Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 France 10-Year OAT Auction Avg. Yield
France 10-Year OAT Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Retail Sales MoM (Oct)
Euro Zone Retail Sales MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Retail Sales YoY (Oct)
Euro Zone Retail Sales YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil GDP YoY (Q3)
Brazil GDP YoY (Q3)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Challenger Job Cuts (Nov)
U.S. Challenger Job Cuts (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Challenger Job Cuts MoM (Nov)
U.S. Challenger Job Cuts MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Challenger Job Cuts YoY (Nov)
U.S. Challenger Job Cuts YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)
U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Ivey PMI (SA) (Nov)
Canada Ivey PMI (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Ivey PMI (Not SA) (Nov)
Canada Ivey PMI (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Non-Defense Capital Durable Goods Orders Revised MoM (Excl. Aircraft) (SA) (Sept)
U.S. Non-Defense Capital Durable Goods Orders Revised MoM (Excl. Aircraft) (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Excl. Transport) (Sept)
U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Excl. Transport) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Sept)
U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Excl. Defense) (Sept)
U.S. Factory Orders MoM (Excl. Defense) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks ChangeA:--
F: --
P: --
 Saudi Arabia Crude Oil Production
Saudi Arabia Crude Oil ProductionA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central Banks
U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central BanksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)
Japan Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Repo Rate
India Repo RateA:--
F: --
P: --
 India Benchmark Interest Rate
India Benchmark Interest RateA:--
F: --
P: --
 India Reverse Repo Rate
India Reverse Repo RateA:--
F: --
P: --
 India Cash Reserve Ratio
India Cash Reserve RatioA:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Leading Indicators Prelim (Oct)
Japan Leading Indicators Prelim (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Halifax House Price Index YoY (SA) (Nov)
U.K. Halifax House Price Index YoY (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. Halifax House Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)
U.K. Halifax House Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)
France Current Account (Not SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Italy Retail Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)
Italy Retail Sales MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)
Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone GDP Final YoY (Q3)
Euro Zone GDP Final YoY (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone GDP Final QoQ (Q3)
Euro Zone GDP Final QoQ (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Employment Final QoQ (SA) (Q3)
Euro Zone Employment Final QoQ (SA) (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Employment Final (SA) (Q3)
Euro Zone Employment Final (SA) (Q3)--
F: --
 Brazil PPI MoM (Oct)
Brazil PPI MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Consumer Confidence Index (Nov)
Mexico Consumer Confidence Index (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)
U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Dallas Fed PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Dallas Fed PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)
U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Dec)
U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)
U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)
U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
President Donald Trump has taken to routinely maligning Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell as “too late” because interest rates..
President Donald Trump has taken to routinely maligning Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell as “too late” because interest rates have been on hold at 4.25%-4.5% since he took office. On Tuesday alone, he characteristically took to social media to demand three percentage points of rate cuts — something that is never going to happen outside of a recession. Trump’s needling aside, the latest inflation data show that Powell’s wait-and-see approach is the exact right tack for today’s economic outlook.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics said Tuesday that the core consumer price index rose 0.2% in June from a month earlier, a slightly encouraging surprise that leaves the year-over-year rate at 2.9%. But the reading remains well above the Fed’s 2% target, and the details of the report show that tariffs are starting to fan higher prices and that larger effects might start to feed through over the next couple of months.
