Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Jan)
U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 2-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 2-Year Note Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Shop Price Index YoY (Jan)
U.K. BRC Shop Price Index YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Dec)
China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany 2-Year Schatz Auction Avg. Yield
Germany 2-Year Schatz Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Trade Balance (Dec)
Mexico Trade Balance (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
 U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Gasoline StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)
Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)
Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. Yield
Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)
India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)
India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW
U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Overnight Target Rate
Canada Overnight Target Rate--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Monetary Policy Report
BOC Monetary Policy Report U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Press Conference
BOC Press Conference Russia PPI MoM (Dec)
Russia PPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia PPI YoY (Dec)
Russia PPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances
U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target
U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)--
F: --
P: --
 FOMC Statement
FOMC Statement FOMC Press Conference
FOMC Press Conference Brazil Selic Interest Rate
Brazil Selic Interest Rate--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)
Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)
Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --



























Adrian Mer
ID: 4465924






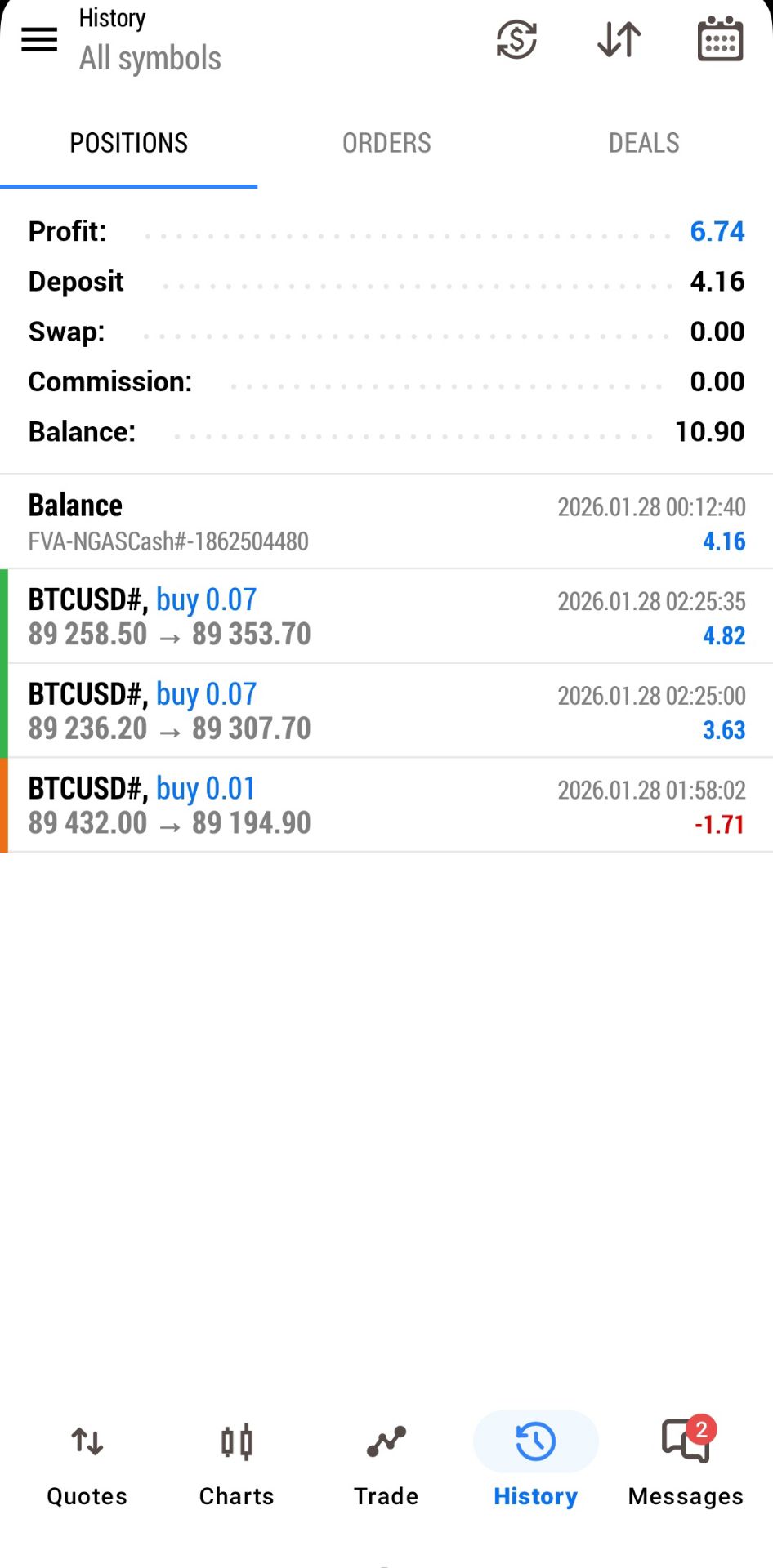


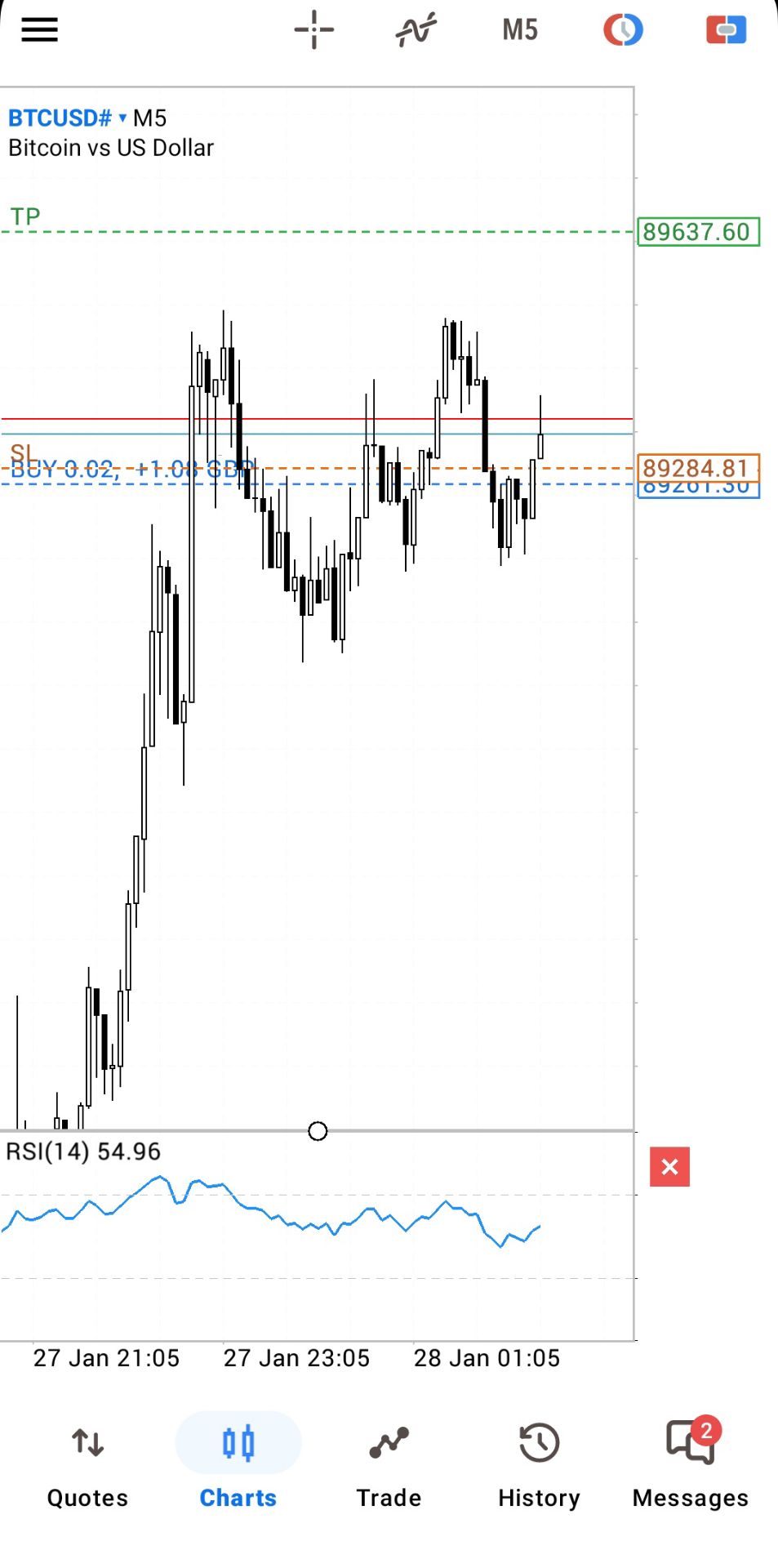


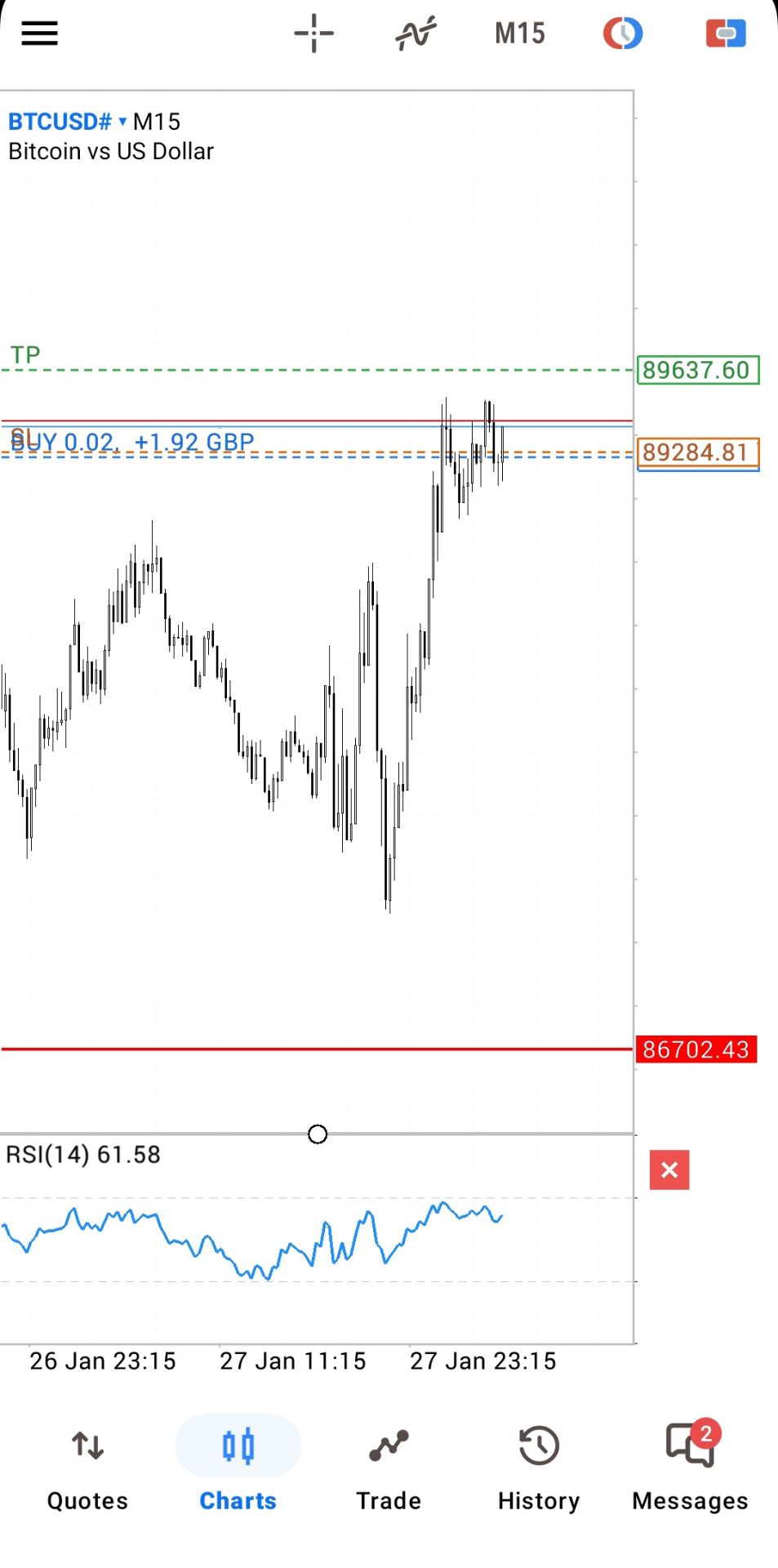




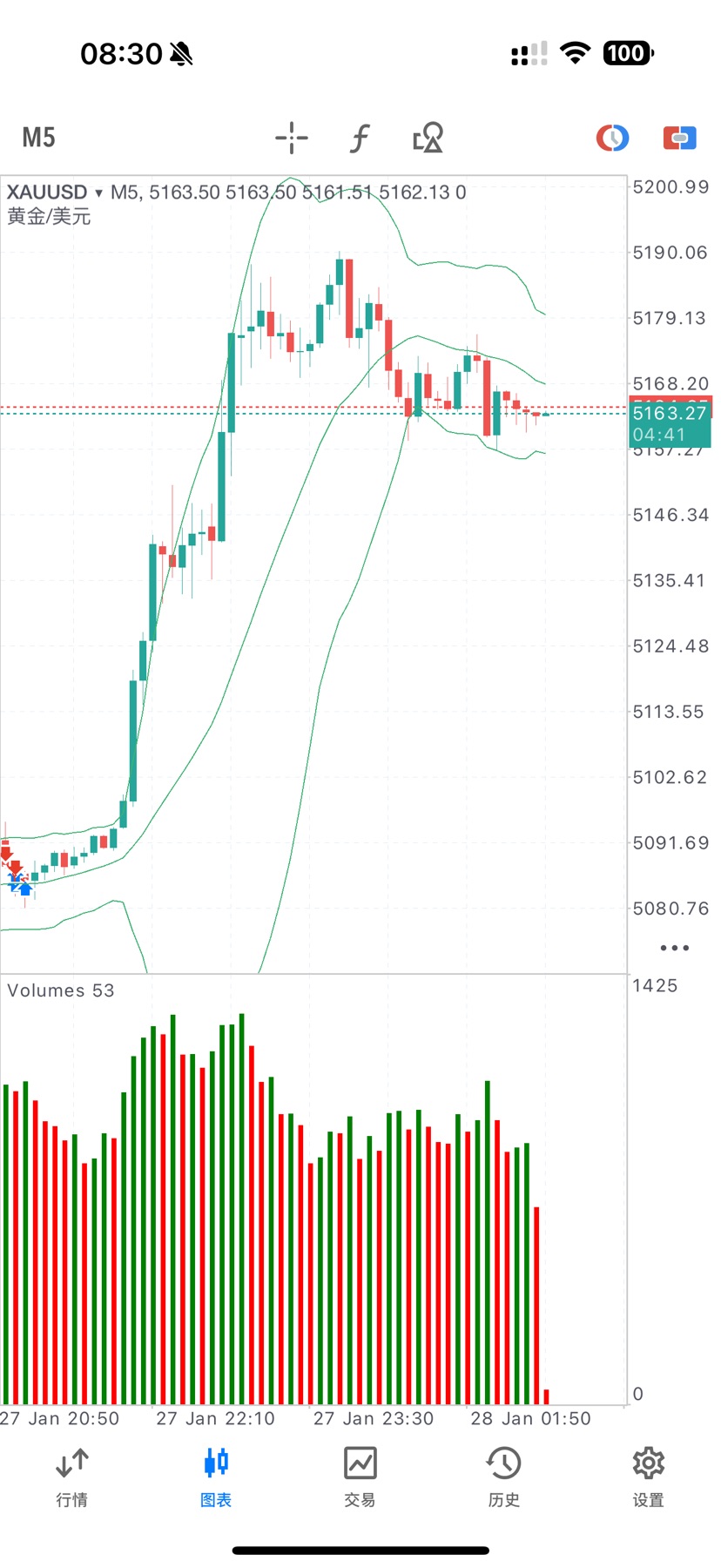






No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
The inverse correlation between bonds and stocks has returned, broadening potential for risk-adjusted returns in multi-asset portfolios.



With Donald Trump soon making a return to the White House, the trade deficit with the EU is likely to come under renewed scrutiny. The President-elect has been vocal about what he perceives as unfair trade practices, particularly in the automotive and agricultural sectors. He has threatened to impose blanket tariffs ranging from 10% to 20% on all imports and to match tariffs raised by other countries to achieve a level playing field. But is the difference really that significant?
Effectively applied tariffs are not vastly different between the two countries, with the simple average standing at 3.95% for products from the US and 3.5% for EU products – but there are notable differences in certain sectors.
Trump has a point regarding tariffs on cars, agriculture, and food. For example, the EU tariff rate is 10% compared to 2.5% in the US for cars, and there is approximately a 3.5 percentage point difference for average tariffs on food and beverages. Additionally, tariffs on chemicals are on average 1ppt higher in the EU than in the US. However, the EU faces higher tariffs on commodities and transactions not classified elsewhere (miscellaneous or unspecified items) when exported to the US. Given this context, the EU might indeed face intense tariff threats and challenging negotiation rounds moving forward.

