Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.K. Trade Balance Non-EU (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance Non-EU (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Services Index MoM
U.K. Services Index MoMA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)
U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)
U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France HICP Final MoM (Nov)
France HICP Final MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India CPI YoY (Nov)
India CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Deposit Gowth YoY
India Deposit Gowth YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)
Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia Trade Balance (Oct)
Russia Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech
Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)
Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)
U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)
China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)
Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)
Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)
Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations
U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)
Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
Global lithium prices down over 80% in past 12 months. Analysts expect mining of lepidolite in China to be hit. Almost half of China's lithium output in 2023 came from lepidolite, Fastmarkets says.
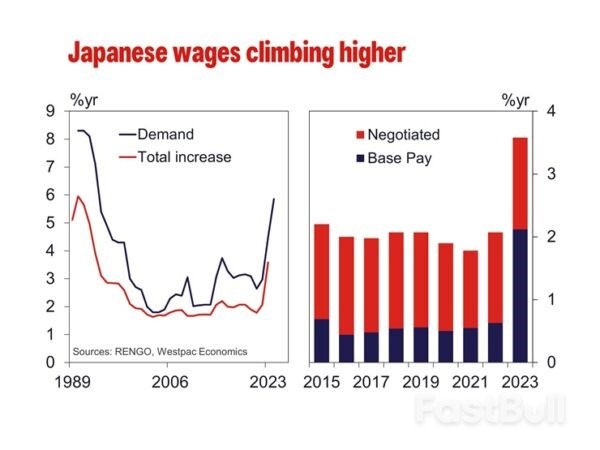 As of 2023 Q4, the inflation outlook for 1, 3 and 5 years came to 2.4%, 2.2% and 2.1% respectively. While still above the circa 1% average for all three time periods 2014 to 2019, it is also materially below where inflation has been. Still-elevated current inflation expectations may support wage growth in the near-term, but this effect looks set to dissipate as actual inflation prints come in weaker.
As of 2023 Q4, the inflation outlook for 1, 3 and 5 years came to 2.4%, 2.2% and 2.1% respectively. While still above the circa 1% average for all three time periods 2014 to 2019, it is also materially below where inflation has been. Still-elevated current inflation expectations may support wage growth in the near-term, but this effect looks set to dissipate as actual inflation prints come in weaker.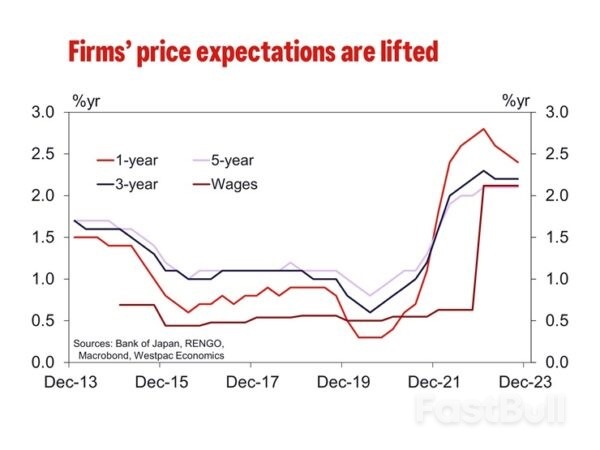 Rising profitability has also been used to argue for stronger wage growth in 2024 with a focus on strength in ordinary profits. However, operating profits are only slightly above the pre-COVID peak and below the 10-year pre-COVID trend. Operating profit as a share of sales are also relatively unimpressive, hovering around pre-COVID rates. The disparity between operating profits, which do not include investment-related income, and ordinary profits implies profitability is being flattered by financial investment returns not firms' underlying profitability. It is only the latter that would given businesses confidence to increase wages at or above the rate of inflation.
