Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. Average Hourly Wage MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Average Hourly Wage MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Average Weekly Working Hours (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Average Weekly Working Hours (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. New Housing Starts Annualized MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.S. New Housing Starts Annualized MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Total Building Permits (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Total Building Permits (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Annual New Housing Starts (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Annual New Housing Starts (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 U.S. U6 Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. U6 Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Manufacturing Employment (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Manufacturing Employment (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Private Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Private Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Nonfarm Payrolls (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Average Hourly Wage YoY (Dec)
U.S. Average Hourly Wage YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
 Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Dec)
Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Dec)
Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)
Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Government Employment (Dec)
U.S. Government Employment (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Employment (SA) (Dec)
Canada Employment (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Jan)
U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Jan)
U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Jan)
U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Indonesia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Jan)
Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 India CPI YoY (Dec)
India CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Nov)
Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 FOMC Member Barkin Speaks
FOMC Member Barkin Speaks U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield
U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Nov)
Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Nov)
Japan Trade Balance (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Dec)
U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Dec)
U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Turkey Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Dec)
U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Services Growth YoY (Nov)
Brazil Services Growth YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Income MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Real Income MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. CPI MoM (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. CPI MoM (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI YoY (Not SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. New Home Sales Annualized MoM (Oct)
U.S. New Home Sales Annualized MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Annual Total New Home Sales (Oct)
U.S. Annual Total New Home Sales (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Cleveland Fed CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Cleveland Fed CPI MoM (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Dec)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Dec)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --









































No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
The EU has greenlit a landmark Mercosur trade deal after 25 years, navigating fierce farmer protests and French opposition with concessions, though environmental concerns persist.
The European Union has greenlit a landmark trade deal with the South American Mercosur bloc, concluding over 25 years of complex negotiations. The agreement, the largest in the EU's history, secured the necessary support from member states despite fierce opposition and widespread farmer protests.
At least 15 countries, representing 65% of the bloc's population, voted in favor of the deal with Mercosur, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Some EU diplomats reported that the number of supporters was as high as 21 nations.
France, the EU's largest agricultural producer, led the charge against the agreement, ultimately voting no. The French government argues that the deal will flood the European market with cheaper food imports like beef, poultry, and sugar, directly harming its domestic farmers. Austria, Hungary, Ireland, and Poland joined France in opposition, while Belgium abstained.
This political resistance is amplified by massive protests on the ground. Farmers have blockaded highways in France and Belgium and marched in Poland, demonstrating their deep-seated anger over the deal's potential impact on their livelihoods.
The backlash in France has been particularly severe. Mathilde Panot, a leader of the far-left France Unbowed party, claimed France had been "humiliated" by Brussels. Both far-right and far-left parties are now planning to file no-confidence motions against the government over the agreement's expected approval.
French Agriculture Minister Annie Genevard insisted the fight is not over, vowing to rally opposition ahead of a crucial vote in the EU assembly.
Proponents, including Germany and Spain, view the Mercosur agreement as a critical strategic move. They contend it will help offset business losses from U.S. tariffs and reduce the EU's economic dependence on China by securing access to vital minerals.
German Chancellor Friedrich Merz hailed the vote as a "milestone" for Germany and Europe, though he criticized the lengthy negotiation process. "25 years of negotiations is too long," he stated. "It's vital that the next free trade agreements are concluded swiftly."
The economic stakes are high. The agreement is projected to eliminate €4 billion ($4.66 billion) in tariffs on EU exports. Mercosur nations currently impose steep duties on European goods, including:
• 35% on car parts
• 28% on dairy products
• 27% on wines
The EU and Mercosur aim to boost their goods trade, which was valued at €111 billion in 2024. While the EU primarily exports machinery, chemicals, and transport equipment, Mercosur's exports are dominated by agricultural products, minerals, and paper goods.
To win over wavering countries, the European Commission introduced several key concessions. These include safeguards to halt imports of sensitive agricultural products if markets are disrupted, stricter import controls for pesticide residues, and a new crisis fund for farmers.
These measures proved decisive in swaying Italy, which shifted from a "no" vote in December to a "yes." Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni described the revised terms as a "sustainable" balance.
