Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. Average Hourly Wage MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Average Hourly Wage MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Average Weekly Working Hours (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Average Weekly Working Hours (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. New Housing Starts Annualized MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.S. New Housing Starts Annualized MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Total Building Permits (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Total Building Permits (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Annual New Housing Starts (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Annual New Housing Starts (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 U.S. U6 Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. U6 Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Manufacturing Employment (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Manufacturing Employment (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Private Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Private Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Average Hourly Wage YoY (Dec)
U.S. Average Hourly Wage YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
 Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)
Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Government Employment (Dec)
U.S. Government Employment (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Jan)
U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Jan)
U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Indonesia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Jan)
Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 India CPI YoY (Dec)
India CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Nov)
Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Employment Trends Index (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Conference Board Employment Trends Index (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia CPI YoY (Dec)
Russia CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 FOMC Member Barkin Speaks
FOMC Member Barkin Speaks U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield
U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Nov)
Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Nov)
Japan Trade Balance (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Dec)
U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Dec)
U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Turkey Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Dec)
U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Services Growth YoY (Nov)
Brazil Services Growth YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Income MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Real Income MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI MoM (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI MoM (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. New Home Sales Annualized MoM (Oct)
U.S. New Home Sales Annualized MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Annual Total New Home Sales (Oct)
U.S. Annual Total New Home Sales (Oct)--
F: --
P: --












































No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
US presses allies to cut China mineral reliance amid supply chain vulnerability and Beijing's market dominance.
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent is set to press top finance officials from the Group of Seven (G7) and other major economies to accelerate efforts to reduce their reliance on critical minerals from China, according to a senior U.S. official.
The high-stakes meeting in Washington will bring together finance and cabinet ministers from the G7, the European Union, Australia, India, South Korea, and Mexico. Combined, these nations account for 60% of the world's demand for these essential materials.
"Urgency is the theme of the day," the official stated. "It's a very big undertaking. There's a lot of different angles, a lot of different countries involved and we really just need to move faster."
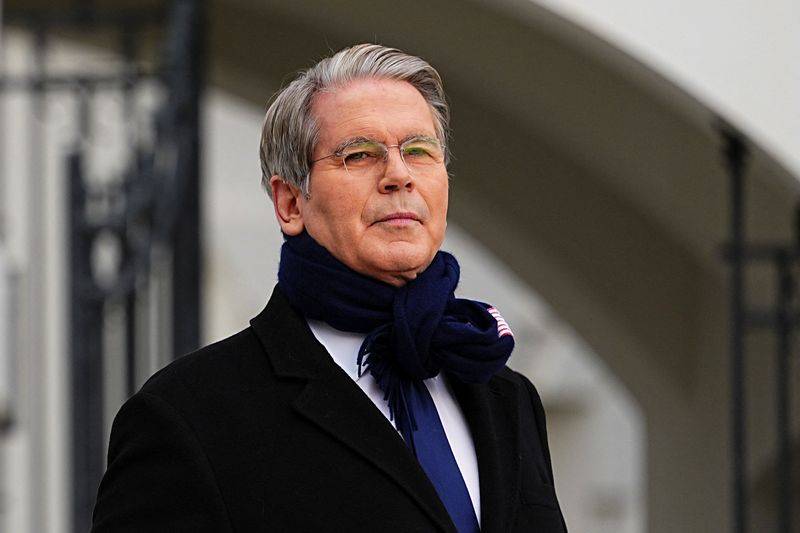

The push for a dedicated meeting on mineral supply chains began after the G7 leaders' summit in Canada in June, where Bessent presented on the strategic importance of rare earths. While leaders agreed to an action plan to secure supply chains, Bessent has reportedly grown frustrated with the subsequent lack of urgency from attendees.
With the exception of Japan, which was forced to diversify after China abruptly cut its mineral supplies in 2010, G7 members remain heavily dependent on China. This leaves them vulnerable to potential export controls, which Beijing has threatened to impose.
China's control over the critical minerals supply chain is extensive. According to the International Energy Agency, China refines a significant portion of the world's most vital industrial minerals, including:
• Copper: 47%
• Lithium: 47%
• Cobalt: 47%
• Graphite: 87%
• Rare Earths: 87%
These materials are indispensable for a wide range of modern technologies, from defense systems and semiconductors to renewable energy components and electric vehicle batteries.
