Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Jan)
U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 2-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 2-Year Note Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Shop Price Index YoY (Jan)
U.K. BRC Shop Price Index YoY (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Dec)
China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany 2-Year Schatz Auction Avg. Yield
Germany 2-Year Schatz Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Trade Balance (Dec)
Mexico Trade Balance (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoYA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 10-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Composite Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Present Situation Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Expectations Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Shipments Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)
U.S. Richmond Fed Services Revenue Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)A:--
F: --
 U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 5-Year Note Auction Avg. YieldA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Gasoline StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia RBA Trimmed Mean CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI YoY (Q4)
Australia CPI YoY (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)
Australia CPI QoQ (Q4)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)
Germany GfK Consumer Confidence Index (SA) (Feb)--
F: --
P: --
 Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. Yield
Germany 10-Year Bund Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)
India Industrial Production Index YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)
India Manufacturing Output MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW
U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Overnight Target Rate
Canada Overnight Target Rate--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Monetary Policy Report
BOC Monetary Policy Report U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 BOC Press Conference
BOC Press Conference Russia PPI MoM (Dec)
Russia PPI MoM (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia PPI YoY (Dec)
Russia PPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Lower Limit (Overnight Reverse Repo Rate)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances
U.S. Interest Rate On Reserve Balances--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target
U.S. Federal Funds Rate Target--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)
U.S. Target Federal Funds Rate Upper Limit (Excess Reserves Ratio)--
F: --
P: --
 FOMC Statement
FOMC Statement FOMC Press Conference