Beyond agricultural and economic concerns, the deal faces strong opposition from environmental groups. Organizations like Greenpeace argue that the agreement will fuel deforestation in the Amazon rainforest as commodities are produced for the European market.
"This unpopular deal is a disaster for the Amazon rainforest," said Greenpeace EU campaigner Lis Cunha, urging progressive members of the European Parliament to reject it.
Before the trade deal can take effect, it must be formally signed and then pass a final vote in the European Parliament. Bernd Lange, chair of the parliament's trade committee, anticipates that the deal will ultimately pass, with a final vote likely scheduled for April or May.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy announced Friday that he is in discussions with the United States about a potential free-trade agreement, a cornerstone of a wider prosperity package designed to fuel the nation's recovery after the war.
In a phone interview with Bloomberg, Zelenskiy explained the deal would establish zero tariffs on trade with the U.S. and would apply to certain industrialized regions of Ukraine. He argued this would provide the country with "very serious cards" against neighboring states, potentially attracting significant investment and new businesses.
The Ukrainian leader emphasized that he needs to discuss the proposal's details directly with President Donald Trump. He also framed the agreement as an additional guarantee for Ukraine's economic security.
Zelenskiy's comments followed a report from his top negotiator, Rustem Umerov, who held a call with Trump's special envoys, Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner. According to Zelenskiy, the U.S. representatives have recently been in contact with Russia in "some kind of format," though he did not know if they planned to travel to Russia for in-person meetings.
The diplomatic process involves Ukraine submitting feedback on territorial proposals to the U.S. team. These proposals are then relayed to Russian officials for their input before a response is delivered back to Kyiv.
Zelenskiy expressed hope of receiving Russia’s response to a 20-point framework by the end of this month. This timeline would coincide with his efforts to finalize a recovery plan and security guarantees with Trump. He expects to meet Trump either in the U.S. or at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland.
Demand for Concrete Security Guarantees
A key focus for Zelenskiy is securing specific U.S. commitments in the event of renewed Russian aggression.
"I don't want everything to end up in them merely promising to react," Zelenskiy said. "I really want something more concrete."
While talks on security guarantees with allies have progressed, territorial disputes remain the primary obstacle in negotiations to end the invasion. Earlier this year, Trump stated he was "not thrilled" with Russian President Vladimir Putin but has not yet publicly committed to new measures to support Ukraine.
To address the military stalemate, Ukraine is considering two distinct plans, including one proposed by the United States to create a special economic zone.
1. The Free Economic Zone
This proposal, separate from the broader free-trade deal, is a localized plan for the battlefield area. If a truce is reached, a buffer area would be established as troops pull back. This zone would allow businesses to operate and people to live under a special legal and tax regime.
"The format is difficult but fair," Zelenskiy noted. He added that the plan would require Russia to "mirror" Ukraine's actions and would need domestic discussion. The zone could be created in parts of the Donbas region, serving as a compromise that requires both sides to withdraw their forces.
2. Freezing the Contact Line
A second option involves halting the fighting while leaving forces in their current positions, with unresolved issues addressed through diplomacy.
"It's about freezing the contact line, not the conflict," Zelenskiy clarified, adding that this arrangement would be easier for Ukraine's foreign allies to implement and monitor.
Zelenskiy reiterated that Russia’s actions indicate it is not prepared for genuine diplomacy. He affirmed that Ukraine will never recognize its occupied territories as Russian, though it expects to restore full sovereignty in the future.
In this context, he urged the U.S. to provide a more systematic response to Russian aggression, noting that Ukraine has still not received all pledged Patriot air-defense systems and ammunition. His call came as Russia launched a major air attack on Kyiv early Friday, leaving large parts of the capital without power, heat, and water.
While Kyiv's mayor urged residents to leave the city to avoid freezing, Zelenskiy criticized the call as alarmist, stating that efforts should focus on restoring normal operations.
Regarding recent calls from European leaders for renewed dialogue with Moscow, Zelenskiy said he was not opposed, as long as Putin understands the discussions are serious. "We are moving toward the final stage, even if we don't yet know what it will look like," he concluded.