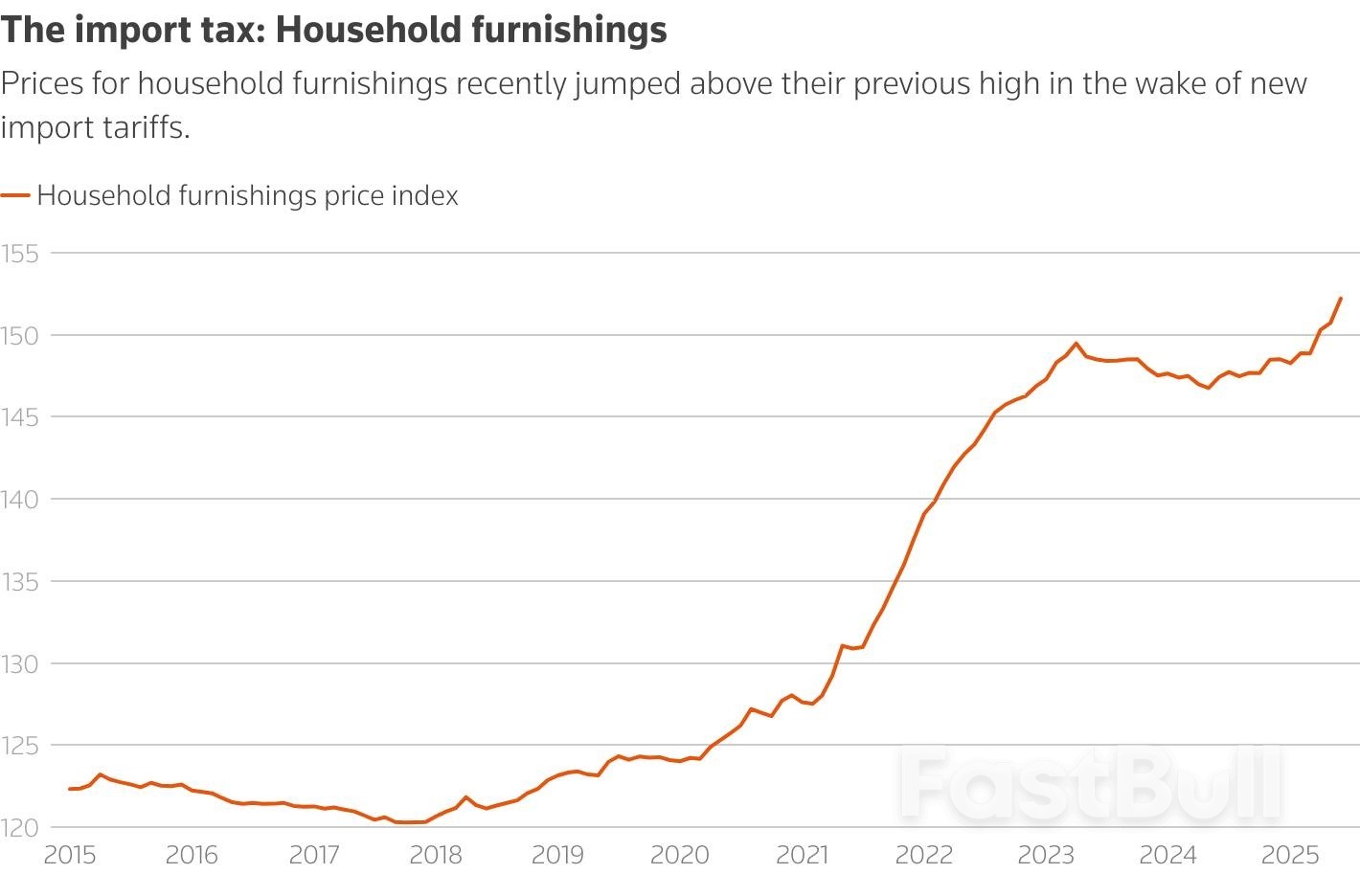
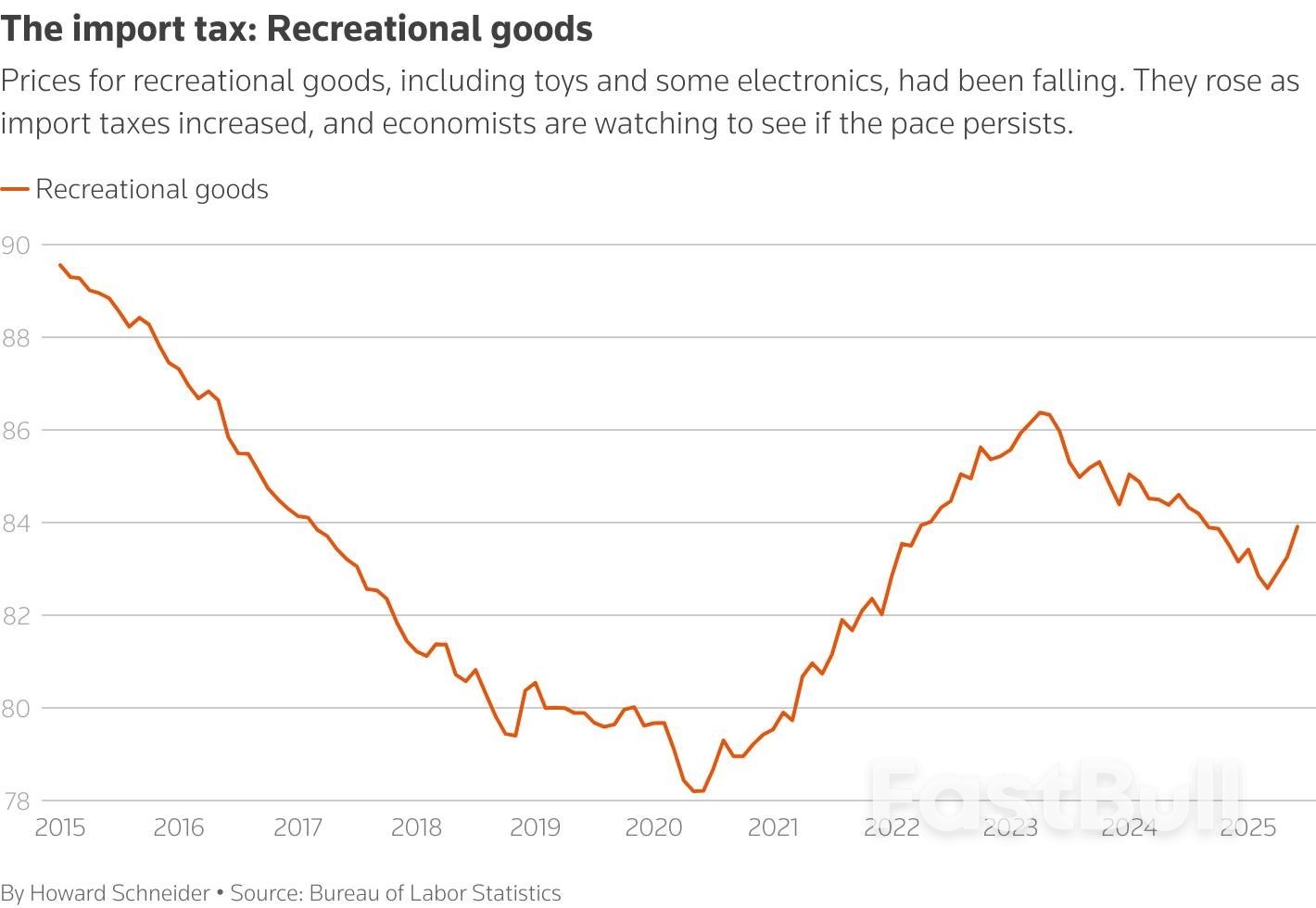
More specifically, core goods rose 0.2% in June from a month earlier, the most brisk pace since February, driven in large part by a jump in household furnishings and supplies — a telltale sign of tariff passthrough. That category (think appliances, rugs, housekeeping supplies, etc.) jumped by 1% from the prior month, the biggest such increase since January 2022. Also notching the biggest month-on-month jump since 2022 were recreation commodities (sporting goods, toys, video equipment, etc.). Not only were tariff impacts undeniable this month, they appeared to be broadening out from what had been a very light and scattered influence in previous months’ data.
Still, this was neither a month to panic nor celebrate. With the backdrop of a steady unemployment rate, it’s time to do as the embattled Fed chair — whom Trump has committed to replacing when his term is up next year — has been advising all along: Wait for more data.
Among Fed policymakers and private sector economists, the general view of tariffs has been that they would hit sometime over the summer. For starters, Trump’s biggest and broadest tariff salvo didn’t come until April. Goldman Sachs Group Inc. economists estimate that it takes about a month for many imports to reach US shores, and goods were exempt if they were already on the ship at the time of the “Liberation Day” duties. What’s more, businesses stockpiled inventory in advance of the deadline and Customs and Border Protection allows many importers to delay payments for up to a month and a half. Hence, many forecasters expected June to be the start of a tariff-impact story that could become more evident in July and August.