FOMC Press Conference Brazil Selic Interest Rate
Brazil Selic Interest Rate--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)
Australia Import Price Index YoY (Q4)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)
Japan Household Consumer Confidence Index (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)
Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Jan)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)
Euro Zone M3 Money Supply (SA) (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone Private Sector Credit YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone 3-Month M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)
Euro Zone 3-Month M3 Money Supply YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 South Africa PPI YoY (Dec)
South Africa PPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --










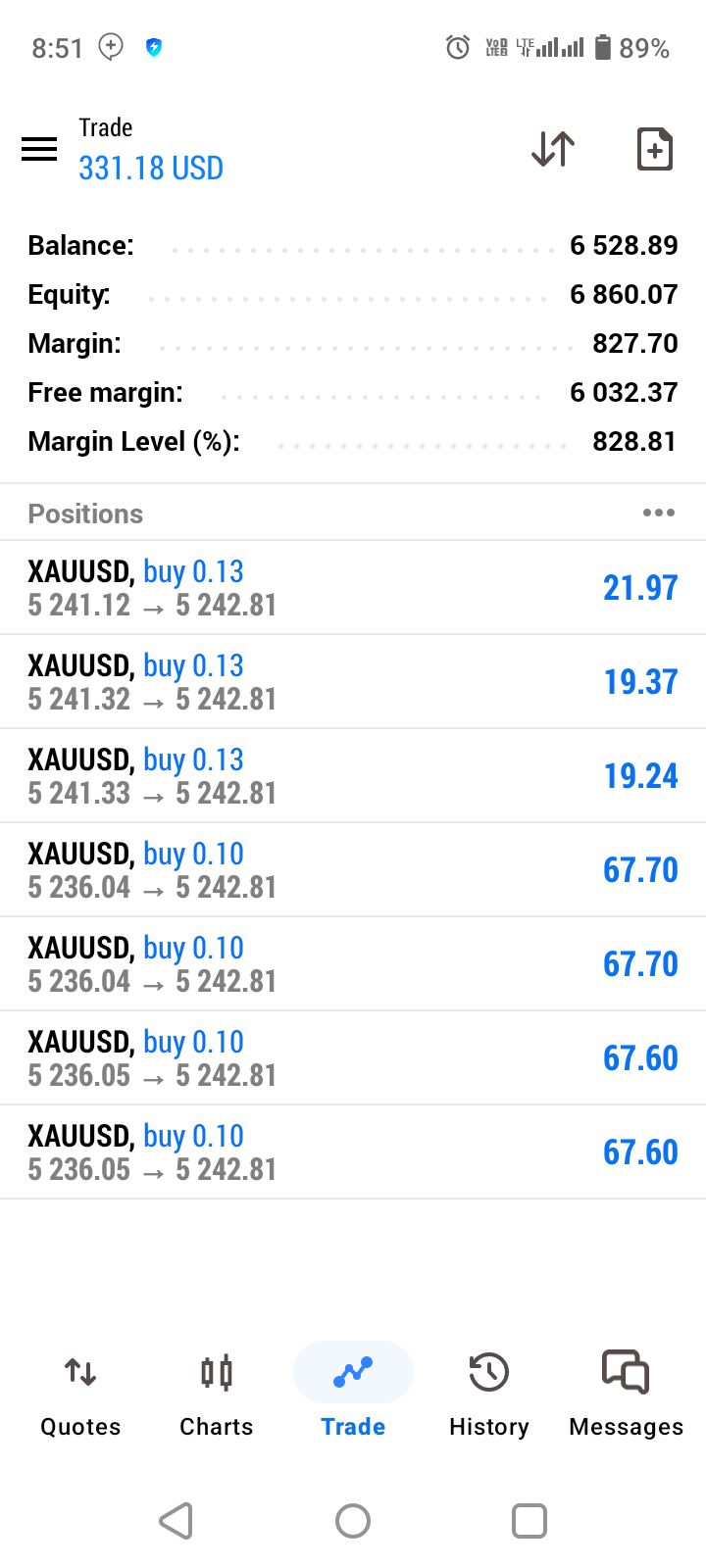


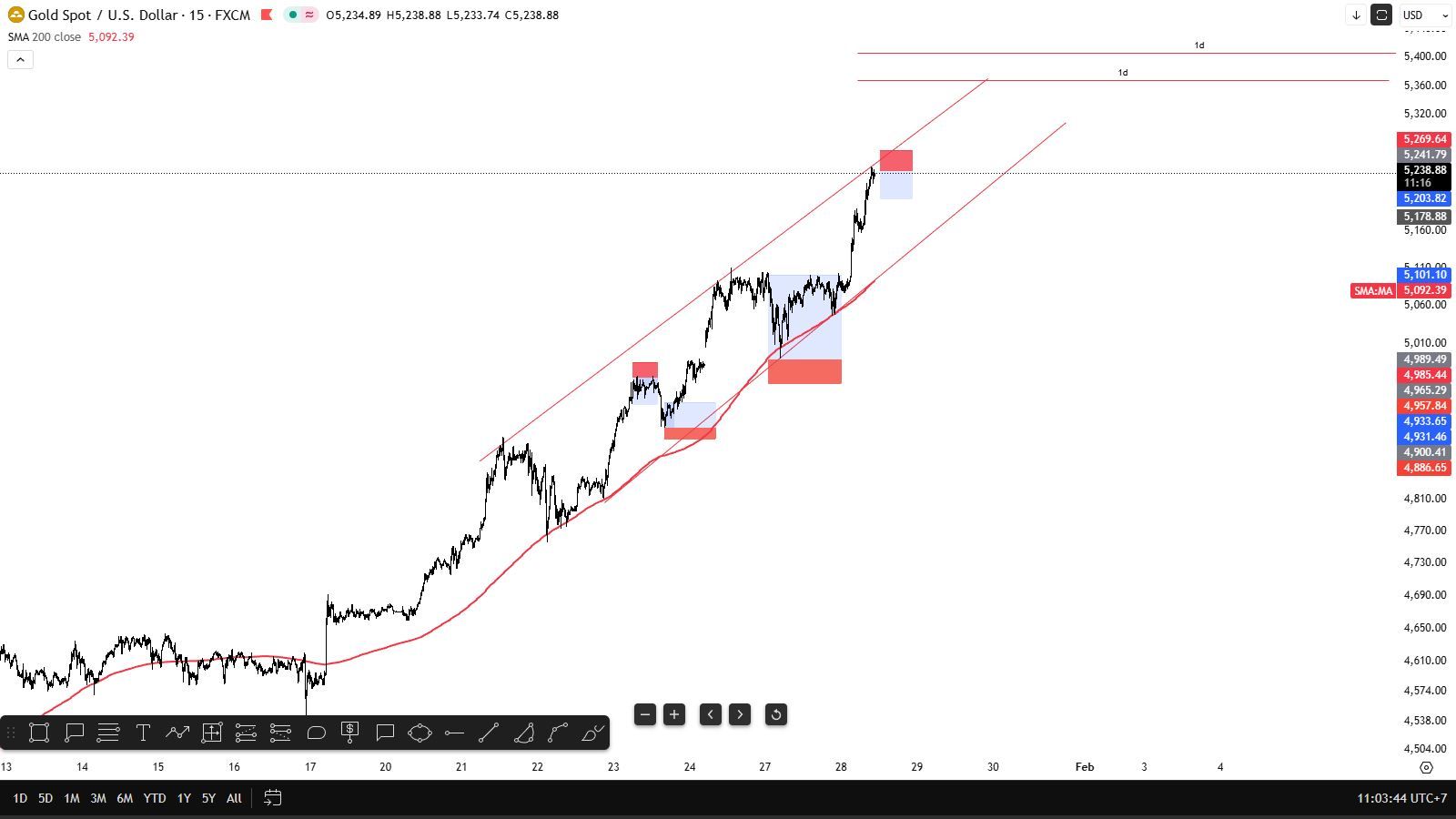




















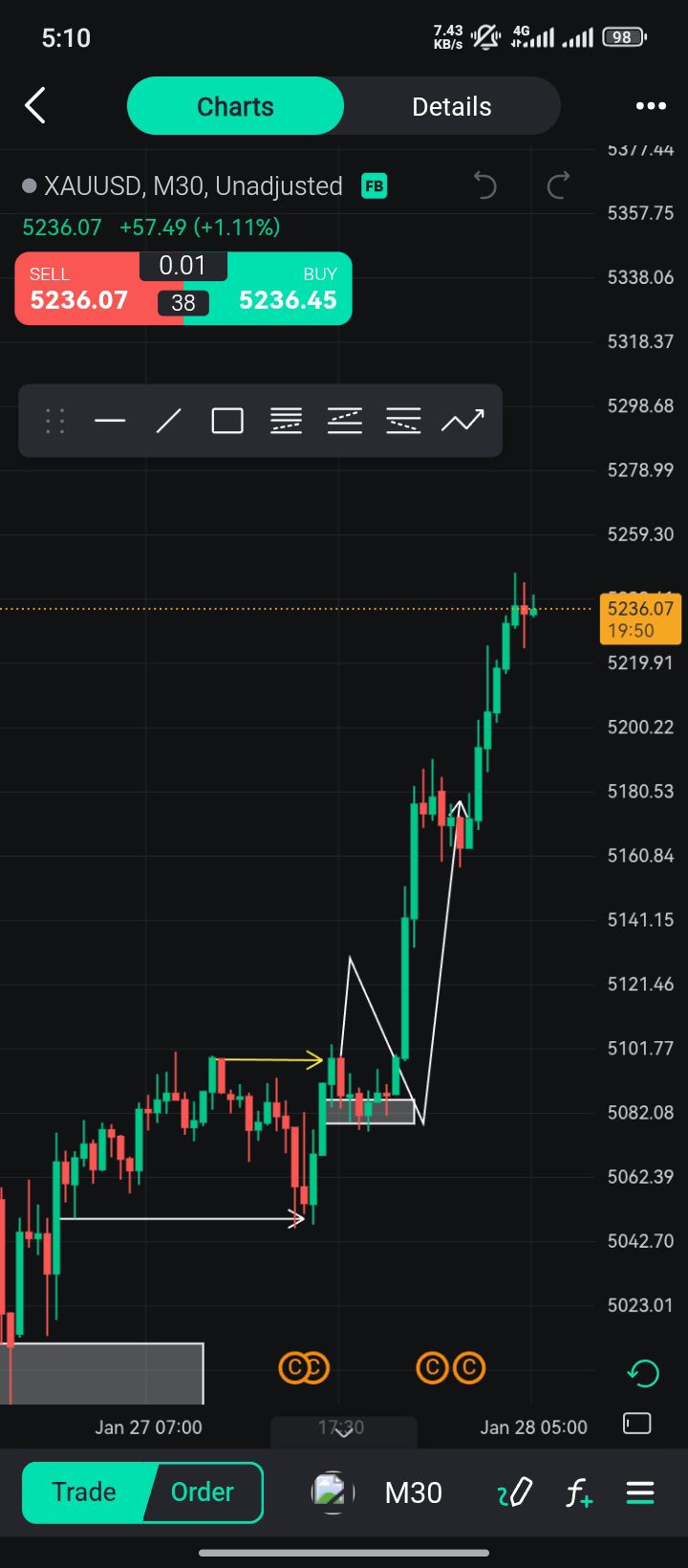











No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
The two Federal Reserve policymakers who dissented against the U.S. central bank decision's to leave interest rates unchanged last month appear not to have been joined by other policymakers in voicing support for lowering rates at that meeting, a readout of the gathering released on Wednesday showed.