Rising profitability has also been used to argue for stronger wage growth in 2024 with a focus on strength in ordinary profits. However, operating profits are only slightly above the pre-COVID peak and below the 10-year pre-COVID trend. Operating profit as a share of sales are also relatively unimpressive, hovering around pre-COVID rates. The disparity between operating profits, which do not include investment-related income, and ordinary profits implies profitability is being flattered by financial investment returns not firms' underlying profitability. It is only the latter that would given businesses confidence to increase wages at or above the rate of inflation.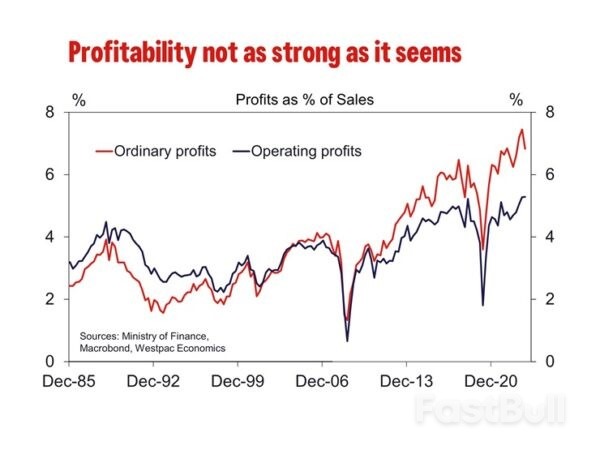 Rather than being a support for wage growth, beyond 2024, we expect structural factors to act at a headwind for sustained wages growth. In Japan, wage increases depend on seniority, so job mobility is low and companies typically find it unnecessary to raise wages to retain staff. This also disincentivises employees from reskilling or making career changes into higher growth areas. In 2016, then Govenor Kuroda outlined low job mobility as a key challenge for the labour market and the country's growth potential.
Rather than being a support for wage growth, beyond 2024, we expect structural factors to act at a headwind for sustained wages growth. In Japan, wage increases depend on seniority, so job mobility is low and companies typically find it unnecessary to raise wages to retain staff. This also disincentivises employees from reskilling or making career changes into higher growth areas. In 2016, then Govenor Kuroda outlined low job mobility as a key challenge for the labour market and the country's growth potential.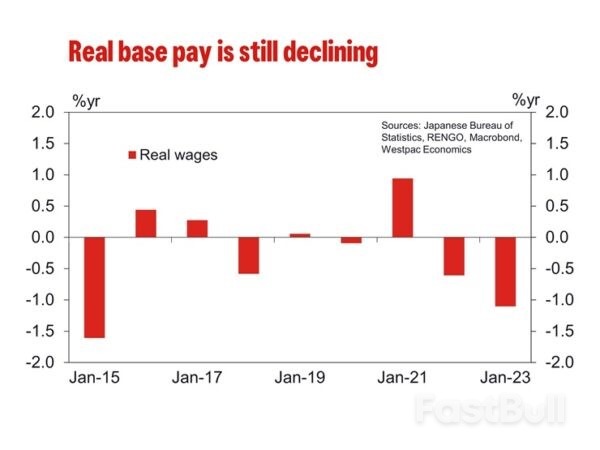 Further, participation has recently been rising thanks to a growing cohort of part-time workers, primarily women and those aged 65 and above. Wage growth is slower for part time workers, and the loss of tax and social benefits for secondary income earners dissaude many from labour market and the country's growth potential.
Further, participation has recently been rising thanks to a growing cohort of part-time workers, primarily women and those aged 65 and above. Wage growth is slower for part time workers, and the loss of tax and social benefits for secondary income earners dissaude many from labour market and the country's growth potential.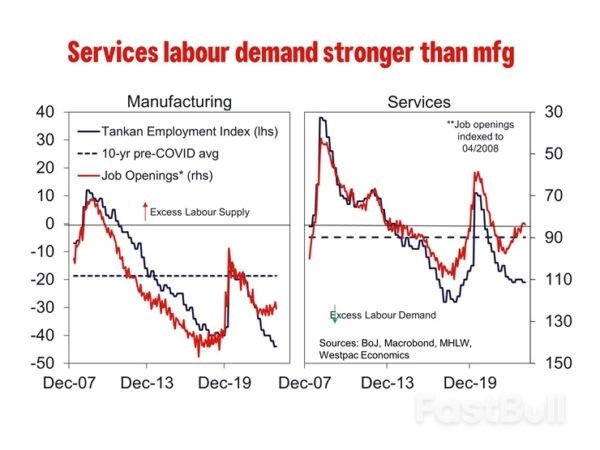 Small businesses have been particularly unenthusiastic about raising wages. As an example, a survey completed by Johnan Shinkin Bank and the Tokyo Shimbun daily reported 72.8% of small and medium-sized businesses in the Tokyo metropolitan area said they ” have no plans to raise wages this year”. Smaller employers tend to make up the bulk of employers and so can have a significant effect on aggregate outcomes. Their reluctance is arguably principally due to an inability to pass on higher costs to consumers, particularly when households are price sensitive as they are now, but also as they are much less able to scale up and therefore benefit from efficiency and large markets.
