Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.K. Trade Balance Non-EU (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance Non-EU (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Services Index MoM
U.K. Services Index MoMA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)
U.K. Trade Balance EU (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Manufacturing Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)
U.K. GDP MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)
U.K. GDP YoY (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
U.K. Industrial Output MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)
U.K. Construction Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France HICP Final MoM (Nov)
France HICP Final MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland Outstanding Loans Growth YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India CPI YoY (Nov)
India CPI YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Deposit Gowth YoY
India Deposit Gowth YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)
Brazil Services Growth YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Mexico Industrial Output YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia Trade Balance (Oct)
Russia Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech
Philadelphia Fed President Henry Paulson delivers a speech Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Building Permits MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Inventory YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)
Canada Wholesale Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)
Germany Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Non-Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Outlook Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Small Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large Manufacturing Diffusion Index (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)
Japan Tankan Large-Enterprise Capital Expenditure YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)
U.K. Rightmove House Price Index YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Industrial Output YoY (YTD) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)
China, Mainland Urban Area Unemployment Rate (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)
Saudi Arabia CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output YoY (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)
Euro Zone Industrial Output MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)
Canada Existing Home Sales MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)
Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations
U.K. Inflation Rate Expectations--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)
Canada New Housing Starts (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Employment Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)
U.S. NY Fed Manufacturing Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Unfilled Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing New Orders MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)
Canada Manufacturing Inventory MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI MoM (Nov)
Canada CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)
Canada CPI YoY (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)
Canada Core CPI MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
Trump’s Fed meddling risks higher inflation, soaring mortgage rates, and lost credibility—echoing Nixon and Erdogan—potentially worsening living costs instead of easing them.

By seeking to isolate his rivals, Donald Trump could well get the opposite effect. Under the pressure of his trade sanctions, the countries of the BRICS bloc, long divided, are beginning an unprecedented strategic rapprochement. As tensions rise, China, India, Russia and their partners seem more willing than ever to cooperate economically and diplomatically.
Since his return to the White House, Donald Trump has chosen to confront the BRICS head-on through an aggressive trade policy, marked by unprecedented tariff increases. The figures speak for themselves and illustrate a resolutely punitive strategy:
Ajay Srivastava, a former senior Indian trade official, points out that these sanctions only fuel a common front: “they give them a common incentive to reduce their dependence on the United States, even if their agendas differ”.
Faced with this external pressure, BRICS alliance countries are responding convergently. The group’s central banks have increased their gold purchases, and bilateral trade agreements in national currencies (yuan, rupee, ruble) are multiplying. This momentum, once sporadic, now takes the form of a deliberate strategy to reduce dependence on the US dollar.
As trade tensions with the United States intensify, leaders of the main BRICS members are preparing to display their unity at the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summit, to be held in Tianjin, China.
For the first time in six years, a trilateral summit between China, India and Russia is planned. The Kremlin is pushing in this direction, hoping to “strengthen the core of the BRICS alliance” and ease historic tensions between New Delhi and Beijing. This is a deliberate attempt to consolidate the group’s hard core in the face of Western pressure.
This initiative is accompanied by bilateral détente signals. Beijing and New Delhi, long at odds over their 3,500-kilometer border, have reopened direct flights, facilitated visa access and engaged in discussions on rare earth supply, a sector in which China holds over 85% of the world’s processing capacity.
During an official visit, Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi confirmed that China is committed to increasing deliveries to India, essential for its defense industries and energy transition.
Nevertheless, mistrust persists, notably due to Beijing’s closeness to Islamabad and the controversial Chinese dam project on the Tibetan plateau, which worries New Delhi. This geopolitical complexity limits the scope of a true rapprochement, especially as India continues to rely heavily on the American market, with $77.5 billion in exports to the US in 2024, against much smaller volumes to China or Russia.
However, beyond tensions, a pragmatic logic seems to emerge. BRICS is no longer a mere ideological platform. The bloc becomes a variable geometry cooperation space, focused on trade, finance and supply chains. Thus, projects for settlement in local currencies, “Buy BRICS” campaigns, and ambitions to reform global governance (notably via the WTO) attest to this. While the BRICS single currency project is on hold, alternatives to the dollar are taking shape.