The United States is positioning itself as a leader in building alternative supply chains. The senior official noted that the U.S. is "ready to move with those who feel a similar level of urgency," encouraging others to recognize the seriousness of the situation.
While the official did not detail the Trump administration's next steps, the U.S. is already working to boost domestic production and has forged agreements with producers like Australia and Ukraine. In October, the U.S. signed a deal with Australia to counter China's dominance, which includes a project pipeline valued at $8.5 billion. The agreement leverages Australia's proposed strategic reserve for metals like rare earths and lithium.
Canberra has since reported receiving interest in similar partnerships from Europe, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore. Despite this progress, the official conceded that more work is needed, stating, "It's not solved."
The meeting follows recent reports that China has begun restricting exports of rare earths and related magnets to Japanese companies. However, U.S. officials clarified that the Washington gathering was planned well in advance of these developments. A statement from the U.S. is expected after the meeting concludes, but no specific joint action is anticipated.
Tehran has issued a stark warning to the United States and Israel, threatening retaliation if the US military intervenes in the escalating anti-government protests sweeping across Iran. The threat comes as Israeli sources confirmed the nation is on high alert, preparing for potential fallout from any US action.
U.S. President Donald Trump has made several statements about the situation, cautioning Iranian leaders against using force on demonstrators and saying on Saturday that the U.S. stands "ready to help."
In a direct response, Iranian Parliament Speaker Mohammad Baqer Qalibaf warned against any "miscalculation" during a parliamentary session on Sunday.
"Let us be clear: in the case of an attack on Iran, the occupied territories (Israel) as well as all U.S. bases and ships will be our legitimate target," stated Qalibaf, a former commander in the elite Revolutionary Guards.
The wave of protests, which began on December 28 over soaring inflation, has since evolved into a broader movement against the clerical establishment that has governed Iran since the 1979 Islamic Revolution. The government, in turn, accuses the United States and Israel of orchestrating the unrest.
Authorities have intensified their efforts to suppress the demonstrations. According to the U.S.-based human rights group HRANA, the death toll has reached 116. This figure includes protesters and 37 members of the security forces.
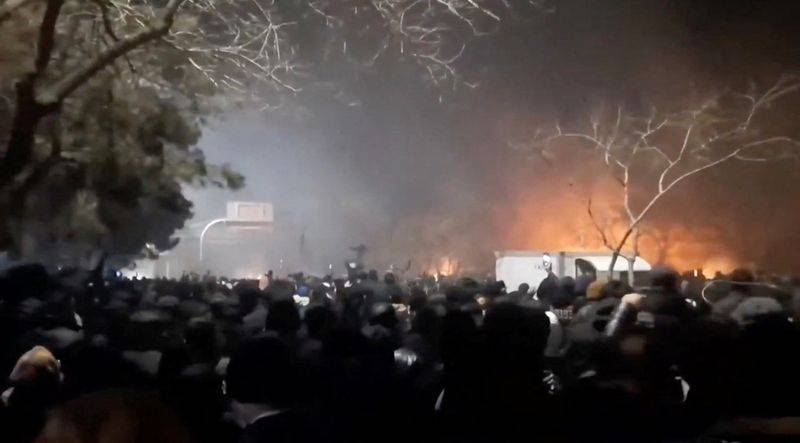

The government has also imposed an internet blackout since Thursday, severely limiting the flow of information. The internet monitoring organization Netblocks reported that national connectivity was at approximately 1% of normal levels.
Despite the blackout, a verified social media video from Tehran’s Punak neighborhood showed large crowds gathering at night, rhythmically drumming on metal objects in a display of protest.
Iranian state television has broadcast funeral processions for security personnel killed in the protests in cities like Gachsaran and Yasuj. While authorities have not released an official total, state media reported that 30 security members would be buried in Isfahan and that six were killed by "rioters" in Kermanshah. It also reported that a mosque in Mashhad was set on fire Saturday night.
Iran's police chief, Ahmad-Reza Radan, confirmed that security forces have increased their operations against "rioters," while the Revolutionary Guards accused "terrorists" of attacking security facilities.