Small businesses have been particularly unenthusiastic about raising wages. As an example, a survey completed by Johnan Shinkin Bank and the Tokyo Shimbun daily reported 72.8% of small and medium-sized businesses in the Tokyo metropolitan area said they ” have no plans to raise wages this year”. Smaller employers tend to make up the bulk of employers and so can have a significant effect on aggregate outcomes. Their reluctance is arguably principally due to an inability to pass on higher costs to consumers, particularly when households are price sensitive as they are now, but also as they are much less able to scale up and therefore benefit from efficiency and large markets.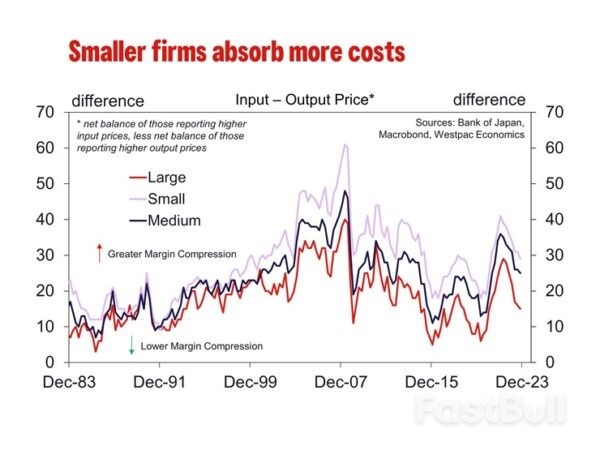 One segment of the labour market that is showing increasing wages is younger Japanese workers. They are more likely to have in demand skills, particularly for high-skill work, and are also more likely to job hop being early in their careers. As such, wage gains are thought to be skewed towards younger workers. BoJ research also shows that wages for high