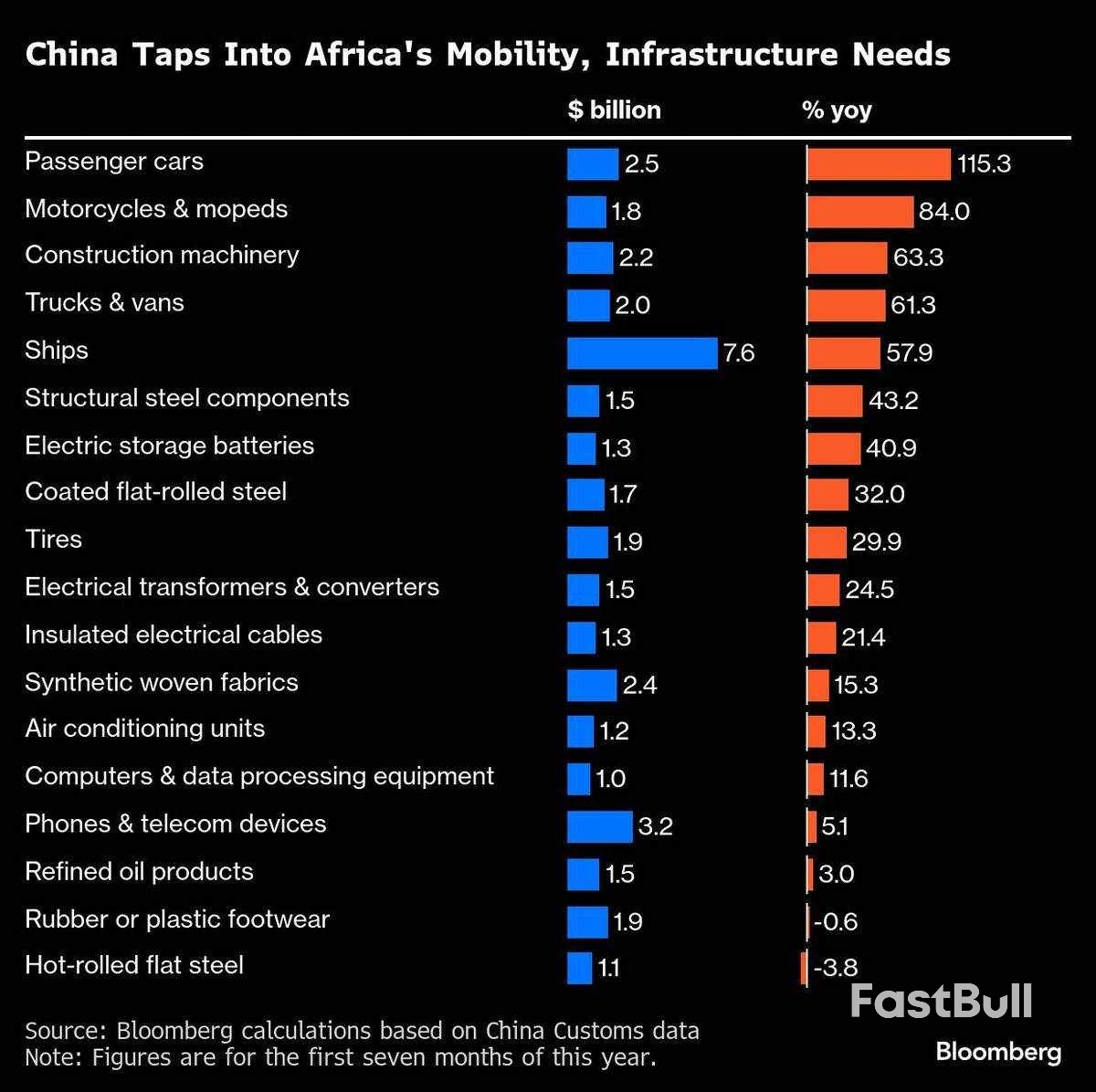
Africa has become a new hotspot for Chinese exports as Donald Trump’s tariffs redraw trade for the world’s biggest manufacturing nation.With a 25% on-year jump to US$122 billion (RM514.78 billion), growth in sales to the continent of 1.5 billion people has far outpaced other major markets this year while orders from the US slumped. China’s exports to Africa so far in 2025 are more than in the whole of 2020 and on track to exceed US$200 billion for the first time.
Although the trading relationship shows no sign of becoming less lopsided, with China running a far wider surplus with Africa than last year, Beijing is cracking open its domestic market while seizing on the chance to meet the continent’s infrastructure needs.“Chinese exporters have done a genuinely impressive job of diversifying into emerging markets in recent years, including in Africa,” said Christopher Beddor, deputy China research director at Gavekal Dragonomics. “The weaker yuan this year has probably also made Chinese exports more competitive in African countries.”
The trade war has supercharged a boom that was years in the making, spearheaded by President Xi Jinping’s Belt and Road Initiative unveiled in 2013. And as Chinese companies snapped up contracts to build everything from railways to industrial parks across the continent, the demand for the machinery and materials to complete these projects followed this year.