Three Israeli sources involved in security consultations confirmed that Israel is on a high-alert footing, though they did not specify what measures this entails. The Israeli government and military have not officially commented on the situation.
Tensions between the two adversaries remain high, fueled by a 12-day war in June of last year, during which the U.S. participated in airstrikes alongside Israel. Iran responded to those strikes by launching missiles at an American air base in Qatar.
In a Friday interview with the Economist, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu warned of "horrible consequences" for Iran if it were to attack Israel. Referring to the internal unrest, he added, "Everything else, I think we should see what is happening inside Iran."
President Trump has continued to voice support for the protesters, posting on social media Saturday: "Iran is looking at FREEDOM, perhaps like never before. The USA stands ready to help!!!"
An Israeli source confirmed that Prime Minister Netanyahu and U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio discussed the possibility of U.S. intervention in a phone call on Saturday. A U.S. official acknowledged the call but did not disclose the topics discussed.
A senior U.S. intelligence official characterized the situation as an "endurance game." The official explained that the opposition is attempting to maintain pressure until government figures defect, while the authorities are trying to restore order without provoking direct U.S. intervention.
The future of Venezuela is in question following a dramatic U.S. strike that led to the capture of its leader, Nicolas Maduro. In the aftermath, Washington has signaled its intent to take a commanding role in the nation's vast and lucrative oil sector.
President Donald Trump has suggested that the U.S., in partnership with major American energy companies, will assume control over a significant portion of Venezuela's oil reserves, possibly on an indefinite basis. This stance was underscored by recent U.S. actions, including the seizure of two tankers linked to Venezuela in the Atlantic Ocean.
According to Trump, Venezuela has also agreed to export 50 million barrels of oil directly to the United States. This move could potentially divert supply from China, which has long been Venezuela's largest customer and a major creditor.
The potential shift in Venezuela's oil exports poses a significant challenge for Beijing. Approximately 30% of Venezuela's crude oil shipments are directed to Chinese state-owned enterprises as repayment for loans.
Analysts estimate that since 2007, China has extended as much as $60 billion in loans to Venezuela, with oil proceeds serving as collateral. Following the recent events, Chinese companies with interests in the country are reportedly consulting with Beijing to determine their next steps.
Analysts at Barclays have described Maduro's removal as a catalyst for a "political and oil sector reset." The U.S. plans to selectively lift sanctions to permit the global sale and transport of Venezuelan oil. However, the proceeds from these sales will reportedly be funneled into U.S.-controlled accounts, with funds released to Venezuela at Washington's discretion.
In a note, Barclays analysts including Alejandro Arreaza and Jason Keene outlined a potential path for economic recovery. They argue that an easing of sanctions and new access to multilateral financing could spark a rebound.
Key projections include:
• The potential for double-digit GDP growth from a low base.
• An increase in oil production by 200,000-300,000 barrels per day (b/d) by 2026, up from the current level of roughly 1 million b/d.
However, the analysts cautioned, "the sustainability of that recovery will depend on the final shape of the political transition."
Despite Maduro's capture, members of his socialist government remain in place. Former Vice President Delcy Rodriguez is now serving as the country's leader and is reportedly under pressure to comply with U.S. demands. Reports suggest the White House is prioritizing stability over an immediate push for a democratic transition.
"This closes a chapter in Venezuelan history and opens a path towards a political transition that would likely be welcomed by markets, as it could pave the way for an economic recovery and debt restructuring," the Barclays analysts concluded. "Nonetheless, this should be seen only as the beginning of a process that is still fragile and likely to be complex."
Mexico's economic outlook for 2026 points to a fragile recovery, with growth heavily influenced by trade uncertainty surrounding the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) review rather than domestic policy.
According to Bank of America, Mexico's economy is forecast to grow by approximately 1.2% in 2026. This marks a modest improvement from the projected 0.4% expansion in 2025, but the recovery faces significant constraints.
On the domestic front, the economic picture is clearing up. Uncertainty tied to the 2024 constitutional changes is diminishing, allowing for less restrictive government policies.
Key positive factors include:
• Easing Fiscal Policy: The government is not expected to pursue sharp fiscal tightening.
• Looser Monetary Policy: The central bank has started moving interest rates toward a neutral position.
• External Boost: The economy will benefit from stronger U.S. growth and a temporary lift from the FIFA World Cup.