Powell has been broadly in that camp. At the post-decision press conference in June, he said that he expected to learn more “over the summer” about tariffs. “We hadn’t expected them to show up much by now, and they haven’t,” he said. “And we will see the extent to which they do over coming months.” In markets, his comments have been broadly interpreted to mean that further rate cuts were possible (though hardly guaranteed) as soon September, and that still feels appropriate. By that time, the committee will have additional inflation data in hand for the months of July and August.
Unfortunately, Trump has used his social media platform to advocate for more immediate cuts, and his Council of Economic Advisers recently published an analysis that found no evidence that tariffs have caused “any economically meaningful inflation.” Inflation Insights President Omair Sharif wrote Monday that the CEA had gotten ahead of itself. “Setting aside the methodology for a moment, if the main point of the CEA’s analysis is to suggest that tariffs are not impacting inflation, then I think they’ve spiked the ball at the 50-yard line,” he said.
It’s entirely possible, of course, that tariff impacts could spread further and that the Fed will still lower policy rates. The central bank doesn’t have to wait for inflation to return to 2% to start lowering rates again; rates are clearly at a level that the median Fed policymaker would deem restrictive. Powell and his colleagues just need to gain confidence that it remains on the right trajectory.
Furthermore, tariffs are generally seen as a one-off increase in prices — the sort of supply shock that monetary policy orthodoxy would tell you to “look through.” The ultimate question as it pertains to trade policy is whether tariffs will shock expectations to such an extent that inflation gets back into the bones of the economy. That may depend on both the magnitude of the tariff impacts and their duration. And all of those variables depend, in turn, on whether Trump decides to temper the policies — as he’s occasionally proved willing to do, especially when financial markets react badly.
To some extent, monetary policy will also depend on what happens with other key categories in the inflation basket. Among major imported goods, the auto sector is a big question mark. While tariffs are driving up car prices and threatening profit margins, the government data showed that prices of both new and used vehicles fell in June from May — a reminder that the duties aren’t the only consideration. Dealers are also contending with high borrowing costs and a general affordability crunch that’s weighing on demand. Many are uncertain about whether they can increase prices without hitting customer traffic and market share.