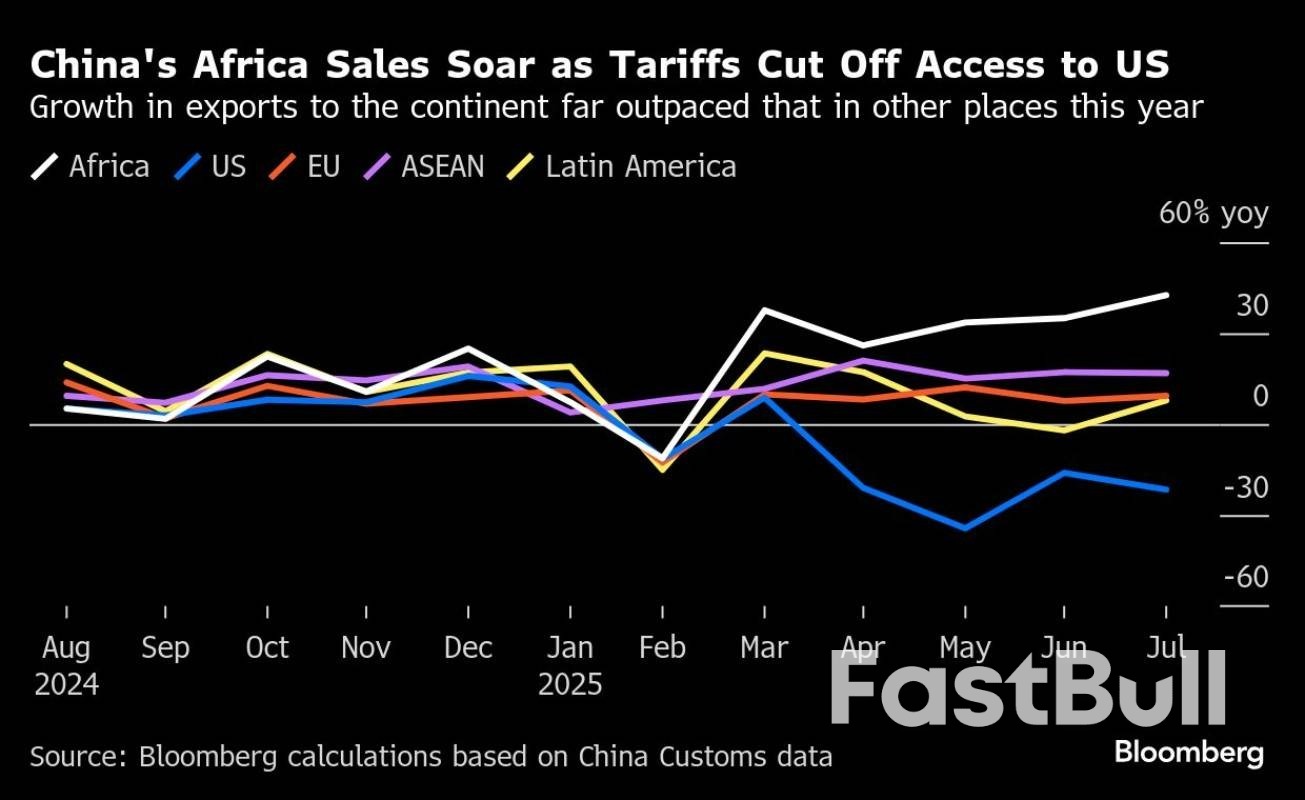
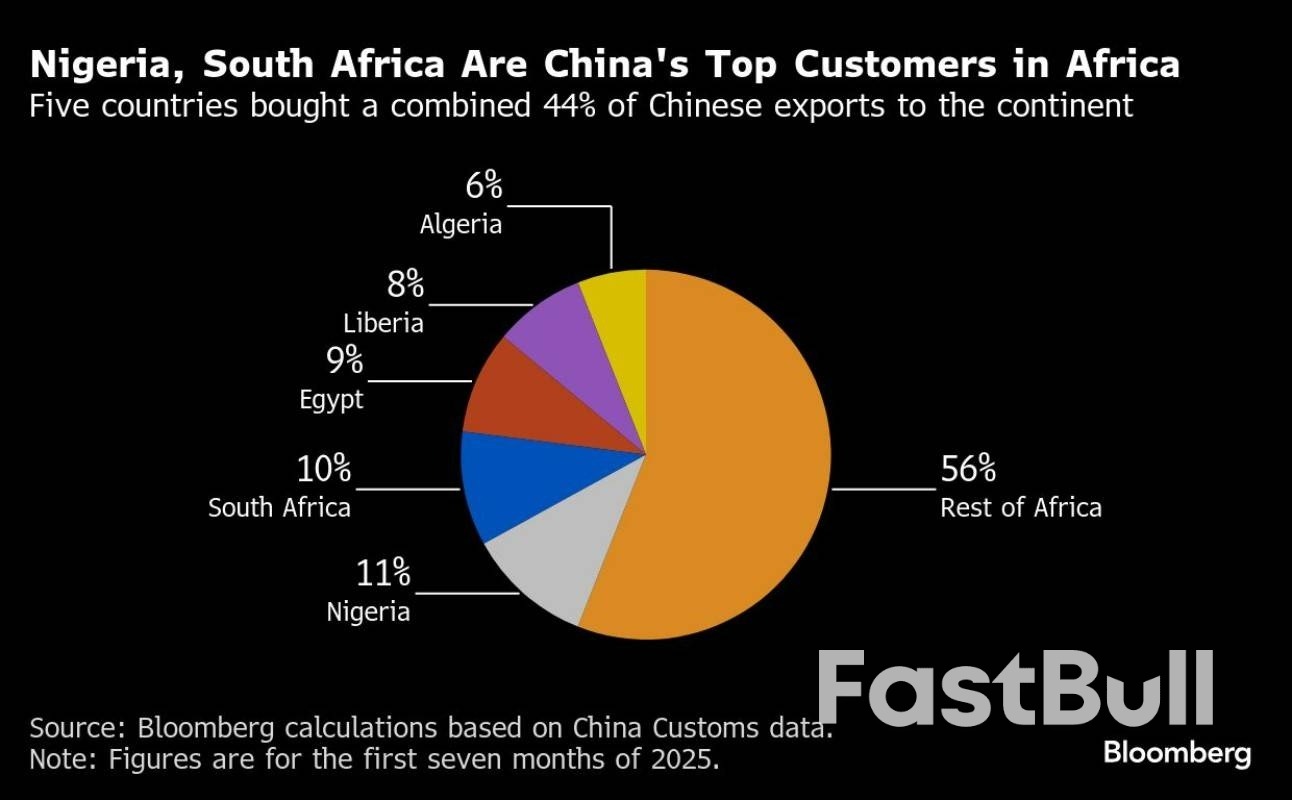
Nigeria, South Africa and Egypt are the biggest African buyers of Chinese products. Construction machinery was among China’s fastest growing exports to Africa in the first seven months, surging 63% year on year.Shipments of passenger cars more than doubled from a year earlier and some steel products expanded in high double digits. At the same time, Africa’s share of China’s total exports remains modest at about 6%, roughly half the level for the US.
Some goods destined for the US are possibly being diverted through Africa, according to Gavekal’s Beddor, a tactic known as transshipment.Rising protectionism in Washington has given extra incentive for Africa to buy from Beijing. A number of goods from more than 30 nations on the continent that had duty-free access to American markets granted under the African Growth and Opportunity Act are now being subjected to a range of tariffs by the Trump administration.
In a counterpoint to Trump, Xi said in June that China is removing levies on imports from all African nations with which it has diplomatic ties.During the same month, the government in Beijing allowed imports of agricultural products from Ethiopia, Congo, Gambia, and Malawi, bringing to 19 the number of African countries with access to China’s market.
In Africa, China could bring know-how and its vast industrial machine to a continent struggling with costly logistics and held back by its patchy infrastructure, with less than half of the population having reliable electricity access.In the first half of 2025 alone, Africa inked US$30.5 billion in construction contracts with China, according to a July report from Griffith University in Australia and the Green Finance & Development Center, founded at Shanghai-based Fudan University. That’s five times the amount during the same period last year and the most among all regions included in Xi’s infrastructure initiative.
“Energy resources remain unevenly distributed in Africa, with some nations heavily reliant on imports” like oil, said Zhou Mi, a senior researcher at the Chinese Academy of International Trade and Economic Cooperation, a think tank under the Ministry of Commerce.“Alternatives offered by China, such as solar and wind power as well as electric cars, can help African countries overcome energy bottlenecks, prompting them to increase imports from the country in pursuit of energy independence and economic development,” he said.
