Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests


[Ethereum Plunges Below $2600, 24-Hour Loss Extends To 4.9%] January 31, According To Htx Market Data, Ethereum Dropped Below $2600, With A 24-Hour Decline Widening To 4.9%
[Melania Trump's Documentary Released, Costing Over 500 Million Yuan, Fails At Global Box Office, Receives 1.7 Rating] According To Xinhua News Agency, The Documentary "Melania: 20 Days To History" (hereinafter Referred To As "Melania"), Featuring First Lady Melania Trump, Was Released In Theaters Worldwide On January 30th, But Has Been Met With A Lukewarm Reception In Many Countries. Multiple International Media Outlets Reported That Ticket Sales In Theaters In The UK, Canada, And Even The US Have Been Dismal, With Some Screenings Almost Entirely Empty. On Rotten Tomatoes, A Globally Renowned Film And Television Rating Website, The Film Received A Low Score Of 1.7. The Film's Production And Promotion Costs Reached A Staggering $75 Million (approximately 521 Million Yuan, Similar To The Rumored Cost Of "Ne Zha 2"), Drawing Criticism For Amazon Founder Jeff Bezos's Massive Investment
Four Killed In Gas Explosion At Residential Building In Iran's Ahvaz - Iran's State-Run Tehran Times
IAEA: Chornobyl Site Briefly Lost All Off-Site Power. Ukraine Working To Stabilize Grid And Restore Output, No Direct Impact On Nuclear Safety Expected
IAEA: Ukrainian Npps Temporarily Reduced Output This Morning After Technological Grid Issue Affected Power Lines
Tigrayan Official And Humanitarian Worker: One Person Killed, Another Injured In Drone Strikes In Ethiopia's Tigray Region
Explosion In Iran's Southern Port Of Bandar Abbas , Iranian Media Denies Report Commander Of Revolutionary Guards Targeted
[Epstein Documents Continue To Be Released, Involving Multiple US Political And Business Figures] The US Department Of Justice Announced On January 30 That It Would Release The Remaining Documents, Totaling Over 3 Million Pages, Related To The Case Of The Late Billionaire Jeffrey Epstein. According To US Media Reports, The Documents Reveal That Numerous Prominent US Political And Business Figures Knew And Associated With The Businessman, Who Was Suspected Of Sex Crimes And Died Mysteriously In Prison. These Include Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, Entrepreneur Elon Musk, And Stephen Bannon, An Advisor During Trump's First Presidential Term
Moldova's Government: Problems In Ukraine's Power Grid Led To Moldova's Energy System Emergency Shutdown
[Bitcoin Falls Below $83,000, 24-Hour Gain Narrows To 0.53%] January 31, According To Htx Market Data, Bitcoin Fell Below $83,000, With A 24-Hour Growth Narrowing To 0.53%
[Canada Plans To Establish Defense Bank With Multiple Countries] Canadian Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne Said On January 30 That Canada Will Work Closely With International Partners In The Coming Months To Establish A Defense Bank To Raise Funds For Maintaining Collective Security. Champagne Posted On Social Media Platform X That Day That More Than 10 Countries, Under Canada's Auspices, Discussed The Establishment Of A "Defense, Security And Reconstruction Bank." He Did Not Specify Which Countries Were Involved In The Discussions. According To Reuters, Supporters Hope The Proposed Defense Bank Will Be A Global Nation-support Institution With A AAA Credit Rating, Raising $135 Billion For Defense Projects In Europe And NATO Member States
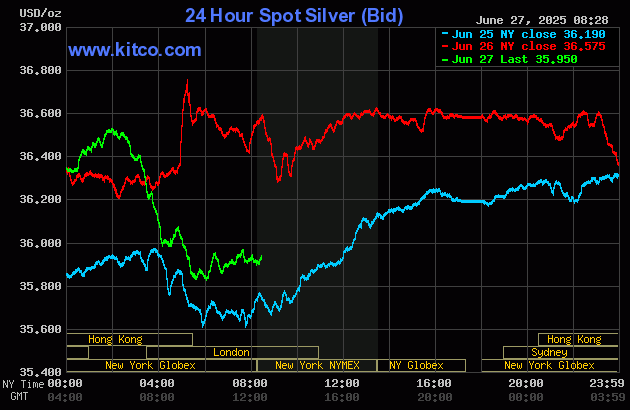
[A Silver Long Whale With A $29M Long Position Gets Fully Liquidated, Losing Over $4M] January 31, According To Lookintochain Monitoring, With Today'S Spot Silver Price Falling Below $75 Per Ounce, A Single-Day Plunge Of Over 35% Set The Record For The Largest Single-Day Drop In History. The Whale "0X94D3" Who Was Long On Silver Saw Their $29 Million Long Position Liquidated, Resulting In A Loss Of Over $4 Million

 U.K. M4 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)
U.K. M4 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.K. M4 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
U.K. M4 Money Supply YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Italy Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)
Italy Unemployment Rate (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Unemployment Rate (Dec)
Euro Zone Unemployment Rate (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone GDP Prelim QoQ (SA) (Q4)
Euro Zone GDP Prelim QoQ (SA) (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone GDP Prelim YoY (SA) (Q4)
Euro Zone GDP Prelim YoY (SA) (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Italy PPI YoY (Dec)
Italy PPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico GDP Prelim YoY (Q4)
Mexico GDP Prelim YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Unemployment Rate (Dec)
Brazil Unemployment Rate (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 South Africa Trade Balance (Dec)
South Africa Trade Balance (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Deposit Gowth YoY
