Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Services Index MoM
U.K. Services Index MoMA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)
U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)
U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France HICP Final MoM (Nov)
France HICP Final MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India CPI YoY (Nov)
India CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Deposit Gowth YoY
India Deposit Gowth YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)
Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia Trade Balance (Oct)
Russia Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech
Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)
Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)
U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)
China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)
Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)
Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)
Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations
U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)
Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
The likelihood of a Federal Reserve rate cut in September is now seen near 100% after new data showed U.S. inflation increased at a moderate pace in July and Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said he thought an aggressive half-point cut was possible given recent weak employment numbers.
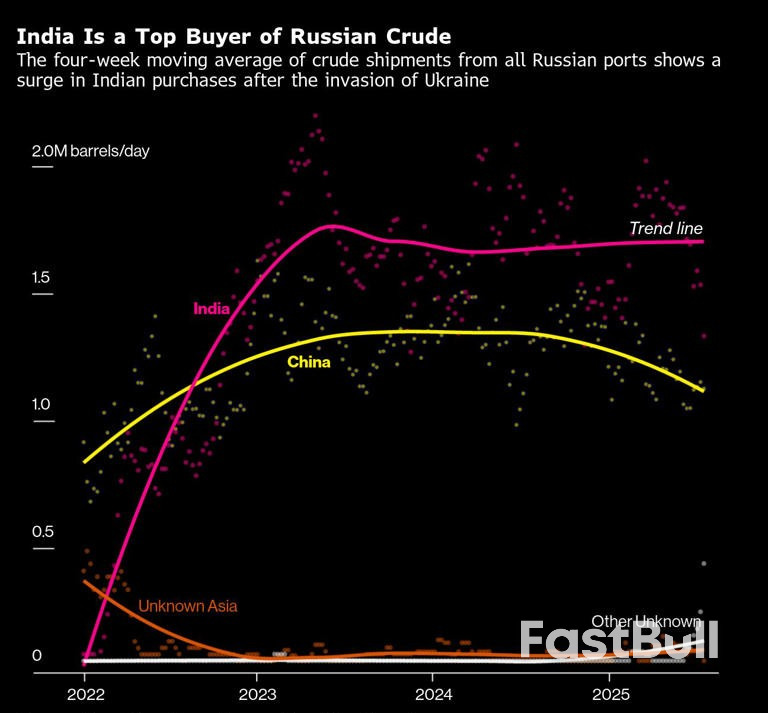
In the face of blistering criticism from President Donald Trump, Goldman Sachs economist David Mericle on Wednesday stood by a controversial forecast that tariffs will begin to hit consumer wallets.
Trump lashed out at the bank in a Tuesday post on Truth Social, suggesting that CEO David Solomon "get a new Economist" or consider resigning.
Mericle, though, said in a CNBC interview that the firm is confident in its research, the president's objections notwithstanding.
"We stand by the results of this study," he said on "Squawk on the Street." "If the most recent tariffs, like the April tariff, follow the same pattern that we've seen with those earliest February tariffs, then eventually, by the fall, we estimate that consumers would bear about two thirds of the cost."
The source of the president's ire was a Goldman note over the weekend, authored by economist Elsie Peng, asserting that while exporters and businesses thus far have absorbed most of Trump's tariffs, that burden will switch in the months ahead to consumers.
In fact, Peng wrote that Goldman's models indicate consumers will take on about two-thirds of all the costs. If that's the case, it will push the personal consumption expenditures price index, the Federal Reserve's main inflation forecasting gauge, to 3.2% by the end of the year, excluding food and energy. Core PCE inflation for June was at 2.8%, while the Fed targets inflation at 2%.
"If you are a company producing in the U.S. who is now protected from foreign competition, you can raise your prices and benefit," Mericle said. "So those are our estimates, and I think actually, they're quite consistent with what many other economists have found."
Of note, Mericle said Trump likely still will get at least some of the interest rate cuts he's been demanding of the Fed.
"I do think most of the impact is still ahead of us. I'm not worried about it. I think, like the White House, like Fed officials, we would see this as a one-time price level effect," he said. "I don't think this will matter a whole lot to the Fed, because now they have a labor market to worry about, and I think that's going to be the dominant concern."
Following modest gains reported this week for the consumer price index, and a weak July nonfarm payrolls report that featured sharp downward revisions to the prior two months, markets are pricing in cuts from the Fed at each of its three remaining meetings this year.