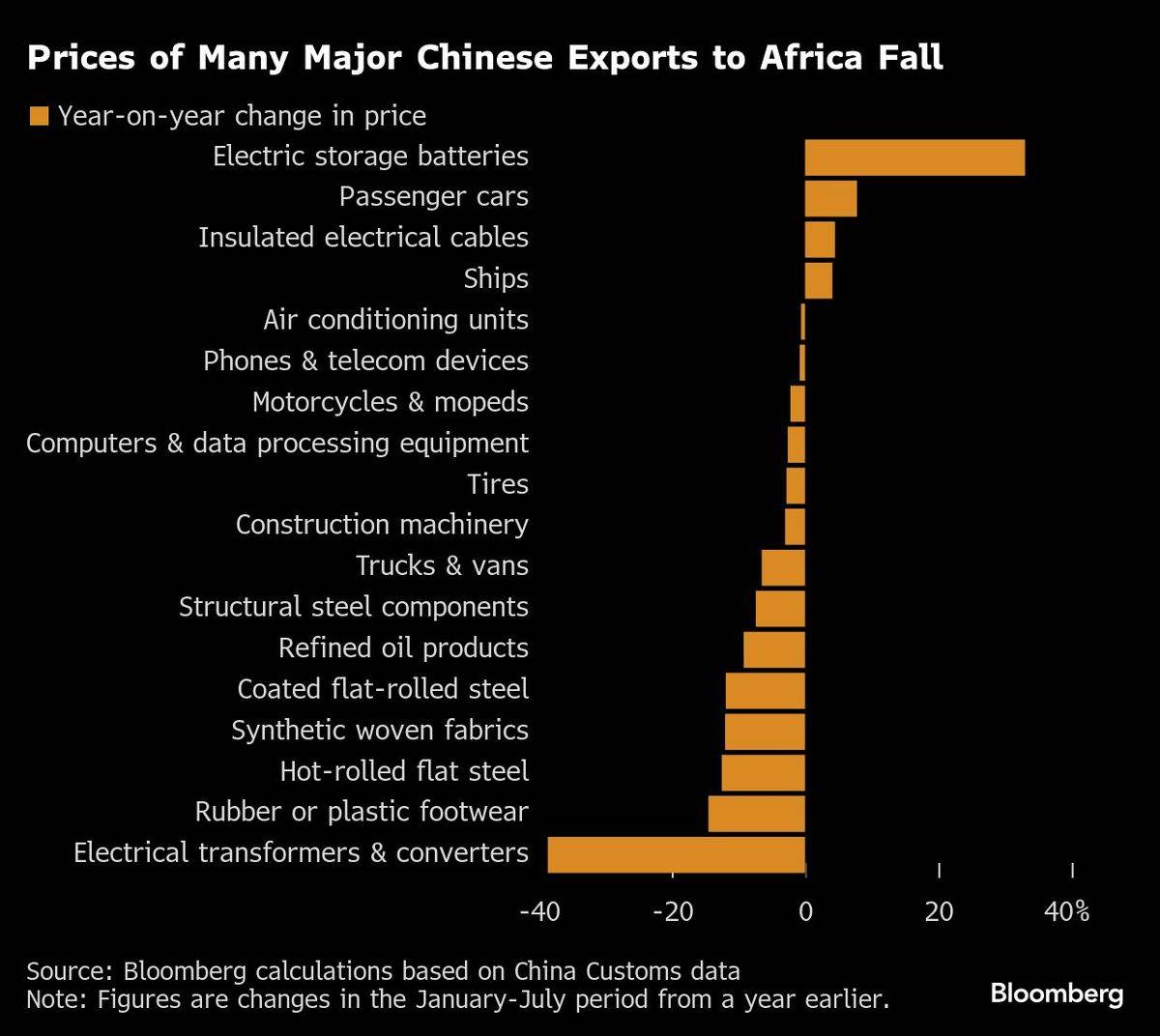
Affordability is another factor working in China’s favour. Despite higher demand, prices for 14 out of the 18 major Chinese goods shipped to Africa actually fell on a yearly basis in the January-July period, with transformers and converters posting the deepest decline of 39%.
China is also bringing financial muscle to the continent with the world’s fastest-growing population, often in the form of backing from state-owned banks. Only in recent months, China Development Bank released a €245 million (US$286 million or RM1.2 billion) first tranche of funding for a railway project in Nigeria and extended a loan for infrastructure construction in Egypt.
Although most of the commodities imported from Africa to China are priced in dollars, the expanding trade footprint will probably help the yuan make inroads in corporate and government balance sheets.Nigeria, South Africa and Egypt are among the four countries on the continent that already have bilateral currency swaps with the central bank in Beijing — a list that includes Mauritius. Kenya has announced it’s in talks to convert some dollar-denominated loans to yuan to help ease the strain of debt.