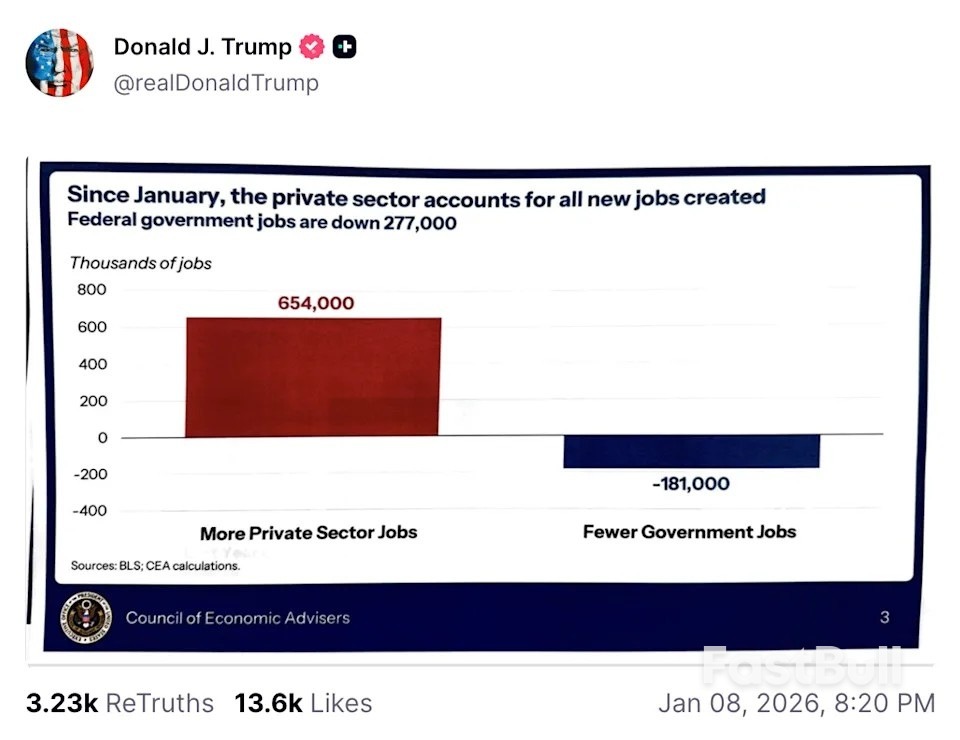
Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic has identified inflation as his primary economic concern, describing the current job market as being in a state of "low-hire, no-fire" amid ongoing uncertainty.
In a radio interview on Friday with WLRN in Florida, Bostic stressed that the central bank must remain sharply focused on taming price pressures.
Bostic stated that "inflation is still too high," arguing that the Federal Reserve's effort to manage prices is currently a more significant challenge than its employment mandate.
"You've got to get it under control, and we need to be laser-focused on making sure that everything we do is contributing to that," he explained.
He warned that persistent high prices are squeezing consumers and could ultimately weaken the economy in ways that become more difficult for the Fed to manage. "We still have this big concern around inflation, and we know that consumers across the spectrum are feeling the pressure of high prices," Bostic added.
Bostic's comments followed the release of December's employment data, which provided new context on the state of the labor market. The report showed:
• A modest payroll gain of 50,000 jobs.
• A decline in the unemployment rate to 4.4%, down from 4.5% the previous month.
While acknowledging that labor markets have cooled, Bostic expressed some doubt that they are on a path toward significant weakness. This relative stability in hiring gives the Federal Reserve more time to deliberate before making a decision on interest rates, according to many economists.
The Fed's three-quarters of a percentage point in rate cuts last year was intended to support the job market while maintaining enough policy restraint to guide inflation back toward the 2% target.
Many economists still anticipate that the Fed will cut interest rates this year as price pressures ease and the effects of tariffs diminish. However, the steady employment figures reduce the immediate pressure on the central bank to act.
When asked about a plan by President Donald Trump to direct $200 billion from government-sponsored housing companies to buy mortgage bonds, Bostic did not comment on the specific proposal.
Instead, he pointed to more fundamental issues driving housing costs. "I do think that a lot of the housing affordability challenges are about more than just financing," Bostic noted. "There's a supply and demand issue that has persisted in many major markets."
Bitcoin was trading near the $90,000 mark on Friday, finding stability after the U.S. Supreme Court delayed a key decision on Donald Trump's tariff policies, temporarily calming macroeconomic uncertainty across markets.