Despite domestic improvements, the recovery will likely be held back by trade-related volatility. The mid-2026 review of the USMCA is the central source of this uncertainty.
While analysts expect the agreement to remain largely intact with only minor changes and continued low U.S. tariffs, the review process itself creates risk. The United States is anticipated to use trade policy as a bargaining chip to address other issues like migration, security, and Chinese investment in Mexico. This could lead to more frequent or targeted reviews, keeping exporters and investors on edge, especially with unresolved disputes in energy, labor, and agriculture.
Fiscal policy is expected to shift from a drag on growth to a neutral factor in 2026. Following a major consolidation in 2025, spending pressures from infrastructure projects and support for the state-owned oil company Pemex suggest a mild easing.
Bank of America analysts project the public sector borrowing deficit to reach about 4.9% of GDP, exceeding the government's 4.1% target. This gap will keep sovereign rating risks on the radar for investors.
Meanwhile, Mexico's central bank, Banxico, is projected to continue cutting its policy rate. With economic growth below its potential and inflation expectations anchored, the bank is expected to lower the rate from 7% to around 6% by the end of 2026, although temporary price pressures might slow the pace of these cuts.
This economic landscape creates a less favorable environment for the Mexican peso (MXN). After a strong performance in 2025, the currency is expected to lose momentum in 2026.
The combination of interest rate cuts, which reduce the currency's "carry appeal," and the persistent uncertainty surrounding the USMCA review is expected to weigh on the peso. As a result, the USD/MXN exchange rate is forecast to approach 19 by the end of the year.
Europe's economy is on a collision course with itself. A new analysis from Deutsche Bank reveals a "two-economy problem" shaping the continent's trajectory into 2026, pitting cyclical resilience against deep-seated structural flaws that threaten its future competitiveness.
The outcome of this conflict will determine whether Europe sustains its economic momentum or buckles under the pressure of an increasingly fractured global landscape.
On the surface, annual GDP growth projections seem to show a slowdown, dropping from 1.4% in 2025 to 1.1% in 2026. However, a closer look at quarter-over-quarter growth—a better indicator of immediate momentum—tells a different story. According to the report by chief economist Mark Wall, this metric is expected to accelerate from 1% to 1.5%.
A key factor supporting this near-term growth is Germany's expansionary fiscal policy, which is poised to offset tightening measures in other parts of the bloc.
Meanwhile, the European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to hold its policy rates steady at 2% throughout 2026. However, the bank may be forced to start hiking rates again by mid-2027, as fiscal stimulus and tight labor markets could push medium-term inflation higher.
Beyond the headline numbers, Europe faces a persistent competitiveness challenge that currency fluctuations alone can no longer explain.
Before the global financial crisis, competitiveness was closely tied to currency movements. That relationship has broken down over the last decade. Data from the European Commission confirms that European firms have been hit by an unusually persistent shock to their competitiveness since Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
The structural headwinds are significant:
• Energy Prices: Costs remain roughly three times higher than in the United States.
• Supply Chains: The EU is grappling with vulnerable supply lines.
• Regulation: Burdensome rules hinder business agility.
• Labor Market: Access to skilled labor remains a constraint.
"The world is changing. It is becoming more geopolitical, more frictional," Deutsche Bank noted. "The direction of travel with geopolitics is the opposite to how the EU was formed and developed on the back of openness to trade, integration, and rules-based multilateralism."
There are signs that Europe is finally joining the global technology spending boom. ECB President Christine Lagarde has pointed to an uptick in IT spending and preparations for artificial intelligence, as noted in the ECB's Corporate Telephone Survey. Investment data also shows a recovery is underway after the stagnation caused by the energy shock.
However, critical questions remain. It is unclear if AI spending will translate into substantial GDP growth, especially if it relies heavily on technology imports. Furthermore, Europe's economic rigidities could slow the adoption of AI and limit the productivity gains it promises.
Progress on critical reforms remains sluggish. The implementation of proposals from 2024 reports by Mario Draghi and Enrico Letta, aimed at boosting competitiveness, was slow in 2025 and is expected to crawl at a similar pace in 2026.
The most meaningful signal of progress would be a genuine advancement toward a Capital Markets Union or a Savings and Investment Union. Such initiatives would deepen Europe's financial markets and unlock capital for innovation.