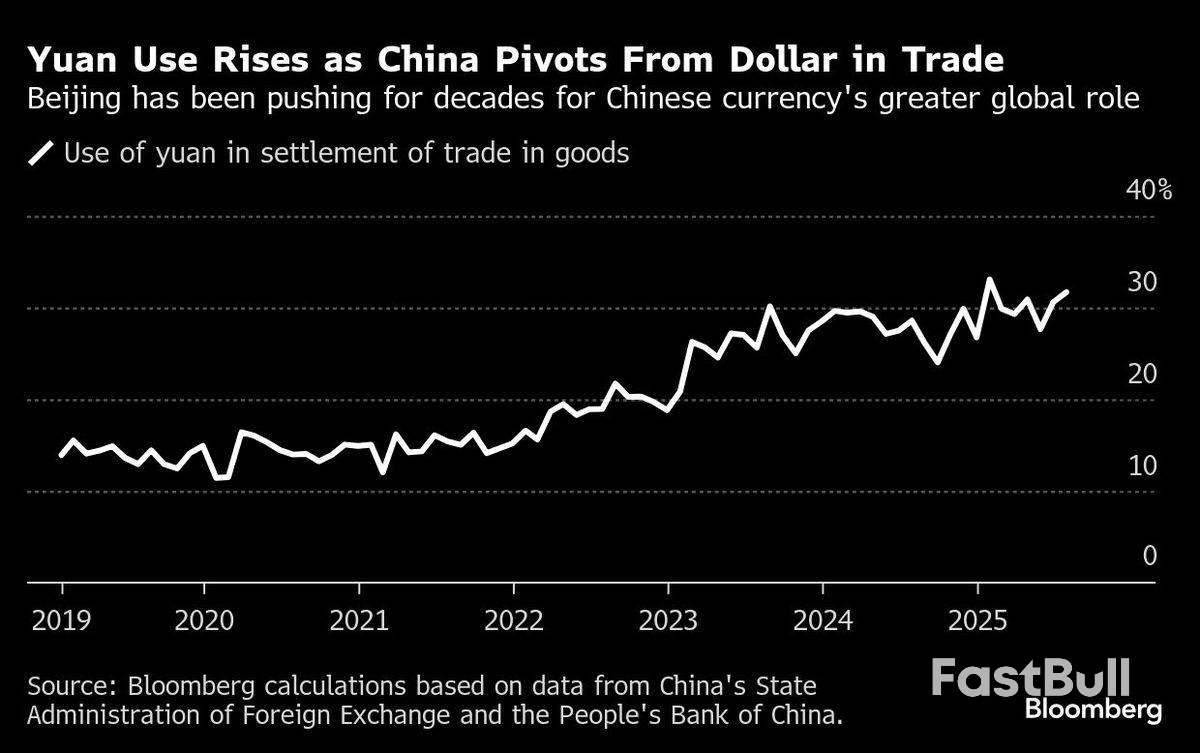
“China obviously benefits from greater use of its currency in the financial system – so that’s the incentive to offer preferential terms if they swap currency debt,” said David Omojomolo, Africa economist at Capital Economics. “I do expect heavily exposed countries to China in terms of debt like Angola will perhaps follow Kenya’s lead on this yuan swap if it’s pulled off.”
Chinese goods barred or resisted elsewhere are meanwhile receiving little pushback in Africa. Exports of steel and iron components — used to build bridges, towers and scaffolding — climbed 43%.Sales of batteries spiked 41%, and transformers and converters, including inverters that adapt electricity from solar panels and wind systems to power home appliances and industrial equipment, soared nearly 25%.
For now, China has yet to encounter the kind of backlash seen from countries around the world that fear the flood of cheaper goods. But it’s a risk in a region already worried about falling further into debt to China, especially if the exports begin to crowd out local producers.But Beijing will tread carefully since the continent is critical as a source of key commodities and a growth market for its companies. What’s more, it’s become a central arena for China’s aspirations on the world stage.
“Africa is where China takes its firms and brands global — they get experience, create markets, and win brand recognition,” said Lauren Johnston, a China-Africa expert of New South Economics, a consultancy in Melbourne. “It is important for China’s global development leadership push.”
In his second term as US president, Donald Trump has used tariffs as a blanket solution to pursue a wide range of goals: increasing domestic manufacturing and foreign market access, boosting federal revenue, and even punishing the government of Brazil for prosecuting his political ally, former President Jair Bolsonaro. Now he’s deployed a tool he calls a “secondary tariff” in an effort to get countries to distance themselves from US adversaries.
Such a tariff on imports from India took effect on Aug. 27. On top of a 25% levy on goods from India imposed earlier, Trump added an additional 25% tariff to penalize India for buying oil from Russia.
The idea behind “secondary tariffs” is to use a weapon against one country to penalize or try to influence a different country. The concept is similar to the one behind so-called secondary sanctions.
The US uses secondary sanctions to multiply the effect of its primary sanctions on countries or entities. Secondary sanctions target commercial activity involving a party under primary sanctions but occurring outside US legal jurisdiction. They are meant to force companies, banks and individuals to make a tough choice: continue doing business with the sanctioned entity or with the US, but not both.
Unlike primary sanctions, which can be enforced by fines and the seizure of US-held assets, secondary sanctions rely on the centrality of the US financial system to the world economy and the widespread use of the dollar as the global reserve currency to work. A company or individual who violates a secondary sanction could be hit by US export controls or be placed on the Treasury Department’s Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons List, which would prevent Americans from doing business with it.
