
A core objective of these campuses is to establish commercial-scale recycling for used nuclear fuel. Currently, U.S. reactors only utilize about 5% of the potential energy in their fuel, and there is no commercial infrastructure to reprocess the remaining material. This initiative aims to change that, turning spent fuel into a valuable asset and diverting it from long-term storage sites like Yucca Mountain.

Ultimately, a single campus could integrate the entire fuel cycle, from uranium enrichment to recycling. These sites could also host advanced reactors, power generation facilities, and co-located data centers, creating a streamlined system that avoids the complexities of transporting nuclear materials.
The timing of the initiative aligns with a surge in demand for nuclear power, driven partly by the massive electricity needs of AI and data centers. The DOE anticipates that one of these innovation campuses could attract as much as $50 billion in private sector capital investment.
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright framed the plan as a key part of a broader strategy. "Unleashing the next American nuclear renaissance will drive innovation, fuel economic growth, and create good-paying American jobs," he said, adding that it aligns with "President Trump's vision to revitalize America's nuclear base."
The Trump administration has consistently positioned nuclear power as a central element of its national energy strategy. While nuclear energy already accounts for roughly 21% of U.S. electricity, the country remains dependent on imports for a significant portion of its uranium.
This new plan builds on several recent policy actions:
• Regulatory Reform: Last May, President Donald Trump signed executive orders to streamline regulations and accelerate the deployment of both large and small nuclear reactors.
• Major Investments: Last fall, the administration finalized a deal with Westinghouse owners Cameco and Brookfield Asset Management to invest $80 billion in constructing large-scale nuclear reactors across the U.S.
• Enrichment Funding: Earlier this year, the DOE announced $2.7 billion to boost domestic enrichment capabilities. This included a $900 million award to Centrus to expand its plant in Piketon, Ohio, though the facility has not yet reached commercial production.
Speaking in November, Wright emphasized the administration's commitment, stating that most of the department's loan capital will be directed toward building new nuclear plants.
"When we leave office three years and three months from now, I want to see hopefully dozens of nuclear plants under construction," Wright stated.
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has sharply criticized the European Union’s new trade agreement with India, accusing Brussels of prioritizing commerce over the interests of the Ukrainian people.
In a statement to CNBC, Bessent expressed his disappointment, arguing that Europe’s actions undermine sanctions against Russia. He pointed out that the EU has been purchasing refined products from India that are made with sanctioned Russian oil.
According to Bessent, Europe was unwilling to match Washington’s higher tariffs on Indian goods precisely because it was negotiating this separate trade pact.
The U.S. Treasury Secretary directly linked the EU's trade ambitions to its reluctance to join American economic pressure on India. Last year, Washington imposed 25% tariffs on India to discourage its purchases of Russian oil. Bessent noted that the EU declined to participate.
"The Europeans were unwilling to join us, and it turns out, because they wanted to do this trade deal," he stated. "So every time you hear a European talk about the importance of the Ukrainian people, remember that they put trade ahead of the Ukrainian people."
These comments follow Bessent’s signal last week that the U.S. might remove its 25% additional tariffs after observing a sharp reduction in India's imports of Russian oil.
On Tuesday, the European Union finalized a long-awaited trade deal with India. The agreement is designed to significantly increase two-way trade and reduce the bloc's economic reliance on the United States amid rising global trade friction.
The EU projects the deal will achieve the following:
• Double EU exports to India by the year 2032.
• Eliminate or reduce tariffs on 96.6% of traded goods by value.
• Generate savings of €4 billion ($4.8 billion) in duties for European firms.
When asked if such deals, which exclude the United States, pose a threat, Bessent remarked, "They should do what's best for themselves, but I will tell you, I find the Europeans very disappointing."
Bessent's critical remarks come at a time of heightened transatlantic tensions. President Donald Trump recently unsettled European leaders by threatening to raise tariffs on certain European countries over their opposition to his interest in pursuing Greenland, although the threat was later withdrawn.
U.S. officials also remain frustrated with the EU's failure to implement tariff reductions promised in a framework trade agreement reached with Washington in July.
This pattern of applying pressure was further highlighted this week when Trump increased duties on imports from South Korea from 15% to 25%. The administration cited the slow pace of the South Korean parliament in implementing a trade agreement reached with the U.S. last year.
Bessent defended the move against South Korea, calling it "helpful to get things moved along" and emphasizing the need for their parliament to ratify the deal. On Tuesday, Trump said he expects the U.S. and South Korea to find a solution, as South Korean officials were scheduled to arrive in Washington for talks.
The Trump administration on Wednesday officially rolled out its "Trump Accounts" program, a new initiative providing government-funded investment accounts for babies born in the United States. According to top officials, more than 500,000 families have already registered for the program.

The White House is establishing these investment accounts as a key strategy to address household affordability concerns ahead of the November midterm elections. The program was created last year as part of the "One Big Beautiful Bill," the Republican party's signature tax and spending legislation.
The initiative targets children born over a specific three-year period, with the U.S. Treasury providing the initial seed money. The goal is to tackle the lack of savings accounts held by many American families.
Key features of the program include:
• Initial Government Deposit: The U.S. Treasury will deposit $1,000 into an investment account for every child born between 2025 and 2028.
• Eligibility: An estimated 25 million families are expected to be eligible for the program.
The government is actively encouraging families to supplement the initial deposit with their own contributions. The program has also attracted significant private investment, including a $6.25 billion contribution from entrepreneur Michael Dell and his wife, Susan.
Potential Growth to $1.1 Million
At a rollout event in Washington, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt highlighted the long-term potential of the accounts. She stated that if a family contributes the maximum allowed amount of $5,000 each year, the account could grow to nearly $1.1 million by the time the child turns 28.
The Trump administration is framing the accounts as a bipartisan achievement. "It's not about red or blue politics," said Cheryl Hines, an actress and the wife of Health Secretary Robert Kennedy, at the launch event.
Despite the official rollout, public knowledge of the program remains limited. A poll conducted by Exclusive Public First and reported by Politico found that:
• 57% of Americans had never heard of a Trump Account.
• 25% had heard of the program but could not explain how it works.
• Only 14% were familiar with the accounts and could describe them.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features


Log In
Sign Up