India Deposit Gowth YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany CPI Prelim YoY (Jan)
Germany CPI Prelim YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany CPI Prelim MoM (Jan)
Germany CPI Prelim MoM (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany HICP Prelim YoY (Jan)
Germany HICP Prelim YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany HICP Prelim MoM (Jan)
Germany HICP Prelim MoM (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PPI YoY (Dec)
U.S. Core PPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Core PPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. Core PPI MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PPI YoY (Dec)
U.S. PPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PPI MoM (SA) (Dec)
U.S. PPI MoM (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada GDP MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada GDP MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada GDP YoY (Nov)
Canada GDP YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PPI MoM Final (Excl. Food, Energy and Trade) (SA) (Dec)
U.S. PPI MoM Final (Excl. Food, Energy and Trade) (SA) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PPI YoY (Excl. Food, Energy & Trade) (Dec)
U.S. PPI YoY (Excl. Food, Energy & Trade) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Chicago PMI (Jan)
U.S. Chicago PMI (Jan)A:--
F: --
 Canada Federal Government Budget Balance (Nov)
Canada Federal Government Budget Balance (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland NBS Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
China, Mainland NBS Manufacturing PMI (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland NBS Non-manufacturing PMI (Jan)
China, Mainland NBS Non-manufacturing PMI (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Composite PMI (Jan)
China, Mainland Composite PMI (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Trade Balance Prelim (Jan)
South Korea Trade Balance Prelim (Jan)--
F: --
 Japan Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)
Japan Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)
South Korea IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
Indonesia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Caixin Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)
China, Mainland Caixin Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia Trade Balance (Dec)
Indonesia Trade Balance (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia Inflation Rate YoY (Jan)
Indonesia Inflation Rate YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Indonesia Core Inflation YoY (Jan)
Indonesia Core Inflation YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 India HSBC Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)
India HSBC Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Commodity Price YoY (Jan)
Australia Commodity Price YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
Russia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
Turkey Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Nationwide House Price Index MoM (Jan)
U.K. Nationwide House Price Index MoM (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Nationwide House Price Index YoY (Jan)
U.K. Nationwide House Price Index YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Actual Retail Sales MoM (Dec)
Germany Actual Retail Sales MoM (Dec)--
F: --
 Italy Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)
Italy Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 South Africa Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
South Africa Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)
Euro Zone Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)
U.K. Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
Brazil IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)
Canada Manufacturing PMI (SA) (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)
U.S. IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI Final (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. ISM Output Index (Jan)
U.S. ISM Output Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. ISM Inventories Index (Jan)
U.S. ISM Inventories Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. ISM Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)
U.S. ISM Manufacturing Employment Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. ISM Manufacturing New Orders Index (Jan)
U.S. ISM Manufacturing New Orders Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. ISM Manufacturing PMI (Jan)
U.S. ISM Manufacturing PMI (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea CPI YoY (Jan)
South Korea CPI YoY (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Monetary Base YoY (SA) (Jan)
Japan Monetary Base YoY (SA) (Jan)--
F: --
P: --












































No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
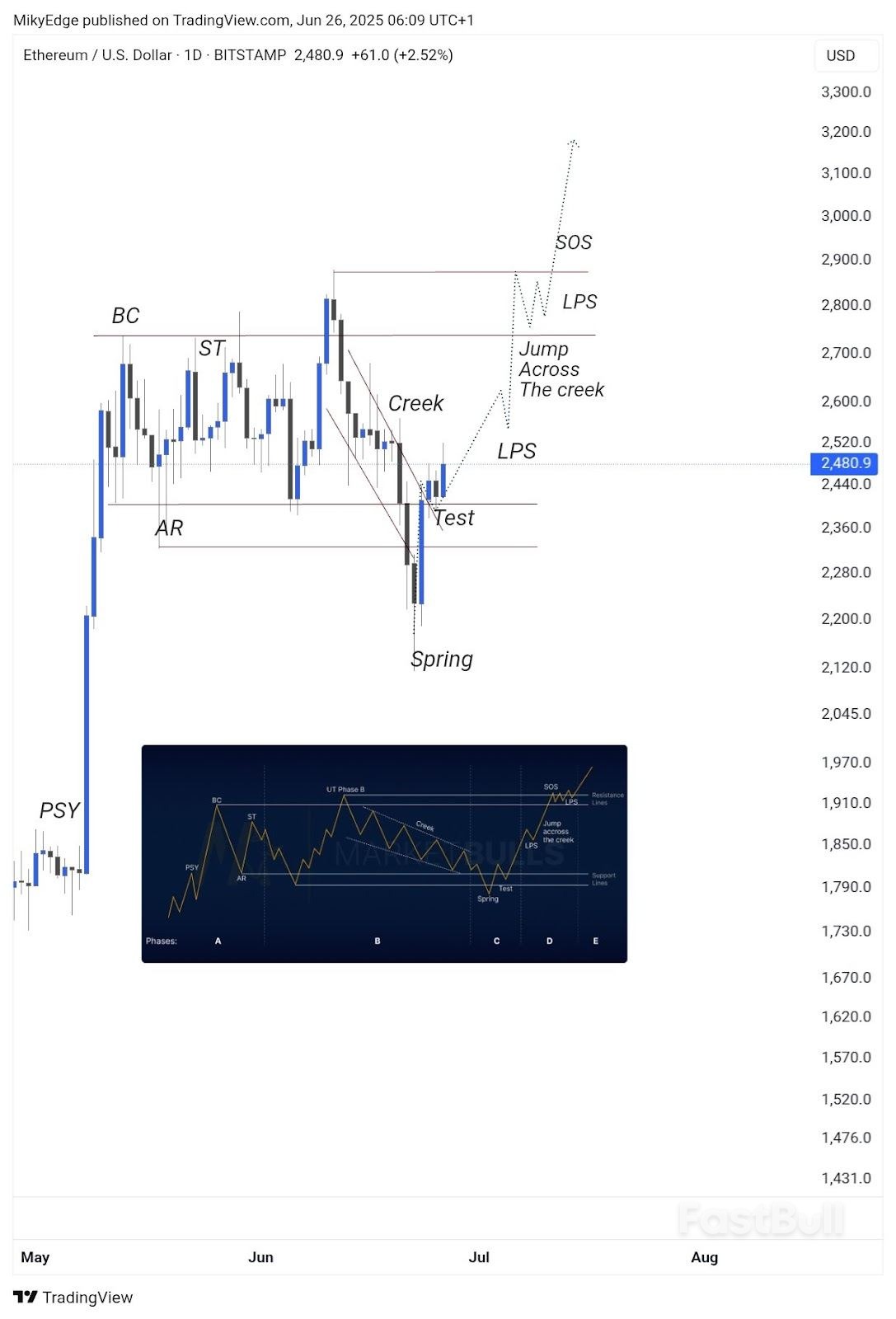
Crypto analysts and several metrics suggest that an "altcoin season" will begin once Ether’s price breaks new all-time highs.
