Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)
U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)
China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)
Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)
Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence IndexA:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)
Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)A:--
F: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Prices Received Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Prices Received Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing New Orders Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing New Orders Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Trimmed CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)
Canada Trimmed CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Federal Reserve Board Governor Milan delivered a speech
Federal Reserve Board Governor Milan delivered a speech U.S. NAHB Housing Market Index (Dec)
U.S. NAHB Housing Market Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Composite PMI Prelim (Dec)
Australia Composite PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Services PMI Prelim (Dec)
Australia Services PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)
Australia Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Japan Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. 3-Month ILO Employment Change (Oct)
U.K. 3-Month ILO Employment Change (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Unemployment Claimant Count (Nov)
U.K. Unemployment Claimant Count (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Unemployment Rate (Nov)
U.K. Unemployment Rate (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. 3-Month ILO Unemployment Rate (Oct)
U.K. 3-Month ILO Unemployment Rate (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Average Weekly Earnings (3-Month Average, Including Bonuses) YoY (Oct)
U.K. Average Weekly Earnings (3-Month Average, Including Bonuses) YoY (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Average Weekly Earnings (3-Month Average, Excluding Bonuses) YoY (Oct)
U.K. Average Weekly Earnings (3-Month Average, Excluding Bonuses) YoY (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 France Services PMI Prelim (Dec)
France Services PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 France Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
France Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 France Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)
France Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Services PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Germany Services PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Germany Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Germany Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone Composite PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Services PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone Services PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone Manufacturing PMI Prelim (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Services PMI Prelim (Dec)
U.K. Services PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)
U.K. Manufacturing PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Composite PMI Prelim (Dec)
U.K. Composite PMI Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (Dec)
Euro Zone ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany ZEW Current Conditions Index (Dec)
Germany ZEW Current Conditions Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (Dec)
Germany ZEW Economic Sentiment Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Trade Balance (Not SA) (Oct)
Euro Zone Trade Balance (Not SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone ZEW Current Conditions Index (Dec)
Euro Zone ZEW Current Conditions Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
Euro Zone Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Retail Sales MoM (Excl. Automobile) (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Retail Sales MoM (Excl. Automobile) (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) annual gathering in the Rocky Mountains is usually a time for central bankers and their wonky friends to kick back, discuss a few complicated economic topics and then go for a hike in the shadow of Grand Teton.
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) annual gathering in the Rocky Mountains is usually a time for central bankers and their wonky friends to kick back, discuss a few complicated economic topics and then go for a hike in the shadow of Grand Teton.This year, the Fed’s Jackson Hole symposium, which wrapped up Saturday, was at times a tense affair and drove home how difficult the path ahead is for the US central bank.
On Friday, Chair Jerome Powell used his keynote speech to signal the Fed is headed for an interest-rate cut as soon as its next policy meeting in September. Yet there are clear divisions among policymakers over whether that’s the right call. Powell, himself, noted the economy has handed Fed officials a “challenging situation”.Policymakers are grappling with inflation that’s still above their 2% goal — and rising — and a labour market that’s showing signs of weakness. That unnerving reality, which pulls policy in opposite directions, is made worse by a high degree of uncertainty about how each of those factors will evolve over the coming months.
“We’re getting some cross-currents and it’s in a difficult environment,” Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee said in an interview on the sidelines of the conference. “I always say the hardest job the central bank has is to get the timing right at moments of transition.”The conference also highlighted the political pressures weighing on the Fed. Those are likely to intensify in coming months as President Donald Trump looks to put his stamp on what may be the most prominent federal institution to have so far escaped his overhaul attempts.
As Powell delivered his speech Friday morning, Trump said he would fire Fed Governor Lisa Cook if she didn’t resign over recent allegations that she committed mortgage fraud. It’s the latest attempt by the administration to pressure the Fed from multiple angles as Trump relentlessly pushes for lower interest rates.Security for the event was noticeably heightened compared to recent years, adding to the tension at the gathering. Officers from the Fed Police, US Park Police and Teton County Sheriff’s Office, some in military-style fatigues and carrying weapons, were a constant presence.
Earlier Friday morning, officers had to remove one person, the Trump-backer and Fed gadfly James Fishback, after he confronted Cook in the lobby of the lodge and shouted questions about the mortgage controversy.
Powell, in what was likely his final Jackson Hole speech at the helm of the Fed, detailed the cloudy signals coming from the economy.While the effect of tariffs on prices is now visible, there are still questions about whether that will reignite inflation in a more persistent way, he said. He called the labour market’s current status — with both falling demand for, and declining supply of workers — “curious”.
Even with those uncertainties, Powell opened the door to a rate cut at the Fed’s Sept 16-17 meeting, though it wasn’t as clear a signal as at last year’s conference. Then, the labour market was deteriorating but inflation worries had receded, and many policymakers shared a desire to cut soon. The backing is not nearly as strong this year.