At the time of writing, Bitcoin's price stood at approximately $90,443, reflecting a 1% decline over the past 24 hours. Daily trading volume reached about $45 billion, while its total market capitalization fell slightly to $1.80 trillion.
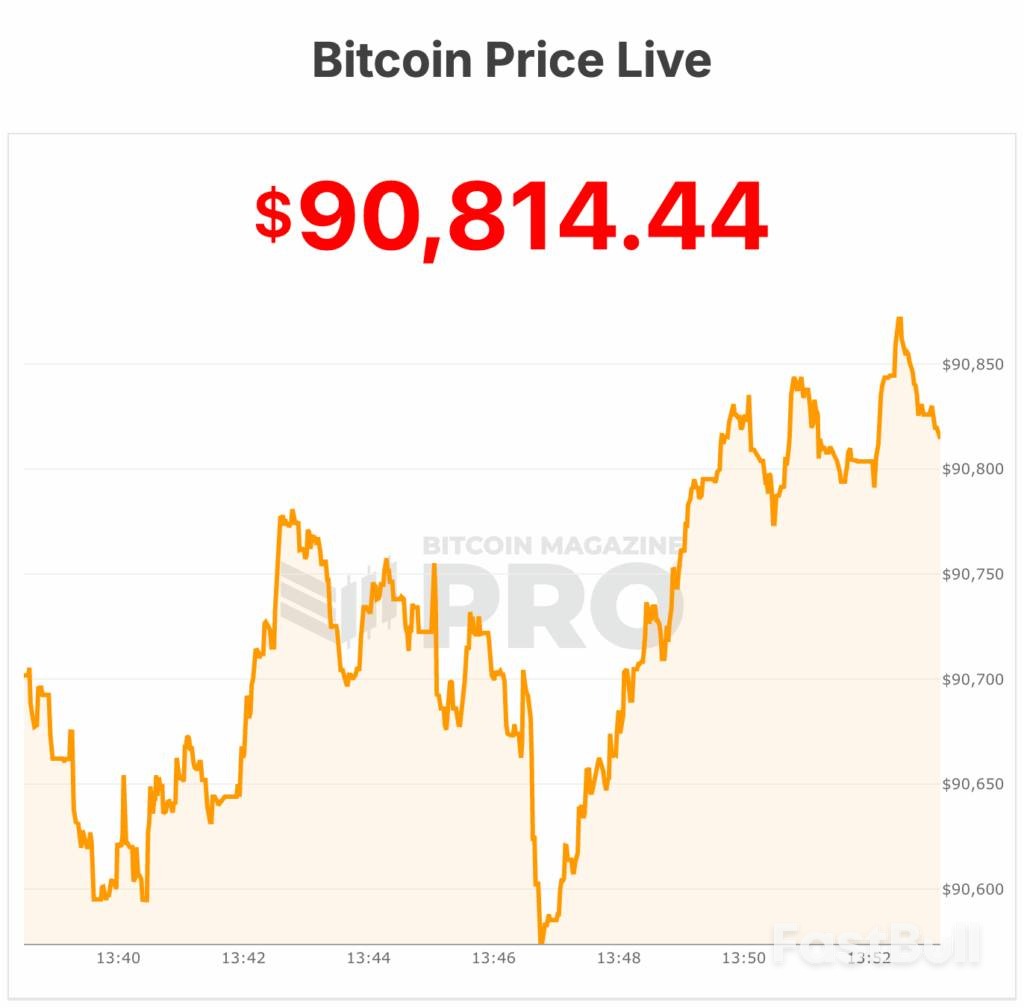
Despite the minor drop, the asset remains in a tight trading range. It is currently trading about 2% below its seven-day high of $91,839 and just 1% above its seven-day low of $89,671. Meanwhile, Bitcoin's circulating supply has reached 19,973,659 BTC, moving ever closer to its hard cap of 21 million coins—a core feature supporting its long-term value proposition.
Crypto markets initially showed signs of weakness this week as traders braced for a potential Supreme Court ruling on the legality of Trump-era global tariffs. The decision was widely seen as a major catalyst for broader market movements.