For 2026, Deutsche Bank’s baseline view is that resilience will likely win out. The European economy is expected to navigate the immediate challenges.
However, the report carries a stark warning: "unless the rigidities are resolved it will be difficult for the European economy to continue to outperform, at least without generating economic frictions."
Two potential bright spots could offer some support. First, Beijing's "anti-involution" policy might ease the flow of deflationary exports to Europe. Second, stronger U.S. demand leading up to its midterm elections could boost European exports, even amidst ongoing trade friction.
Israel has reportedly entered a state of high alert over the possibility of United States intervention in Iran, where the government is facing the most significant anti-government protests in years. According to three sources with knowledge of Israeli security consultations, the country is closely monitoring the situation.
The heightened alert follows several days of statements from U.S. President Donald Trump, who has threatened to intervene and warned Iranian authorities against using force on demonstrators. On Saturday, Trump declared that the U.S. stands "ready to help."
The sources, who participated in security meetings over the weekend, did not provide specific details on what Israel's high-alert status involves operationally. The two nations previously engaged in a 12-day war in June, which saw the U.S. join Israel in launching airstrikes.

The prospect of American action was a key topic in a phone call on Saturday between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio. An Israeli source present for the conversation confirmed that the two leaders discussed potential U.S. intervention in Iran.
While a U.S. official acknowledged that the call took place, they did not comment on the specific subjects discussed.
Despite the escalating situation, Israel has not indicated any intention of intervening directly in Iran. Tensions between the two rivals remain high, largely due to Israeli concerns over Iran's nuclear ambitions and ballistic missile development.
In a Friday interview with the Economist, Netanyahu stated that an attack on Israel would lead to "horrible consequences" for Iran. Addressing the ongoing protests, he adopted a more cautious tone, remarking, "Everything else, I think we should see what is happening inside Iran."
Analysts are bracing for a higher US inflation reading in December, with the core consumer price index (CPI) projected to rise 2.7% year-over-year. This forecast is slightly above the 2.6% annual increase seen in November, a figure that marked the smallest gain since early 2021.
Despite the expected uptick, many consumers report feeling a significant drop in price pressures. This discrepancy highlights the complexity of the upcoming data, with some analysts warning that the December figures could be misleading.
The context for December's report is complicated by issues with the previous month's data. The Bureau of Labor Statistics confirmed it could not publish certain month-to-month adjustments in its last CPI report due to a recent government shutdown.
This disruption particularly affected the agency's ability to gather price data in October, leading to unusually stable readings for key rent indexes in the November report. Consequently, the November data may have painted an overly optimistic picture of declining inflation, setting the stage for a statistical rebound.
The December CPI report, scheduled for release on Tuesday, January 13, is expected to reverse some of November's unusual trends. However, experts caution against interpreting this as a new inflationary surge.
"We believe the CPI report will create some misleading stories," one analysis stated. "We anticipate that the December data will be high, largely due to the correction of some of the downward trends seen in November's data. Some analysts might interpret this high reading as a sign that inflation is coming back, but we think that's not correct."
The same analysis suggested that November's report likely exaggerated the inflation downturn by about 20 basis points. While many retailers have been reducing prices and the effects of tariffs have peaked, the December data will primarily reflect a statistical catch-up rather than a fundamental shift in the inflation trend.
This data uncertainty is a key reason Federal Reserve officials are inclined to keep interest rates unchanged for the time being. With inflation readings lacking clarity and the US job market showing signs of stabilization despite weak wage reports, the central bank appears to be in a holding pattern.
The inflation report is just the start of an eventful week for economic news. Market participants will also be closely watching several other key releases and events:
• Federal Reserve Speakers: New York Fed President John Williams is scheduled to speak on Monday, kicking off a week of public appearances by central bankers. Other officials set to speak include Michelle Bowman, Philip Jefferson, Alberto Musalem, and Anna Paulson.
• Retail Sales Data: On Wednesday, January 14, government data is expected to show another significant rise in retail sales. Analysts forecast a 0.4% increase for November (excluding autos), matching October's pace and confirming strong consumer spending in the fourth quarter.
• Other Key Reports: The week's economic calendar also includes data on October's new-home sales, the November producer price index (PPI), and December's industrial production and home resales.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up