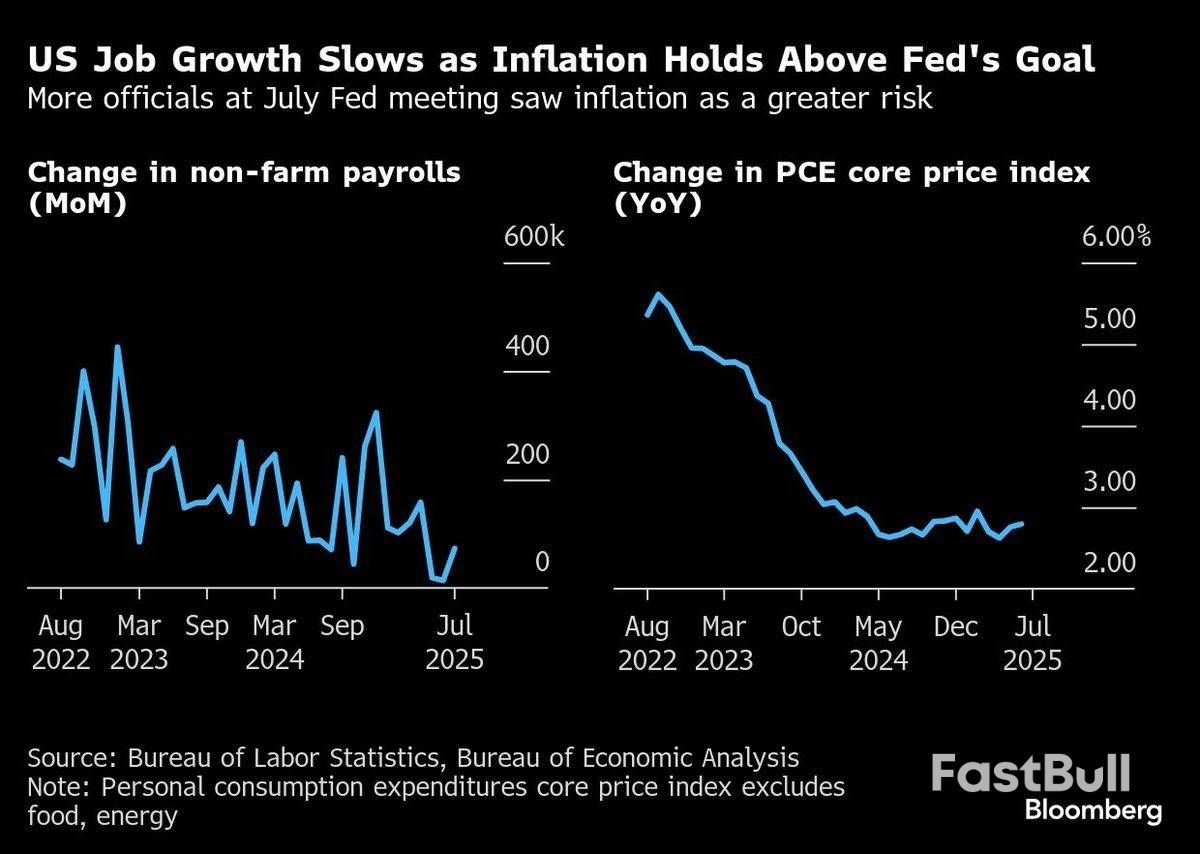
Recent data have shown inflation has stalled above the Fed’s 2% goal, with some measures indicating that price pressures may be spilling over to products and services not directly impacted by tariffs. Meantime, while hiring has slowed significantly over the summer, other labour market indicators, like the low level of unemployment, paint a more stable picture.Without much clarity on how the economy will unfold, disagreements over how to proceed are festering among policymakers. Already, two governors dissented at the Fed’s July meeting, when officials didn’t cut rates. If they do cut in September, others may dissent in the opposite direction.
Policy disagreements could grow in the coming months as Trump names new officials to vacancies at the Fed and Powell’s term as chair ends in May. The president has already tapped Stephen Miran, who chairs his Council of Economic Advisers, to fill an open slot on the Fed board that expires in January.
The discord among Fed officials comes at a time when the central bank is facing intense scrutiny from the White House. The topic seeped into conversations over coffee, during meals and in between sessions, even if there wasn’t much outright discussion of it during official conference proceedings.
Karen Dynan, an economics professor at Harvard University and frequent attendee of the conference, said she wasn’t surprised that central bankers didn’t want to wade into conversations about politics. Still, she said the conference set an example of how big-picture economic issues should be approached.
“This year it feels particularly meaningful that we have a bunch of papers that are grounded in good economics done by people who are prominent experts,” Dynan said. “These are not problems that can be solved by thinking about one’s intuition or talking to just a circle of people around you — you really need this sort of expertise.”