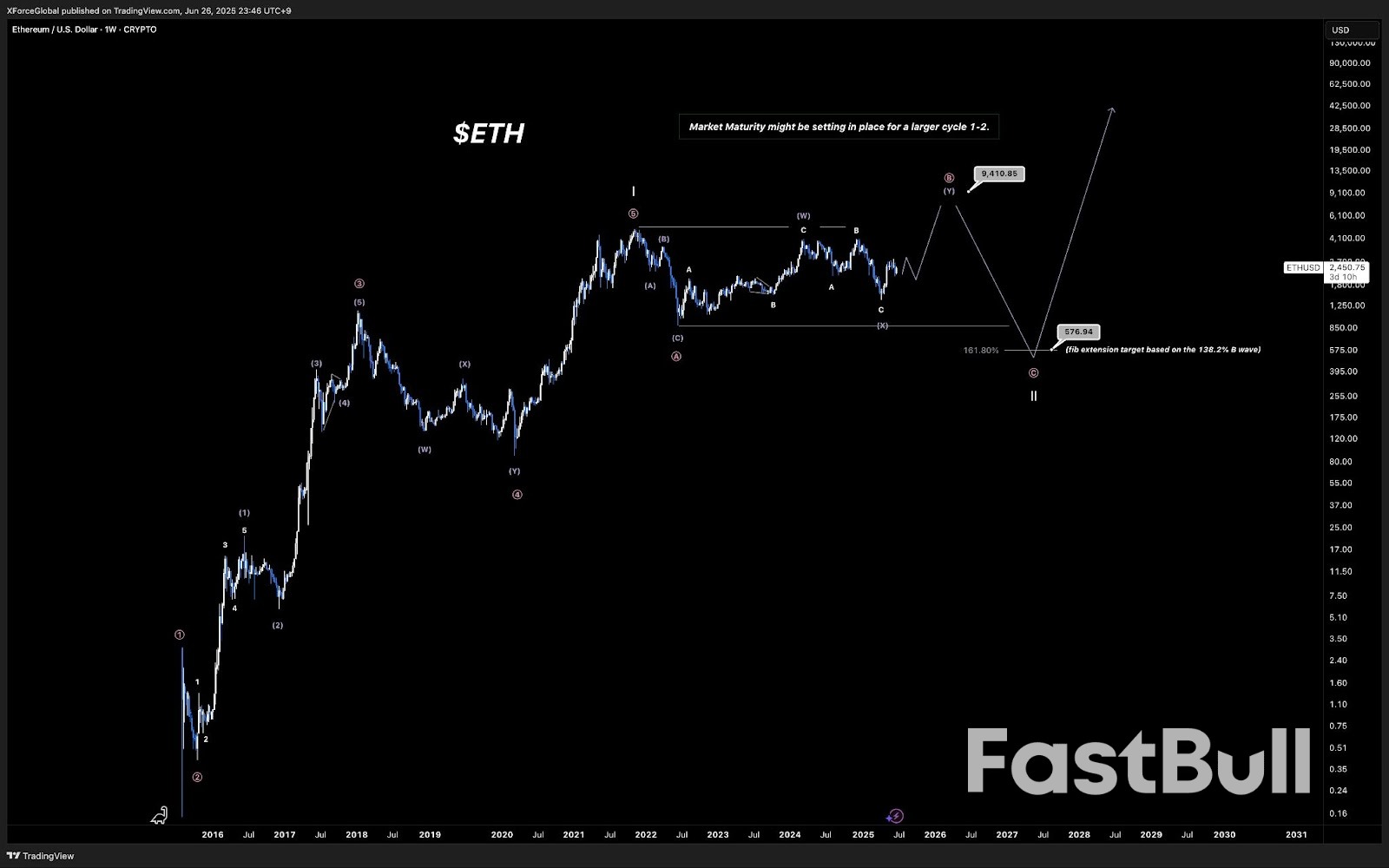 ETH/USD weekly chart. Source: XForceGlobal
ETH/USD weekly chart. Source: XForceGlobal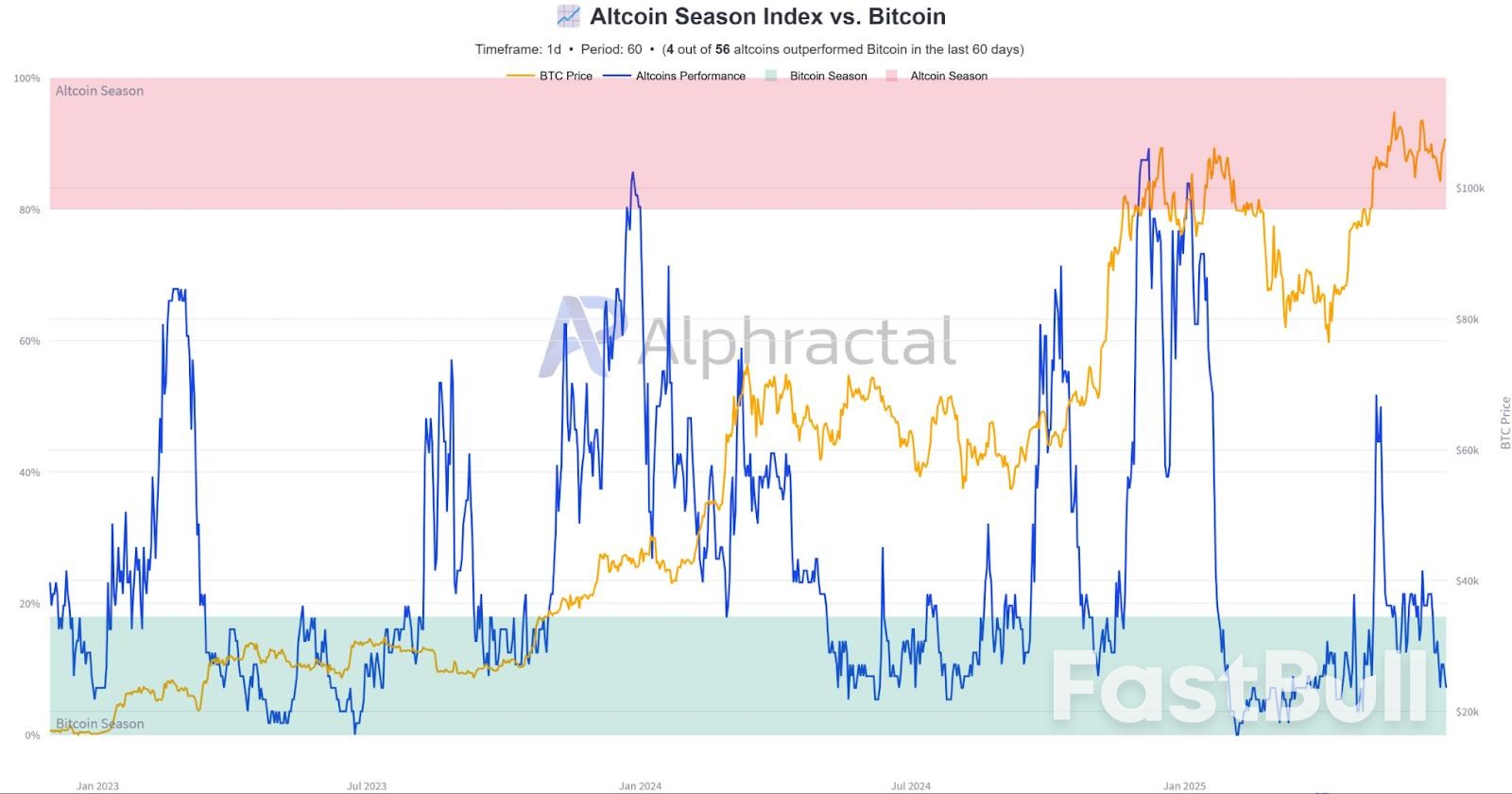
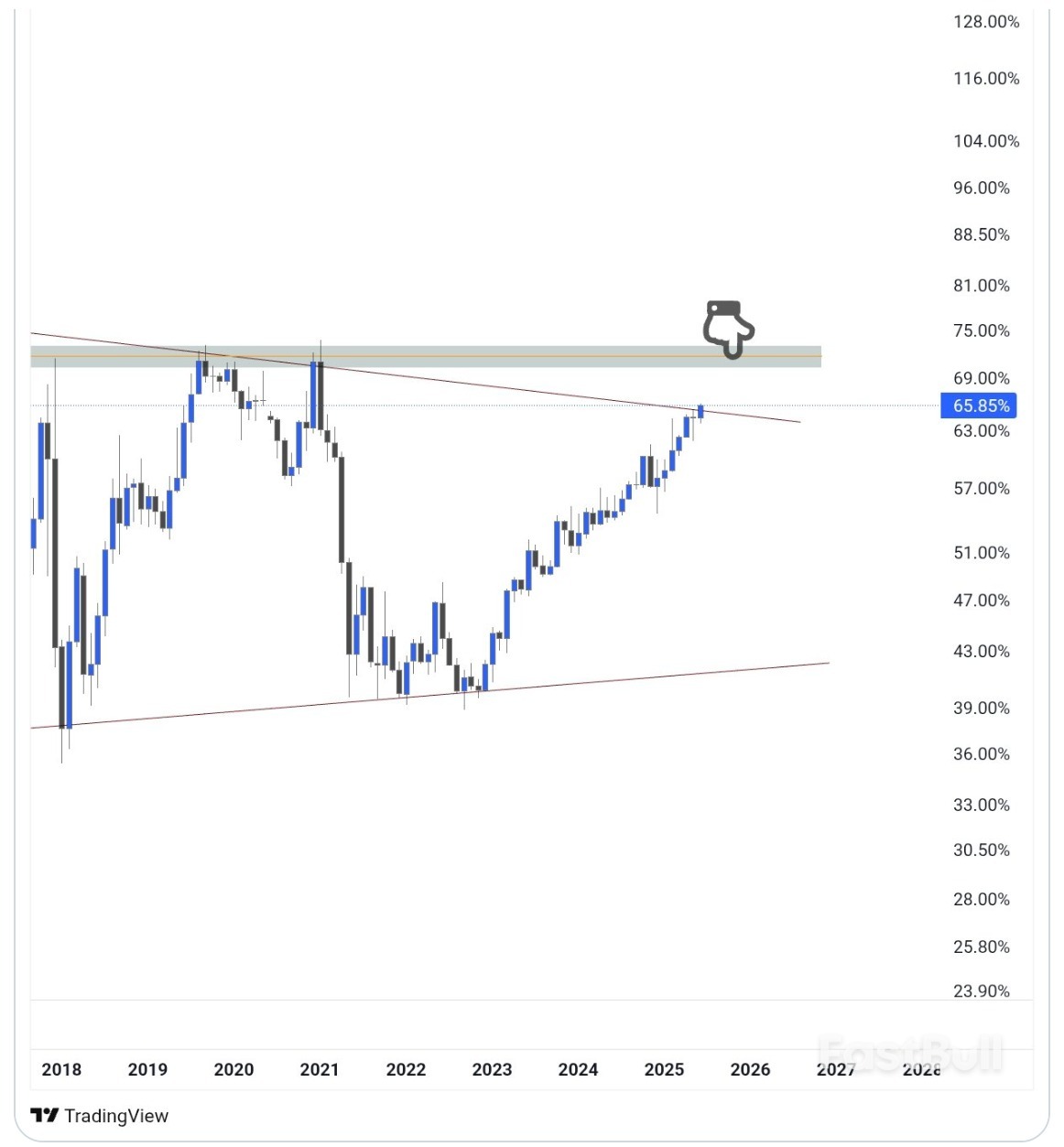 Bitcoin Market Dominance. Source: Mikybull Crypto
Bitcoin Market Dominance. Source: Mikybull Crypto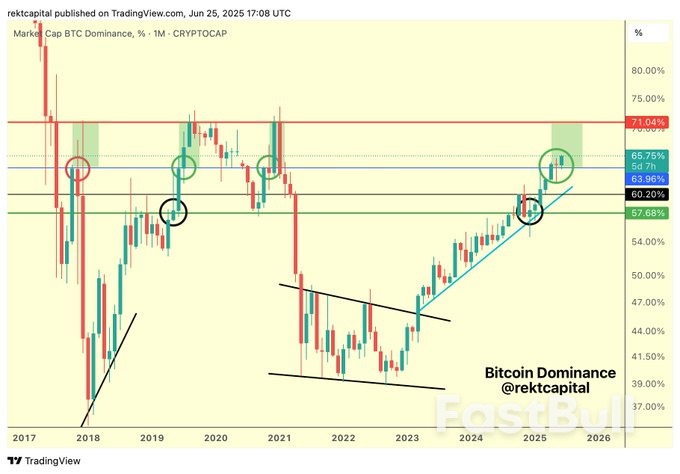
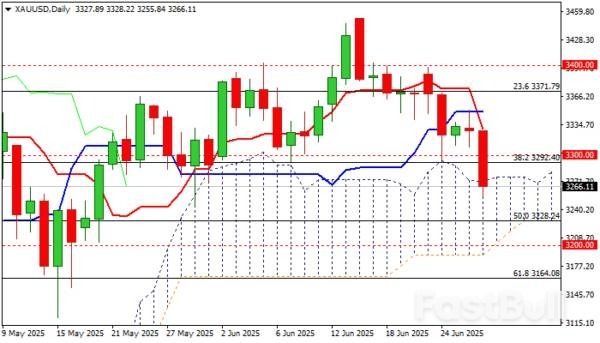
Gold accelerated lower (down almost 2%) on Friday after losing solid supports at $3300 zone, which previously contained several attacks.
The metal lost ground on sharply fading geopolitical tensions, as well as growing positive signs of final US-China trade deal that significantly deflated safe haven demand.
Gold is on track for the second consecutive weekly loss with formation of inverted hammer candle on monthly chart adding to concerns that larger bulls may be running out of steam.
The notion is supported by still strongly overbought monthly RSI and stochastic already out of overbought territory, with weekly indicators being in steep decline and significantly weaker daily studies (14-d momentum is diving deeper into negative territory / daily Tenkan/Kijun-sen created bear cross / price penetrated through the top of daily Ichimoku cloud).