However, prices recovered on Friday after the court announced it would delay its ruling until the following week. This postponement reduced the immediate risk of market disruption, providing a lift to equities, bonds, and digital assets.
Analysts noted that the delay specifically eased concerns over a scenario where the U.S. Treasury might have to refund over $130 billion to importers if the tariffs were deemed illegal. Such an event could have created significant fiscal disruption.
The market's reaction underscores Bitcoin's growing sensitivity to macroeconomic factors, including shifts in policy expectations, liquidity conditions, and geopolitical events. While long-term adoption trends remain a primary driver, major legal and political developments continue to heavily influence its short-term price action.
Bitcoin's current price stability represents a cooling-off period following a surge in the opening days of the year. That early-January rally boosted bullish sentiment but eventually met resistance, triggering a round of profit-taking that stalled its momentum.
From a technical perspective, traders are closely watching the $90,000–$91,000 zone as a critical area of support.
• A sustained break below this level could open the door to further downside, potentially pushing the price toward the high-$80,000 range.
• Conversely, a decisive move back above $92,000 would signal renewed strength and likely clear a path toward higher resistance levels.
For now, Bitcoin remains locked in a consolidation pattern, with compressed volatility as traders await a new catalyst to dictate the next major move.
Looking ahead, Cathie Wood of ARK Invest recently suggested that political dynamics could lead the U.S. government to begin actively purchasing Bitcoin by 2026. In a podcast, Wood argued that cryptocurrency has become an important political issue for President Trump, which could shape future policy.
While the United States currently holds a Bitcoin reserve composed of seized assets, Trump has pledged not to sell any of it. Wood believes the administration's stance could evolve from merely holding confiscated coins to making outright purchases for a national strategic reserve. She noted that the original goal was to acquire one million BTC.
Crypto has also grown into an organized political force, supporting Trump and engaging with the White House through donations and events. This growing influence, combined with executive orders that have already established a reserve and stockpile, sets the stage for a potential policy shift.
Wood sees direct government purchases as a potential market inflection point. With nearly 20 million of the total 21 million BTC already mined, U.S. government buying would introduce a massive new source of demand, likely having a significant positive impact on the Bitcoin price.
As of the time of writing, Bitcoin is priced at $90,814.
Recent reports suggest China is preparing to approve the import of older-generation Nvidia artificial intelligence (AI) chips, potentially reopening a critical market for the U.S. chipmaker after a previous ban.
While details are still emerging, regulators will reportedly allow sales of these AI processors to commercial and technology customers. However, significant limitations will apply. The Chinese government is expected to prohibit the use of these chips by government agencies, military operations, critical infrastructure, and state-owned businesses due to security concerns.

The financial stakes for Nvidia are enormous. In calendar 2024, the last full year of sales to China, the company generated $17.1 billion in revenue from the country despite initial export restrictions on its most advanced chips. Nvidia later estimated it absorbed an $8 billion revenue hit from expanded U.S. export controls.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang has highlighted the "very high" demand for the company's chips in China, suggesting that approved sales could exceed $50 billion annually. This figure may even be conservative.
According to a Reuters report, Nvidia has already received orders from Chinese customers for over 2 million H200 chips, priced at $27,000 each. This alone translates to approximately $54 billion in potential revenue. After accounting for a 25% export levy payable to the U.S. government, Nvidia could still clear more than $40 billion from these existing orders.
Crucially, potential sales to China are not included in Nvidia's current financial guidance, meaning any revenue would represent a significant boost to its forecasts. This comes as the company already expects to generate $500 billion from its AI-focused data center processors in the six quarters ending in early 2027—a figure Huang recently hinted was too conservative.
A return to the Chinese market could dramatically alter Nvidia's financial trajectory. Here’s a breakdown of the potential impact:
• Revenue Boost: Analysts currently forecast Nvidia's revenue for next year at $320 billion. An additional $40 billion would represent a major increase.
• Earnings Per Share (EPS): With a net profit margin of 56%, a $40 billion revenue injection could potentially drive the company's EPS to $8.29.
• Stock Price: Applying Nvidia’s current price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of approximately 46 to that new EPS figure would imply a share price of around $380—more than double its present level.
Simply put, Nvidia's reentry into the Chinese market could unlock substantial growth and deliver a windfall for its shareholders.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up