One issue that received less attention was the new framework Powell unveiled in his speech.The document, which will guide policymakers as they pursue their inflation and employment goals, is the culmination of a months-long review of the previous one, implemented in 2020. The new strategy removes some of the language that more narrowly focused on the pre-pandemic challenge of persistently low inflation.
It’s a return to basics and sets the Fed up to more clearly focus on its mandates of maximum employment and stable prices, said Carolin Pflueger, associate professor at the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.In his remarks, Powell “emphasised that his job is inflation and unemployment, and that can only be achieved within an independent Fed,” Pflueger said. “I think people appreciate that.”
That appreciation became apparent when Powell was greeted Friday morning with a standing ovation from economists and policymakers from around the world — and not for the first time this year.For them Fed independence is not only a matter of principle but also practicality, since decisions taken in Washington inevitably come with consequences that spread far beyond.
The euro strengthened by 1% against the dollar following Powell’s remarks, adding downside risks to euro-area inflation that’s already seen falling to 1.6% next year.“If a cut does come and reflects slower US growth, that probably means slower growth for them given the size of the US,” Maurice Obstfeld, a senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics and the former chief economist at the International Monetary Fund, said of the euro area and other economies.
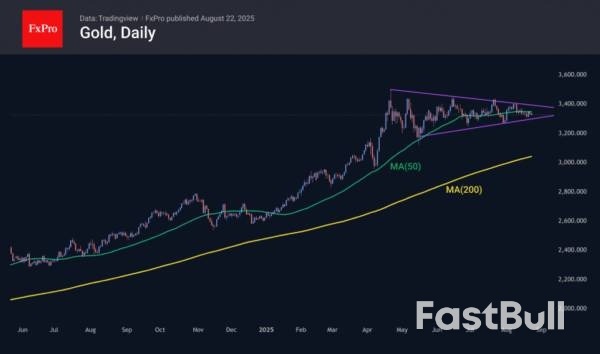
Gold’s hopes for an aggressive cut in the Fed’s federal funds rate, the associated decline in Treasury bond yields, and the weakening of the US dollar have not yet materialised. The Fed is likely to ease monetary policy in September. However, it may then pause again. Its slowness is bringing investors’ interest back to the greenback.
Clouds are gathering over the precious metal due to Donald Trump’s efforts to end the armed conflict in Ukraine. The start of hostilities, followed by the West’s freezing of Russia’s gold and foreign exchange reserves, was the starting point for the Gold’s rally. Since February 2022, gold has risen 1.7x and reached a record high of more than $3,500 per ounce in April. The rally was driven by de-dollarisation, active buying of bullion by central banks, and increased demand for ETFs.
In the second quarter, central bank activity in the precious metals market declined significantly, and capital flows into specialised exchange-traded funds slowed. Without these advantages, XAUUSD can forget about recovering the upward trend. However, the favourable external background in the form of monetary stimulus from the Fed, lower Treasury yields, and a weaker US dollar in the medium term will give gold a boost.
The gold chart clearly shows consolidation since April, with the price right in the middle of the 12% range from peak to correction lows. This tedious five-month movement to the right is likely to end in the coming weeks, as August often marks the start of major trends in gold. The duration of consolidation is often directly proportional to the strength of the breakout.From a technical analysis perspective, given the accumulated overbought condition, the downside potential is huge – up to $3000 or even $2200 per ounce. However, the upside potential is no less impressive: $4600 in an extreme bullish scenario, including the Fed switching to a mode of absolute softness.
Retail spending levels rose 0.5% in the June quarter, beating expectations. Retail sector conditions remain tough, but we are starting to see signs of the long-awaited recovery taking shape.
June quarter retail sales
Year to June
The June retail spending report was better than expected. While overall spending growth is still modest, spending appetites are gradually firming, including a lift in some discretionary categories.Retail spending rose 0.5% over the June quarter. That’s the third quarter in a row that spending levels have been pushing higher. The result was well ahead of our own forecast and the average market forecast for a fall in spending over the June quarter.At first glance, today’s result seems at odds with comments from the retail and hospitality sectors of continued soft trading conditions. But digging under the surface, we can start to see what’s going on.
In several sectors (especially durable items for the home), spending levels remain well down on the levels we saw in 2021. In addition, while spending levels are turning higher, spending growth remains quite modest – the volume of goods sold rose around 2.5% over the past year, compared to gains of around 4.5% per annum before the pandemic.But while the retail sector is still confronting some tough trading conditions, we are starting to see signs that the long-awaited recovery is taking shape. Spending levels have risen for the past three quarter. That includes gains in discretionary areas like recreational goods and electronics. However, it is still a mixed picture with spending in sectors like hospitality still flat.