Gold hit one-month low on Friday, with close within the cloud today, to confirm signal and keep the downside exposed, as the latest fall pushed the price into lower zone of larger consolidation range ($3500/$3120)
Bears eye targets at $3228 (50% retracement of $2956/$3500 rally) and $3203/00 (daily cloud base / psychological).
Meanwhile, corrective upticks (Friday partial profit taking) are likely to be limited, with cloud top ($3276) offering immediate resistance and $3000 to ideally cap and keep fresh bears intact.
Only return and weekly close above $3300 would question bears (scenario of false break lower and bear-trap formation).
Res: 3276; 3300; 3329; 3350.Sup: 3250; 3228; 3200; 3164.
The European Union and the US believe they can clinch some form of a trade agreement before a July 9 deadline, when Washington is set to impose a 50% tariff on nearly all EU products and the bloc plans to unleash its own series of countermeasures.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen told EU leaders behind closed doors at a Thursday summit that she was confident a deal could be reached before the deadline to avoid an economically damaging escalation, according to people familiar with the matter.
Von der Leyen said that the Trump administration had shared a new proposal this week. During the discussion, there was a shift in tone among the leaders, many of whom said they were ready to accept some degree of imbalance in a trade deal to avoid an escalation, said the people, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick echoed von der Leyen’s comments in a Thursday interview with Bloomberg TV, saying that the EU had picked up the pace of the negotiations in recent weeks, laying out the groundwork for an accord.
A spokesperson for the commission, which handles trade matters for the EU, didn’t immediately reply to a request for comment.
“Europe has done an excellent job, they’re working hard,” Lutnick said. “I’m optimistic — I think we can get a deal now.”
European stocks extended their gains after the news, with the Stoxx Europe 600 Index up 1%. The benchmark was up 0.7% before the news. German bonds extended a small drop, sending the yield on the two-year to 1.87%.
Lutnick added that it made sense for a deal with the EU to come at the end of the process since the bloc is the US’s largest trade partner, and as such the two have a deep and complex relationship.