What’s more, it’s important to remember that core services — which aren’t directly impacted by the tariffs — still constitute about three quarters of core CPI and about two thirds of inflation overall. As such, it’s plausible that services disinflation could mitigate the jumps in certain core goods prices, especially if shelter inflation remains as tame as it’s been for the better part of 2025. With all the crosscurrents, the responsible solution is for policymakers to wait for more evidence, and that’s exactly what the Fed is doing under Powell’s stewardship. No matter what the partisans around the White House say, the chairman is handling tariff uncertainty about as well as you could ask for.
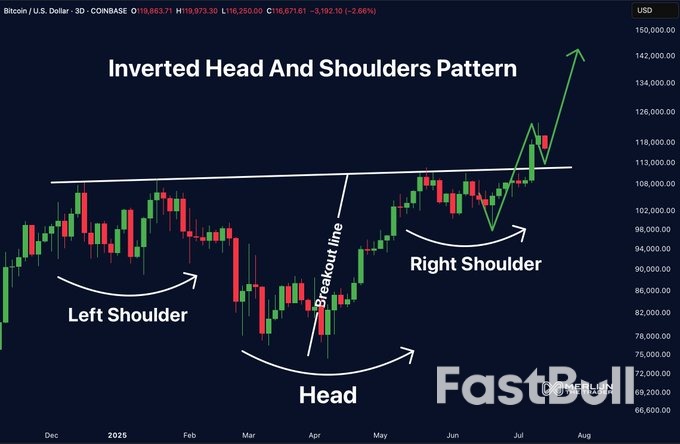
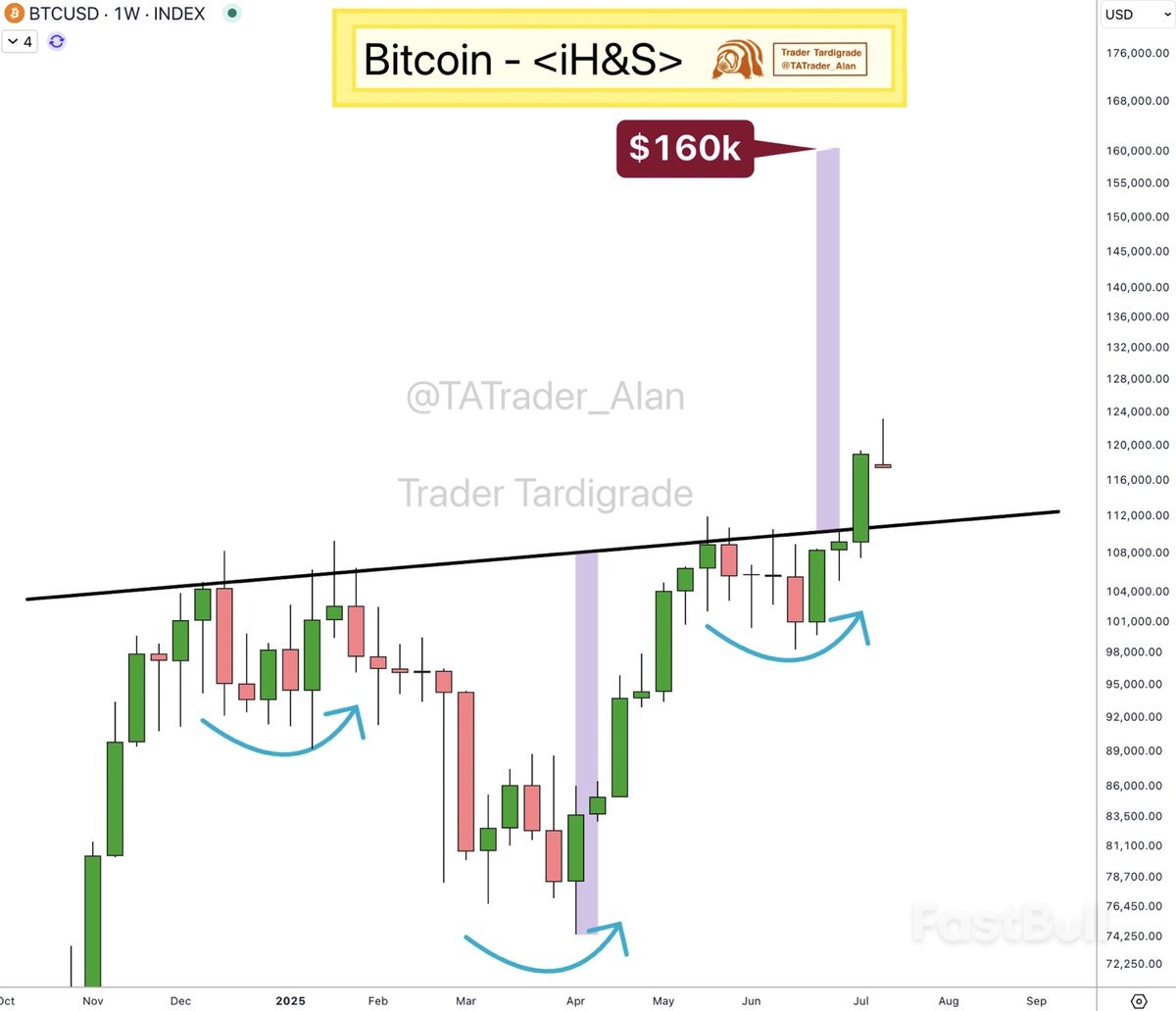
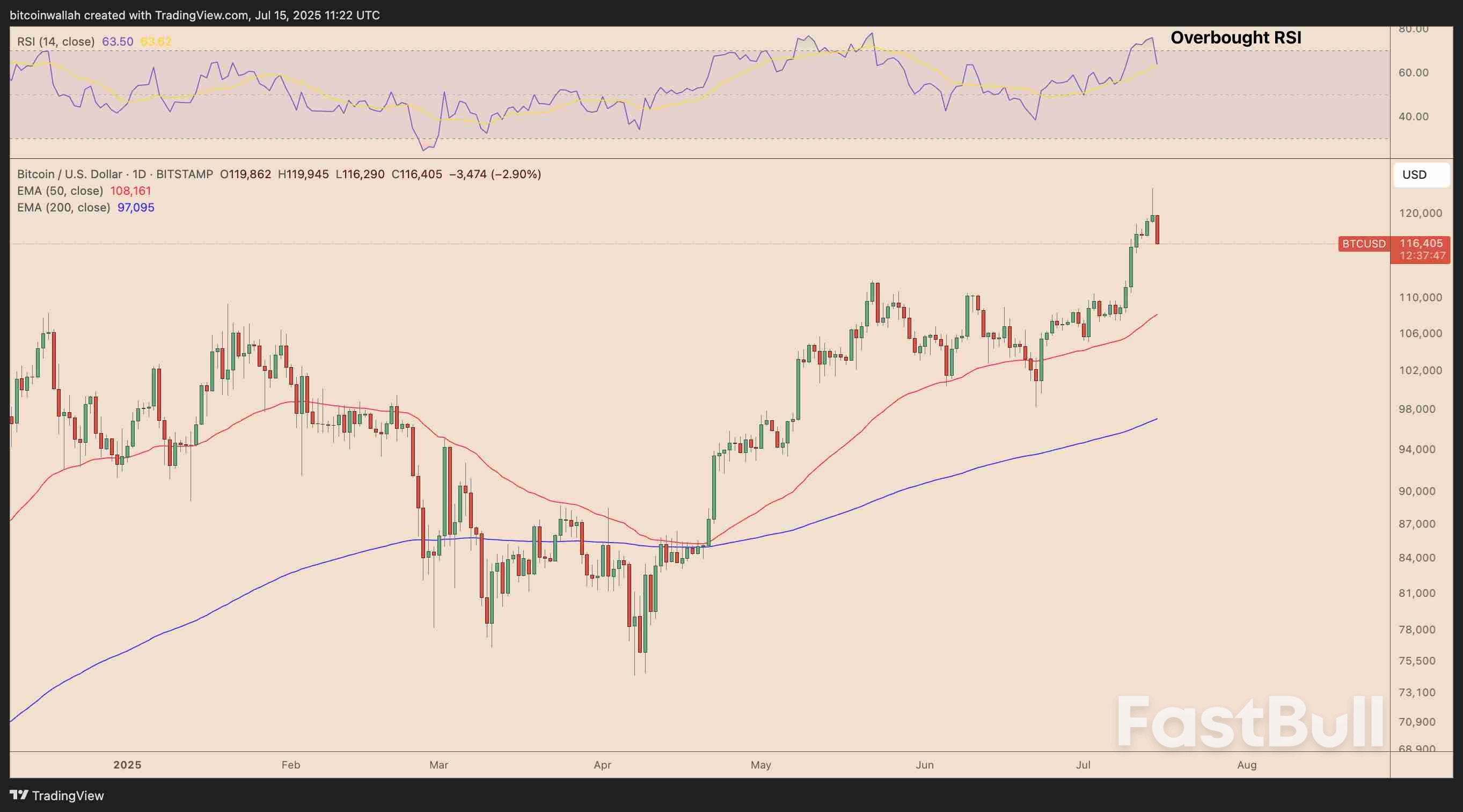
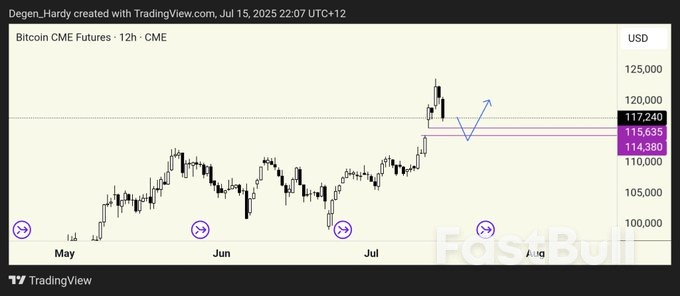
Rising prices across an array of goods from coffee to audio equipment to home furnishings pulled inflation higher in June in what economists see as evidence of the Trump administration's increasing import taxes passing through to consumers.
Overall consumer prices rose 0.3% in June, a roughly 3.5% annual rate, after a 0.1% increase in May.