skill workers are increasing. However given Japan's ageing population and weak immigration program, young people make up a small fraction of the labour force, so wage gains in this cohort is unlikely to drive aggregate wage gains or consumption.
One segment of the labour market that is showing increasing wages is younger Japanese workers. They are more likely to have in demand skills, particularly for high-skill work, and are also more likely to job hop being early in their careers. As such, wage gains are thought to be skewed towards younger workers. BoJ research also shows that wages for high skill workers are increasing. However given Japan's ageing population and weak immigration program, young people make up a small fraction of the labour force, so wage gains in this cohort is unlikely to drive aggregate wage gains or consumption.
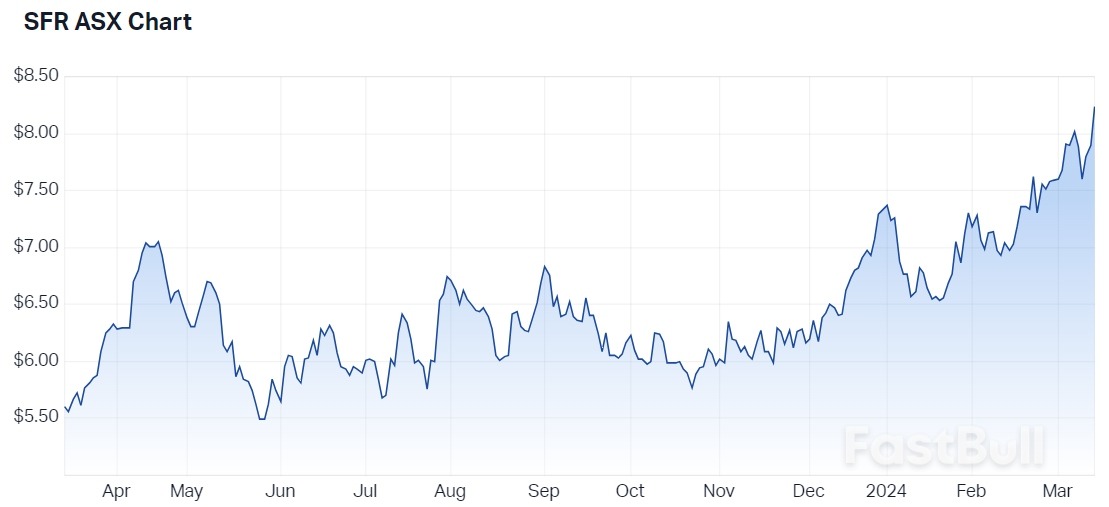
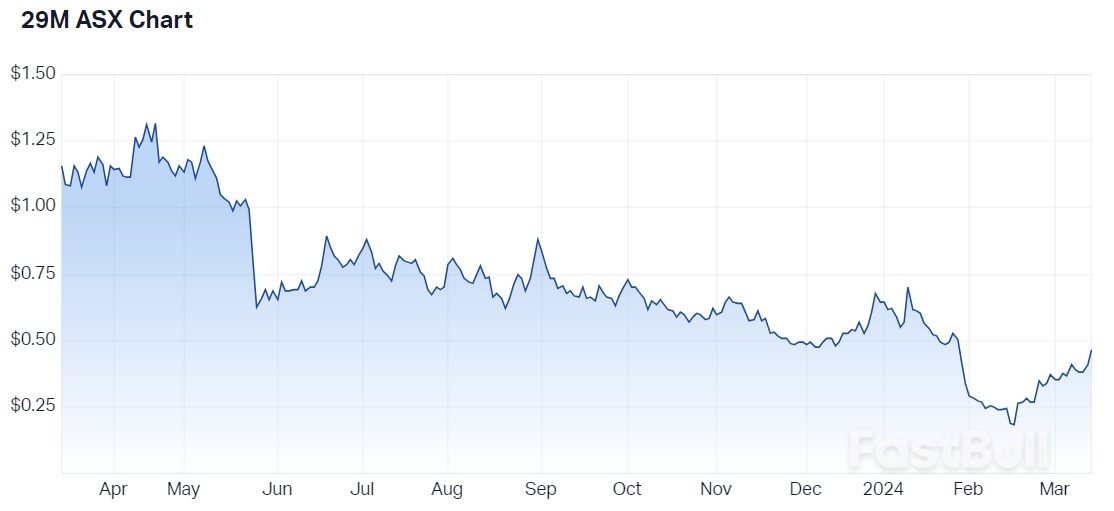 29Metals 12-month price chart
29Metals 12-month price chart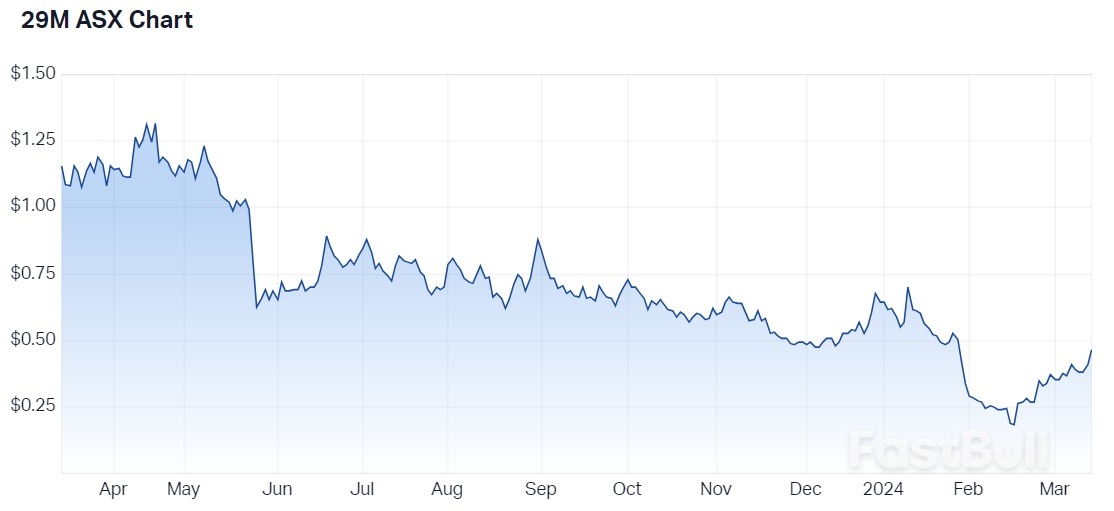
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up