President Donald Trump in April announced a raft of so-called reciprocal tariffs on nearly all US commercial partners, targeting trade barriers American companies face abroad, such as duties, domestic regulations and taxes. Those 50% tariffs are set to be imposed July 9.
In addition to the universal levy, Trump has introduced a 25% tariff on cars and a 50% duty on steel and aluminium. He’s also working to expand tariffs on other sectors, including pharmaceuticals, semiconductors and commercial aircraft.
The US president has often blasted the EU – which he has said was created to “screw” the US – over its goods surplus and perceived barriers to American trade.
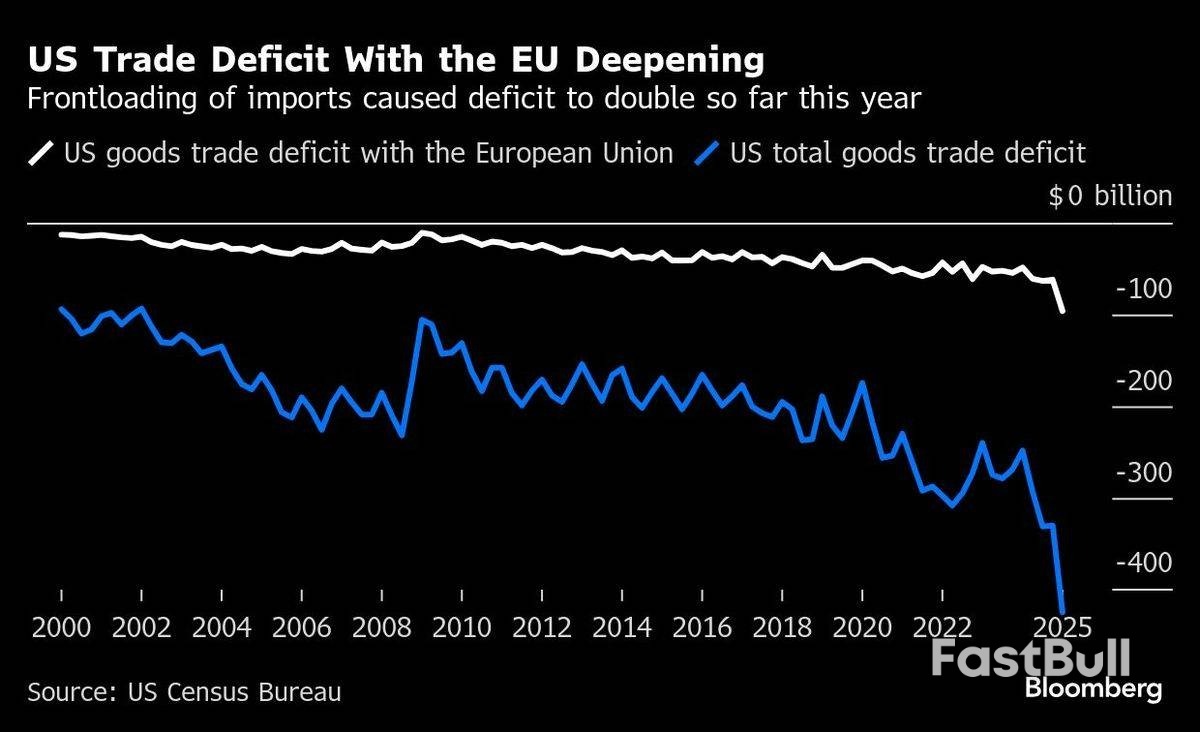
The EU estimates that US duties now cover €380 billion (US$445 billion or RM1.88 trillion), or about 70%, of its exports to the US.
EU officials believe that the best-case scenario from the negotiations remains an agreement in principle that would allow the talks to continue beyond the July deadline, Bloomberg previously reported.
Since intensifying negotiations, the US and EU have been conducting in-depth discussions on critical sectors – such as steel and aluminium, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, semiconductors and civilian aircraft – as well as on tariff and non-tariff barriers, in addition to strategic purchases and economic security.
Thursday’s leaders’ debate didn’t reveal the extent of the imbalances the bloc’s capitals are prepared to stomach, according to the people. The EU, which has been seeking a mutually beneficial deal, will assess any end result and at that stage decide what level of asymmetry it’s willing to accept.
Because of that, in parallel to the negotiations, the bloc continues to prepare countermeasures should talks yield unsatisfactory outcomes and may need to rebalance the agreement targeting some key sectors.
The EU has approved tariffs on €21 billion of US goods that can be quickly implemented in response to Trump’s metals levies. They target politically sensitive American states and include products such as soybeans from Louisiana, home to House Speaker Mike Johnson, as well as agricultural products, poultry, and motorcycles.
The bloc has also prepared an additional list of tariffs on €95 billion of American products in response to Trump’s so-called reciprocal levies and automotive duties. They would target industrial goods including Boeing Co aircraft, US-made cars, and bourbon. The EU is also consulting member states to identify strategic areas where the US relies on the bloc, as well as potential measures that go beyond tariffs.
“We are ready for a deal — at the same time we are preparing for the possibility that no satisfactory agreement is reached,” von der Leyen told reporters after Thursday’s summit. “In short, all options remain on the table.”