Economists - and Fed officials - say they were expecting inflation to gather pace this summer as the lagged impact of tariffs gets passed along by businesses, and the June data suggest central bank policymakers in particular may remain reluctant to cut interest rates until more information is at hand.
The tariff price shock could ultimately prove a temporary, one-time adjustment. But with the final tariff levels still being considered by President Donald Trump, and steeper levies threatened as of August 1, the inflation outlook remains unsettled.
"Today's report showed that tariffs are beginning to bite," said Omair Sharif, head of Inflation Insights, "apparel prices rose, household furnishing prices jumped...and recreation commodities increased."
Those are heavily imported items and the increases were substantial. Prices for audio-video equipment rose 1.1% over the month and have risen 11.1% on a year over year basis, the largest jump ever in a category where globalization had generally meant steady or falling prices.
It will likely strike a note of caution for the Fed, which has been facing almost daily criticism from Trump for not cutting interest rates, a step central bankers have been reluctant to take until it is clear where the tariffs will leave the U.S. economy.
Fed officials see the most likely immediate outcomes as higher inflation, slower growth, or a combination of both. The Trump administration argues that over time its tariff proposals will boost economic growth and keep inflation moderate, and that rates should be lowered in the meantime.
"With increases in categories like household furnishings, recreation, and apparel, import levies are slowly filtering through," wrote Seema Shah, Chief Global Strategist at Principal Asset Management. "It would be wise for the Fed to remain on the sidelines for a few more months at least.”
Investors still expect the Fed in September to cut a quarter of a percentage point from the current 4.25% to 4.5% benchmark interest rate maintained since December, but odds of a cut at the upcoming July 29-30 meeting are now below 5%.
Powell had earlier pinpointed this summer as the time when the U.S. central bank will learn if inflation is responding to the tariffs applied on trading partners and various industrial sectors.
So far the levies were having only a limited impact on inflation, but economists broadly have expected to see them eventually filter into retail prices.
"We know there is a lag between implementation and the inflationary effect," said Gregory Daco, chief economist at EY-Parthenon. "Businesses manage imports using different processes ... We have not seen the full-blown effects of tariffs on CPI data ... I would expect to start to see more."
Overall inflation, excluding volatile food and energy prices increased at a 2.9% annual rate in June, slightly below the 3% consensus forecast, with car prices helping hold down the overall increases. Food and energy costs both increased.
The June CPI data will likely leave the Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index the Fed uses for its 2% inflation target well above that goal, with increased uncertainty now that Trump has threatened tariff levels of 30% or more on Mexico, Canada and the European Union, and more actions always possible.
The PCE index outside food and energy rose at a 2.7% annual rate in May; recent Fed policymaker projections see it hitting 3.1% by the end of 2025; and the most recent round of tariffs threatened by Trump for August 1 could push it even higher.
The new tariff rates "if fully passed through, would add about 0.4 percentage points to the PCE price level," Michael Feroli, chief U.S. economist at JP Morgan, estimated. "Given imperfect pass-through, margin compression, a more likely estimate is 0.2-0.3 points. We think this bolsters the case for the Fed to take a very cautious approach to rate cuts."
Daco said there was already "divergence" beginning across a wide swath of goods where prices are rising faster than they did before Trump's initial rounds of tariffs.
The price of household furnishings, for example, jumped a full percentage point in June. Prices of those products had been dropping, but reversed course in the spring.
Other economists have pinpointed different items that could show where the new import taxes are starting to hit consumer prices.
Sharif, the head of Inflation Insights, said the broad category referred to as "recreational commodities," which includes things like toys and audio and visual equipment that are often imported from China, bears watching -- and rose 0.8% in June, twice as fast as in the preceding two months.
In his press conference following the June 17-18 policy meeting, Powell noted that electronics were an area where "we're beginning to see some effects. And we do expect to see more of them over coming months."
Outdoor equipment and tools are also items that are heavily imported, and while the pace of price increases had picked up in the spring it fell back in June to 0.2% versus 0.6% in May.