Today’s update is an encouraging sign for spending over the remainder of 2025. Spending levels are already pushing higher, and the full impact of the large reductions in interest rates over the past year is yet to be felt.Over the coming months, increasing numbers of borrowers will be rolling on to lower borrowing rates. The related lift in disposable incomes could be sizeable in some cases, and that’s set to boost spending through the latter part of the year.
There are still some headwinds for the retail sector. Most notably, unemployment is likely to rise around to 5.3% before the end of the year.
Even so, it looks like a recovery in the retail sector is now taking shape.
We’re forecasting flat GDP growth over the June quarter. Today’s result was ahead of our expectations. However, we’ll take a closer look at how our forecast for GDP growth is shaping up over the next couple of weeks as additional data on June quarter activity is released.
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell on Friday gave a tepid indication of possible interest rate cuts ahead as he noted a high level of uncertainty that is making the job difficult for monetary policymakers.
In his much-anticipated speech at the Fed's annual conclave in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, the central bank leader in prepared remarks cited "sweeping changes" in tax, trade and immigration policies. The result is that "the balance of risks appear to be shifting" between the Fed's twin goals of full employment and stable prices.
While he noted that the labor market remains in good shape and the economy has shown "resilience," he said downside dangers are rising. At the same time, he said tariffs are causing risks that inflation could rise again — a stagflation scenario that the Fed needs to avoid.
With the Fed's benchmark interest rate a full percentage point below where it was when Powell delivered his keynote a year ago, and the unemployment rate still low, conditions allow "us to proceed carefully as we consider changes to our policy stance," Powell said.
"Nonetheless, with policy in restrictive territory, the baseline outlook and the shifting balance of risks may warrant adjusting our policy stance," he added.
That was as close as he came during the speech to endorsing a rate cut that Wall Street widely believes is coming when the Federal Open Market Committee next meets Sept. 16-17.
However, the remarks were enough to send stocks soaring and Treasury yields tumbling. The Dow Jones Industrial Average showed a gain of more than 600 points following the public release of Powell's speech while the policy-sensitive 2-year Treasury note saw a 0.08 percentage point fall to around 3.71%.
In addition to market expectations, President Donald Trump has demanded aggressive cuts from the Fed in scathing public attacks he has lobbed at Powell and his colleagues.
The Fed has held its benchmark borrowing rate in a range between 4.25%-4.5% since December. Policymakers have continued to cite the uncertain impact that tariffs will have on inflation as a reason for caution and believe that current economic conditions and the slightly restrictive policy stance allow for time to make further decisions.
While not addressing the White House demands for lower rates specifically, Powell did note the importance of Fed independence.
"FOMC members will make these decisions, based solely on their assessment of the data and its implications for the economic outlook and the balance of risks. We will never deviate from that approach," he said.
The speech comes amid ongoing negotiations between the White House and its global trading partners, a situation often in flux and without clarity on where it will end. Recent indicators show consumer prices gradually pushing higher but wholesale costs up more rapidly.
From the Trump administration view, the tariffs will not cause lasting inflation, thus warranting rate cuts. Powell's position in the speech was that a range of outcomes is possible, with a "reasonable base case" being that the tariff impacts will be "short lived — a one-time shift in the price level" that likely would not be cause for holding rates higher. However, he said nothing is certain at this point.
"It will continue to take time for tariff increases to work their way through supply chains and distribution networks," Powell said. "Moreover, tariff rates continue to evolve, potentially prolonging the adjustment process."
In addition to summarizing the current conditions and potential outcomes, the speech touched on the Fed's five-year review of its policy framework. The review resulted in several notable changes from when the central bank last performed the task in 2020.
At that time, in the midst of the Covid pandemic, the Fed switched to a "flexible average inflation targeting" regime that effectively would allow inflation to run higher than the Fed's 2% goal coming after a prolonged period of holding below that level. The upshot is that policymakers could be patient with slightly higher inflation if it meant insuring a more comprehensive labor market recovery.
However, shortly after adopting the strategy, inflation began to climb, ultimately hitting 40-year highs, while policymakers largely dismissed the rise as "transitory" and not needing rate hikes. Powell noted the damaging impacts from the inflation and the lessons learned.
"As it turned out, the idea of an intentional, moderate inflation overshoot had proved irrelevant. There was nothing intentional or moderate about the inflation that arrived a few months after we announced our 2020 changes to the consensus statement, as I acknowledged publicly in 2021," Powell said. "The past five years have been a painful reminder of the hardship that high inflation imposes, especially on those least able to meet the higher costs of necessities."
Also during the review, the Fed reaffirmed its commitment to its 2% inflation target. There have been critics on both sides of the issue, with some suggesting the rate is too high and can lead to a weaker dollar, while others seeing a need for the central bank to be flexible.
"We believe that our commitment to this target is a key factor helping keep longer-term inflation expectations well anchored," Powell said.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up