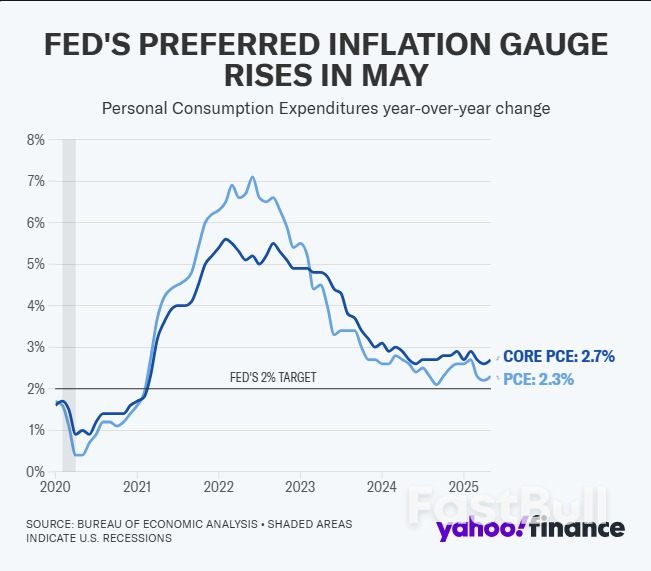
In 2023 and 2024, the Fed was under intense public and media scrutiny for calling the post-pandemic surge in inflation “transitory.” Critics argued that the Fed’s failure to anticipate the persistence and severity of rising prices undermined its credibility. Yet, with the benefit of hindsight and historical context, the Fed’s position wasn’t entirely misguided. Inflation proved temporary in a broader economic sense, and by 2025, the data confirmed a significant cooling of price pressures.
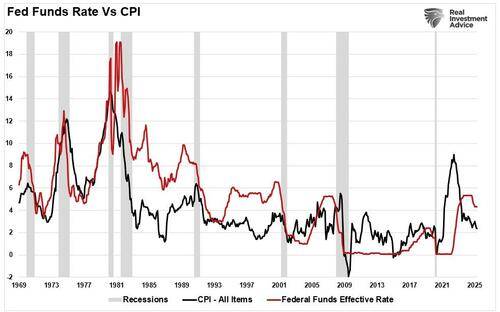
However, the Fed’s mistake wasn’t the “transitory” label—it was the Fed’s late response to raising interest rates and halting quantitative easing. As shown, the combined impact of the massive surge in the Government’s deficit spending (stimulus checks and infrastructure bills) and the Fed’s $120 billion monthly “quantitative easing” campaign caused a massive jump in economic growth and inflation. However, instead of cutting back on stimulus when the economy rebounded, the Fed’s mistake was keeping its “foot on the gas” for too long. These delays allowed the inflationary fire to burn hotter and longer than necessary, exacerbated by an overlooked driver: excessive government spending.
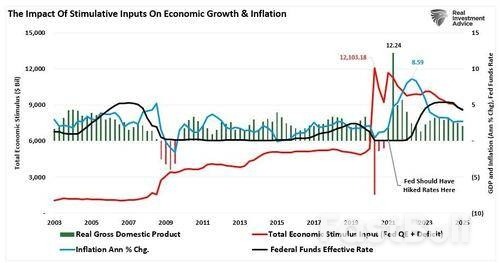
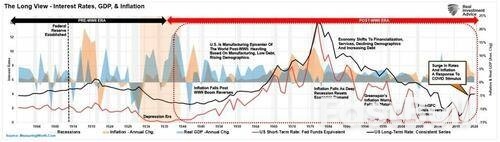
Despite the elevated levels of total economic stimulus, inflation and economic growth have subsided as the economy continues normalizing. However, to understand the Fed’s current policy risks, particularly in light of its recent warnings about tariffs, it’s essential to look back at past inflation spikes
U.S. economic history offers several instructive examples of inflationary episodes and how they eventually resolved.
Post-WWII Inflation (1946–1948): After World War II, inflation surged to nearly 20% as price controls ended and pent-up consumer demand met constrained supply. But this spike was short-lived. As production normalized and demand stabilized, inflation quickly receded. The Fed did not need any drastic monetary tightening.
The 1970s Stagflation: The most notorious inflation era came during the 1970s, driven by oil shocks, wage-price spirals, and loose monetary policy. Inflation remained high for nearly a decade. It wasn’t until Paul Volcker’s aggressive interest rate hikes in the early 1980s, pushing the federal funds rate above 15%, that inflation fell, though at the cost of a deep recession.
Greenspan’s “Inflation Boogyman:” In the late 90s, Alan Greenspan worried that an inflation surge was coming and aggressively began to hike rates into that anticipation. The further tightening of money policy contributed to the blowup of numerous “dot.com” companies that were heavily leveraged with no revenues. Instead of rising, inflation collapsed as the “Dot.com” crash devastated the economy.
Post-GFC Disinflation: After the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, many feared stimulus and Fed intervention would trigger inflation. Instead, the opposite occurred. Inflation remained stubbornly low for over a decade, highlighting how debt overhangs and weak demand can suppress prices even amid central bank easing.
Compared to these episodes, the COVID-driven inflation surge stands out for its rapid onset and similarly swift decline. Prices surged due to supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and historic stimulus. But by 2025, inflation is back to near-target levels. The duration of elevated inflation, from early 2021 through late 2023, was short by historical standards, and it faded as supply chains normalized and stimulus effects waned.
The historical shortcomings of the Fed’s actions, repeated policy mistakes, and flawed outlooks are clearly evident. The Fed hikes rates, creates an economic or credit-related event, and then cuts rates to fix it.
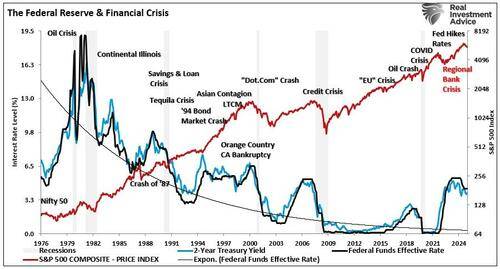
As such, investors should ask themselves why they are confident in the Fed’s current assessment of tariff-induced inflation risks.