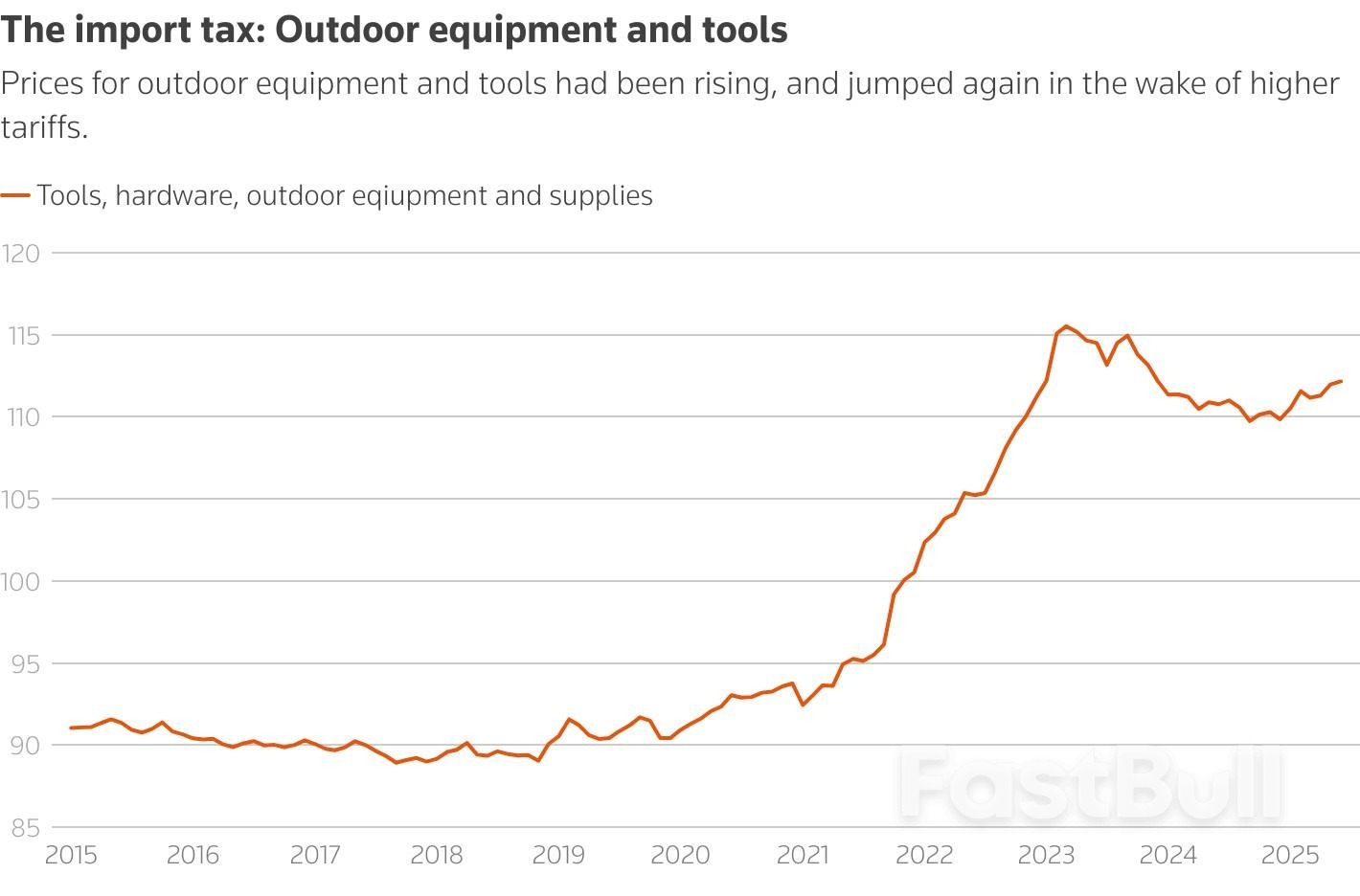
Still, "tariff costs are strikingly visible in June’s CPI data," wrote Samuel Tombs, chief U.S. economist for Pantheon Macroeconomics. Excluding autos, prices for other non-food or energy goods rose at the fastest pace since June, 2022, when the Fed was still in a battle to lower pandemic-era inflation.
"Prices rose especially sharply for goods which are primarily imported," with prices for appliances, sports equipment and toys all rising nearly 2% on the month, he said.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up