In 2023, the US emerged as the leading destination for EU exports, accounting for 19.7% of the EU’s total exports outside the bloc, followed by the UK at 13.1%. When it comes to imports, the US was the second-largest source (after China), providing 13.8% of the EU’s total extra-EU imports; China accounted for 20.6%.
On balance, trade with the US has evolved positively for the EU over the last decade. It peaked in 2021 at 1.1% of the EU’s GDP, as seen in the chart below. Despite a slight decline from 2022 onwards – partly due to increased energy imports – the EU maintained the highest trade surplus with the US in goods trade, amounting to EUR156.7bn (0.9% of GDP) in 2023.

Not all EU policymakers need to be equally concerned about US trade dependencies, though. There are significant differences in trade exposure among member countries and sectors. Nations with strong chemical and pharmaceutical sectors, such as Ireland and Belgium, or robust machinery and transport sectors, like Slovakia and Germany, lead the way in terms of trade exposure. Ireland and Belgium's overall exports to the US are particularly high at 10.1% and 5.6% of their GDP respectively, compared to the overall EU export exposure of 2.9% of GDP.
On the import side, the Netherlands and Belgium, with their major Atlantic ports, import mainly energy and chemical products from the US. Their total imports are valued at 7.1% and 6.1% of their GDP respectively, compared to the overall EU import exposure of 2% of GDP.

Some EU countries therefore have more significant levels of exposure, particularly in the chemical and transport sectors – but the EU still holds an advantage. These exports include strategically important products, i.e., goods that cannot be easily replaced due to limited supply, high dependency from the importing countries, specialised production, and stringent quality requirements.
In 2022, the EU traded 122 strategically important products, representing 4.9% of its overall imports. Yet, the bloc is strategically dependent on the US only for eight products, six of which are chemicals (see the chart below). For instance, the EU relies heavily on beryllium (HS 811212), a metal classified as a Critical Raw Material by the European Commission. Beryllium is essential for defence, transportation, and energy applications. The EU sources 60% of its beryllium from the US, which holds the majority of global resources in a Utah mountain deposit, making substitution difficult.
The US, on the other hand, relies on the EU for 32 strategically important import products, mainly in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors. This dependency balance favours the EU and will provide it with some leverage in negotiations with the incoming Trump administration.

It's no secret that Trump is disgruntled by the EU's trade surplus and has the region in his sights when considering additional tariffs. But the President-elect deems himself something of a dealmaker, and that could make it crucial for the EU to identify areas for concessions and deals. What are the EU’s options?
Europe could increase its purchase of US products, such as further boosting LNG imports. While the promise to ramp up LNG imports from the US was perceived as a gesture to appease Trump during his first term without the expectation of significant impact, the energy crisis has made those imports more valuable for the EU. In terms of defence, the EU could propose increasing its defence spending to 3% of GDP, with a commitment to purchasing more from US companies. Additionally, the EU could open up defence funding initiatives to non-EU companies, as is currently being discussed. Increasing those purchases might be an easy way to reduce the bilateral trade surplus to some extent. Buying more from the US is likely to be a key point in the upcoming trade negotiations.
The EU could target US products by imposing retaliatory tariffs. The Commission is said to have already prepared a list of goods which would be subject to additional tariffs.
The EU could use the Anti-Coercion Instrument (ACI), its “new weapon to protect trade” by launching countermeasures against a non-EU country if negotiations fail. These could include trade, investment or funding restrictions.
Regardless, the EU will go to the World Trade Organisation to prove its case. However, even though WTO panels have found US practices to be unfair and have authorised retaliatory measures in the past, these rulings have not resulted in significant changes. So, while we believe that the EU will try to stand up against Trump, this might be easier said than done. This is especially true given the differing interests of its member states, which were recently highlighted in the vote on additional tariffs on electric cars made in China.
What about the economic impact on Europe? Protectionism is generally bad news for economies, especially export-oriented ones. Yet long before tariffs come into effect, the uncertainty surrounding protectionist trade policy will have an economic impact on sentiment, potentially resulting in delayed investments and hiring.
In the longer term, this may strain trade relations between the EU and the US, further eroding the EU’s struggling manufacturing sector. And as we've written previously, Trump’s second term in office hits the European economy at a much less convenient moment than the first. Back in 2017, the European economy was relatively strong. This time around, it is experiencing anaemic growth and is struggling with a loss of competitiveness. A looming new trade war could push the eurozone economy from sluggish growth into recession. As a result, growth is expected to remain low in 2025 and 2026.


White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features


Log In
Sign Up