For several years – especially since the United States banned ZTE and Huawei in 2018 and 2019, respectively – U.S. export controls on cutting-edge technologies have been framed as a measure to safeguard national security. On the same grounds, the Biden administration banned the sale of certain U.S.-made chips to China in 2022 and 2023. To circumvent such restrictions, Nvidia developed the H20 chip, a downgraded form of its H-100 Graphic Processing Unit (GPU), and AMD developed the MI308, both to serve the Chinese markets.
Nvidia’s CEO Jensen Huang has often vocally opposed the restrictive export controls targeting China, claiming the policy is counterproductive for the United States’ economic and strategic interests. Through active lobbying during the current Trump administration, which is following a more inward-looking approach, Nvidia managed to get an official permit for H20 sales to China – albeit for a fee.In a highly unusual settlement, Nvidia and AMD will hand over 15 percent of their revenue from H20 and MI308 chip sales to China directly to the U.S. government. This arrangement is not a standard export tariff, nor a conventional tax. It is a direct revenue-sharing deal between the government and the two companies, targeted at a single foreign market, i.e., China.
According to estimates by Bernstein Research, by the end of 2025, Nvidia will have sold over 1.5 million H20 chips in China, generating about $23 billion in revenue, and AMD is projected to record $800 million in China chip sales. That means the deal could deliver more than $2 billion directly to the U.S. Treasury.Unlike in China, where the provision of “golden shares” (a shareholding arrangement enabling the Chinese government to buy a certain percentage of shares in private enterprises) highlights the intimate relationship between the Chinese state and its private corporations, such policy moves in the United States are extremely rare. However, the Trump administration in July followed a similar approach when it approved the takeover of U.S. Steel by Japan’s Nippon Steel.
While the Nippon Steel deal aimed at securing critical industries from falling under foreign control, it also indicated a growing trend of state capitalism in the United States. Now the revenue-sharing agreement with AMD and Nvidia exemplifies a larger pattern where companies are falling into quid-pro-quo arrangements to prevent the imposition of tariffs and preserve their own market position, while pledging to bring jobs, revenues, and market concentration to the United States. However, the deal also risks replacing principle-driven trade policy with ad hoc bargaining, leaving both allies and adversaries uncertain about U.S. red lines.For U.S. chipmakers, it’s better to earn some revenue from China than none. While the deal gives direct access to the lucrative China market, it also directly eats into Nvidia’s and AMD’s profits. This will create ripples in the broader market ecosystem, wherein corporate planning, profit margins, and investor confidence could all be affected.
Major U.S. companies with considerable market share in China will be watching closely. If the government is willing to impose a revenue-sharing requirement for chip sales, might it do the same for other strategic sectors? This could prompt firms to rethink their China strategies, diversify supply chains, or intensify lobbying to either pursue or avoid similar arrangements. The message to shareholders becomes clearer after this move: geopolitical risk is no longer an abstract factor; instead, it directly shapes revenue streams.
One possible explanation behind the decision is the “engage to constrain” strategy: selling downgraded chips keeps China reliant on U.S. technology, thereby maintaining a degree of influence over its AI development. The H20 and MI308 chips, being less powerful than flagship models, are intended to fall below the threshold of national security risk.This could prove to be a pitfall for two reasons. First, Washington has previously failed to accurately gauge Chinese firms’ ability to refurbish outdated hardware and optimize it for higher-grade applications. This means that even downgraded chips can accelerate China’s AI capabilities, including in areas with military applications.
Second, the free flow of H20 chips is unlikely to halt China’s renewed drive toward indigenous chip development. In fact, the renewed synergies between governments and private chipmakers in China are likely to take advantage of this policy relaxation to prepare themselves for any future restrictions. Thus the new policy, which resolves to protect domestic interests, will again fuel Beijing’s determination to achieve chip independence and undermine U.S. strategic objectives in the long term.
By reversing the ban and taking a revenue share, Washington risks sending a conflicting message: that security concerns can be waived in exchange for commercial concessions. The shift from safeguarding national security to commodifying strategic concerns poses several questions. If sensitive technology can be sold for a price, how credible will future restrictions appear to allies, adversaries, and U.S. companies alike?
More broadly, U.S. allies involved in semiconductor supply chains – Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and the Netherlands – may see this as a signal to adopt similarly transactional policies, fragmenting the global trade environment. During the Biden administration, these allies were part of the broader export control regime. If this model is perceived as putting a price tag on national security, it could weaken the legitimacy of future export controls, embolden adversaries to test U.S. resolve, and encourage allies to question U.S. consistency.The United States now walks a fine line. Whether this is a masterstroke of transactional diplomacy or a short-sighted policy gamble will depend on whether Washington can secure broader strategic gains without undermining its own credibility.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up