At the June 18, 2025, press conference, Fed Chair Jerome Powell expressed concern that rising tariffs could reignite inflation. With trade policy becoming increasingly protectionist, particularly toward China and Mexico, the Fed is wary that tariffs could push up import prices and thus overall inflation. However, there’s an important distinction: inflation data from the last four months has shown no measurable impact from recent tariff actions. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has remained stable or declined, while core inflation has softened. Meanwhile, job growth has slowed, and wage gains have moderated. All classic signs of a cooling economy.
This link between the economy and inflation is evident from the Economic Composite Index, which comprises nearly 100 hard and soft data points. Following the spike in economic activity post-pandemic, economic growth continues to decline. Given that inflation is solely a function of economic supply and demand, it is unsurprising that it continues to cool.
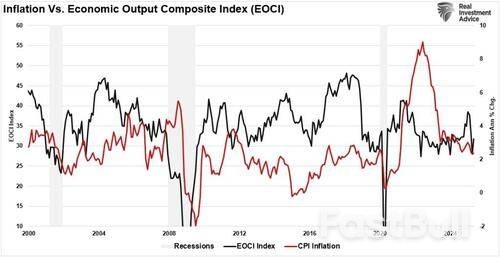
This raises a critical policy question: Is the Fed now over-compensating on the cautious side because of its past missteps with “transitory” inflation?
If so, the risk is that the Fed may once again make another policy mistake, as has repeatedly been the case in the past. After keeping rates too low for too long post-pandemic, policymakers might be too hesitant to cut rates, fearing another inflation flare-up that may never materialize. This fear-based approach risks undermining an already slowing economy.
Tariffs are designed to make foreign goods more expensive. However, supply chains and pricing are far more flexible in today’s globalized economy. If importers can shift production to tariff-free countries, renegotiate supplier contracts, or absorb costs to maintain market share, the inflationary effects of tariffs can be muted or even nonexistent. They are already doing this.
“The bonded warehouse route takes the opposite approach. Rather than mess with a good’s contents or move production elsewhere, businesses can import products from across the world without paying any tariffs when they enter the US — as long as they remain locked up in a special customs-regulated warehouse. Businesses can keep goods in these warehouses for up to five years without paying a tariff. They only pay the current tariff rate when they take goods out of storage. It’s a bet that tariff rates will go down in the short or medium term.”
Furthermore, companies are “reclassifying and redesigning” products to get lower tariff treatments.
“In other words, companies try to say their article or their good is something that gets low tariff treatment relative to what it might be, in essence. For example, Marvel successfully argued in court in 2003 that X-Men action figures are non-human toys (despite the premise of the franchise) rather than dolls, nearly halving their tax rate.”
Lastly, as discussed in “Tariff Risk Isn’t Inflation,” economists always forget the importance of consumer choice. The only payee of tariffs is the producers. Consumers can purchase less, delay, or exclude certain products from their consumption. To wit:
“Today, globalization and technology give consumers vast choices in the products they buy. While instituting a tariff on a set of products from China may indeed raise the prices of those specific products, consumers have easy choices for substitution. A recent survey by Civic Science showed an excellent example of why tariffs won’t increase prices (always a function of supply and demand).”
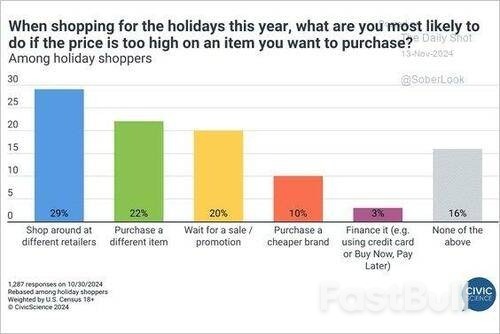
Of course, if demand drops for products with tariffs, prices will fall, reducing inflationary pressures.
Recent economic data suggests exactly that. Despite new levies on Chinese electric vehicles and Mexican steel, consumer durables and core goods prices have not moved materially higher. Businesses appear to be adapting quickly, with many shifting sourcing to Vietnam, India, or reshoring certain elements of production.
This raises the danger of a policy mismatch: If the Fed waits for inflation that doesn’t arrive, it may keep real interest rates excessively high for too long, just as it kept them too low following the pandemic. The consequences could be severe:
Slower Economic Growth: Elevated rates in a disinflationary environment slow investment and consumption, slowing GDP growth.
Labor Market Weakness: As rate-sensitive sectors (like housing and manufacturing) continue to weaken, layoffs may rise, further pressuring employment.
Financial Instability: Prolonged tight monetary policy increases the risk of credit defaults, especially among small businesses and lower-income households with floating-rate debt.
If the Fed is fighting a phantom threat, as Alan Greenspan did in the late 90s, and tariff-driven inflation never arrives, it could inadvertently engineer a downturn. And much like in 2021 and 2022, this would be a policy failure driven not by bad data, but by misjudging the economic environment.,
The Fed’s credibility rests not on never being wrong, but on being adaptive and forward-looking. Inflation has cooled, wage growth has moderated, and economic momentum is slowing. Now is the time for the Fed to focus not on headline fears, but on real-time data.
If tariffs have not yet translated into price increases, and employment indicators suggest slack is growing, the Fed should not delay necessary rate cuts to defend its credibility. Doing so risks repeating the mistake it made during the pandemic: ignoring the lagging effects of previous decisions.
Cutting rates too late would be just as damaging as hiking them too slowly.
The media mocked the Fed’s “transitory” narrative, but inflation was short-lived in the grand scheme. What mattered more was how long the Fed waited to act. With tariffs yet to trigger a real inflationary response and the economy showing signs of deceleration, the greater risk may be inaction, not inflation.
Investors should be alert to the Fed’s tendency to overcorrect past mistakes. Just as policy stayed too loose after COVID, it may now stay too tight for too long in 2025. Recognizing that monetary policy must adapt, not just react, will be key for policymakers and market participants navigating the road ahead.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features


Log In
Sign Up