The “secondary tariff” Trump imposed on imports from India isn’t aimed at magnifying the impact of a primary tariff, as the name might suggest. US tariffs on energy from Russia are irrelevant given that such imports were banned in 2022 after the country’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Instead, the extra 25% tariff on imports from India appears to be aimed at compelling its government to adopt a similar ban, with the larger goal of pushing Russia to stop its war.
In March, Trump created a mechanism for imposing tariffs on imports from countries that buy oil from Venezuela, whose regime, he said, poses a threat to US national security.
Ships on the water have identifying transponders that allow third parties to track their location in real time via satellite. That enables analysts in and out of government to, for example, follow oil tankers loading in Russia and unloading in India.
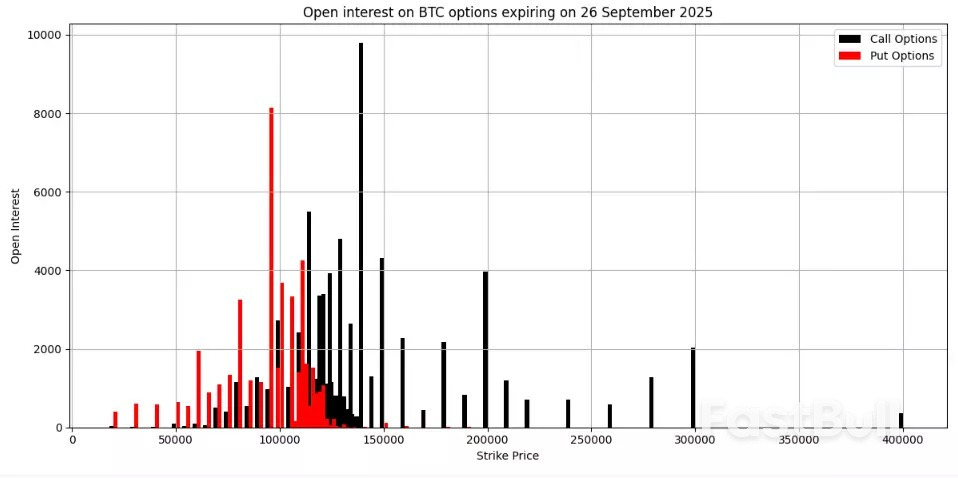 IG as of 26 August 2025
IG as of 26 August 2025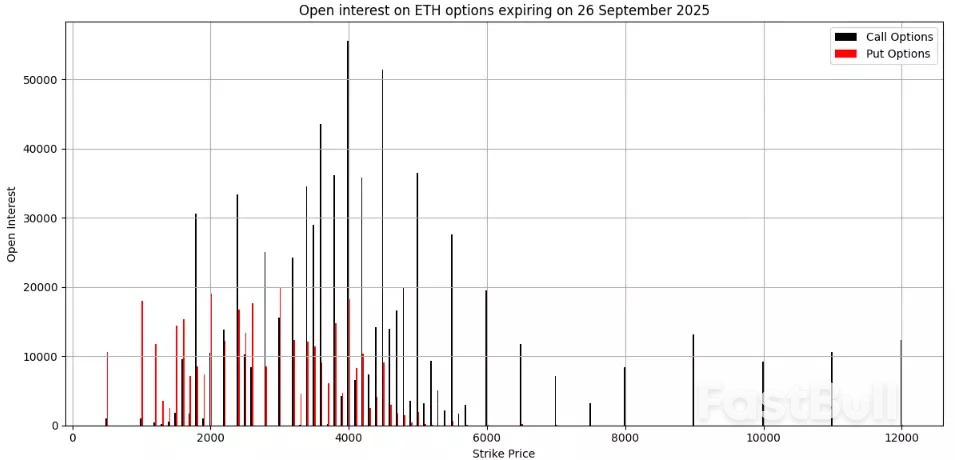 IG as of 26 August 2025
IG as of 26 August 2025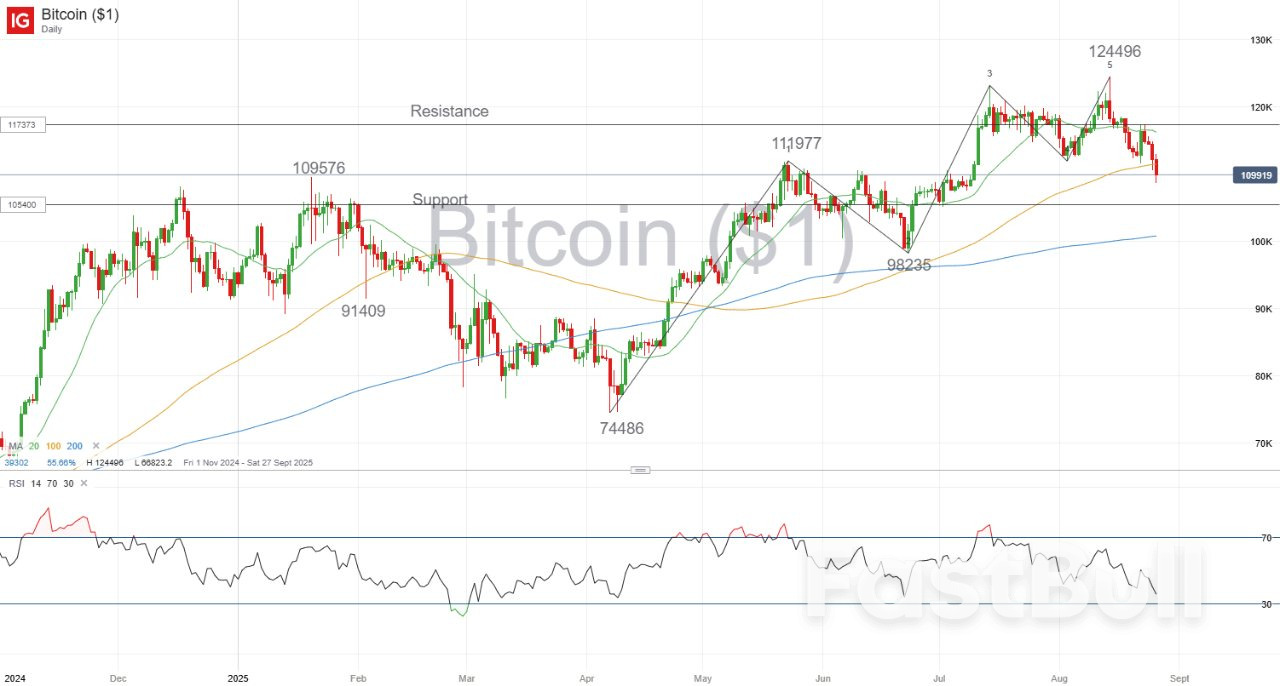 as of 26 August 2025. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
as of 26 August 2025. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.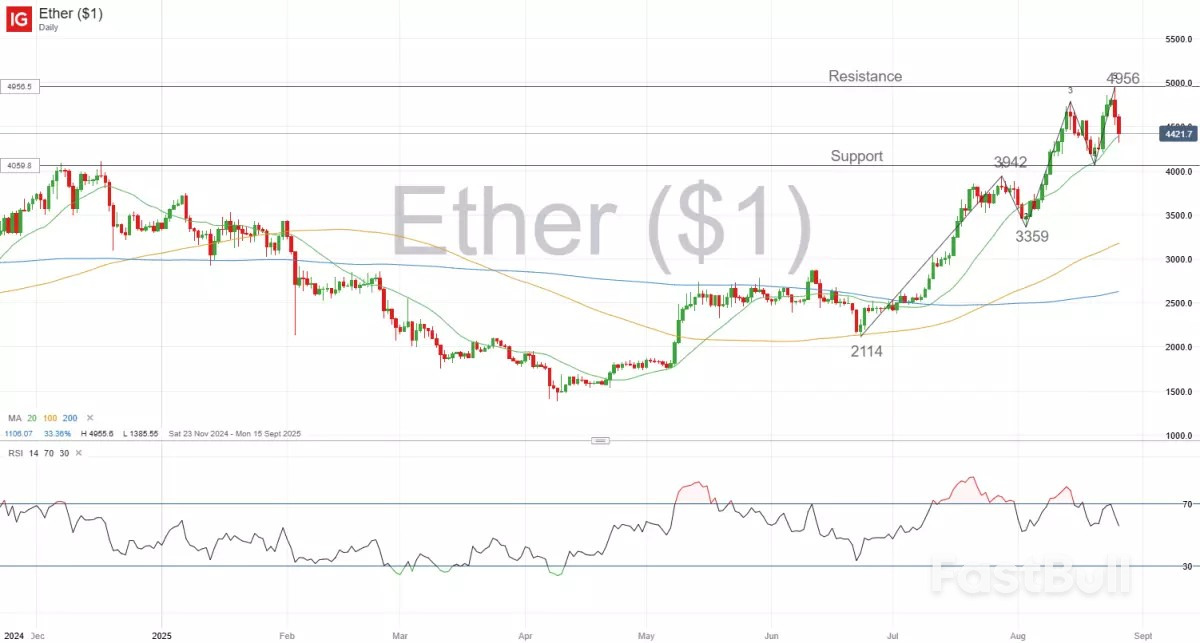 as of 26 August 2025. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
as of 26 August 2025. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up