Key points:
The two Federal Reserve policymakers who dissented against the U.S. central bank decision's to leave interest rates unchanged last month appear not to have been joined by other policymakers in voicing support for lowering rates at that meeting, a readout of the gathering released on Wednesday showed.
"Almost all participants viewed it as appropriate to maintain the target range for the federal funds rate at 4.25% to 4.50% at this meeting," the minutes of the July 29-30 meeting said.
Fed Vice Chair for Supervision Michelle Bowman and Governor Christopher Waller both voted against the decision to leave the benchmark interest rate unchanged, favoring instead a quarter-percentage-point reduction to guard against further weakening of the job market. It was the first time since 1993 that more than one Fed governor dissented against a rate decision.
Not even 48 hours after the conclusion of last month's meeting, data from the Labor Department appeared to validate the concerns of Bowman and Waller when it showed far fewer jobs than expected were created in July, a rise in the unemployment rate and a drop in the labor force participation rate to the lowest level since late 2022.
More unsettling, though, was an historic downward revision for estimates of employment in the previous two months. That revision erased more than a quarter of a million jobs thought to have been created in May and June and put a hefty dent in the prevailing narrative of a still-strong-job market. The event was so angering to President Donald Trump that he fired the head of the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Data since then, however, has provided some fodder for the camp more concerned that Trump's aggressive tariffs risk rekindling inflation to hold their ground against moving quickly to lower rates. The annual rate of underlying consumer inflation accelerated more than expected in July and was followed by an unexpectedly large jump in prices at the producer level.
The minutes showed officials continued an active debate on the effects of tariffs on inflation and the degree of restrictiveness in their policy stance. Several policymakers commented that the current level of the federal funds rate may not be far above its neutral level, where economic activity is neither stimulated nor constrained.
Fed policymakers assessed that the effects of higher tariffs had become more apparent in some goods prices but that the overall effect on the economy and inflation remained to be seen, the minutes showed.
Looking ahead, participants noted they may face difficult tradeoffs ahead if elevated inflation proved more persistent while the job market outlook weakened.
Heading into the release of the minutes, CME's FedWatch tool assigned an 85% probability of a quarter-percentage-point reduction in the Fed's policy rate at the September 16-17 meeting. That rate has been unchanged since December.
The minutes were released just two days before a highly anticipated speech from Fed Chair Jerome Powell at the annual economic symposium near Jackson Hole, Wyoming, which is hosted by the Kansas City Fed. Powell's keynote speech on Friday morning - set to be his last such address as head of the central bank, with his term expiring next May - could show whether he has joined ranks with those sensing the time has come for steps to shield the job market from further weakening or if he remains in league with those more wary of inflation in light of its moves away from the Fed's 2% target.
The lack of rate cuts since Trump returned to the White House has agitated the Republican president, and he regularly lashes out at Powell for not engineering them.
Trump is already in the process of screening possible successors to Powell. After the unexpected resignation earlier this month of one of the seven Fed governors, Trump has a chance to put his imprint on the central bank soon.
The president has nominated Council of Economic Advisers Chair Stephen Miran to fill the seat recently vacated by former Fed Governor Adriana Kugler, a term that expires at the end of January. It is unclear whether Miran will win Senate confirmation before the Fed's next meeting.
On Wednesday Trump demanded that Fed Governor Lisa Cook resign from the central bank over allegations of wrongdoing connected to mortgages on properties she owns in Georgia and Michigan.
Most Federal Reserve officials highlighted the risk to inflation as outweighing concerns over the labor market at their meeting last month, as tariffs fueled a growing divide within the central bank’s rate-setting committee.
Officials acknowledged worries over higher inflation and weaker employment, but “a majority of participants judged the upside risk to inflation as the greater of these two risks,” the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee’s July 29-30 meeting said.
Policymakers left interest rates unchanged in a range of 4.25% to 4.5% last month, citing elevated uncertainty in their outlook as economic activity moderated during the first half of the year. Their statement at the time characterized the labor market as “solid” but said inflation remained “somewhat elevated.”
In his press conference following the meeting, Chair Jerome Powell said the inflationary impact from tariffs could well be temporary, but the central bank needed to guard against a more persistent effect.
Committee members debated whether tariffs would generate a one-time price impact or a more lasting inflation shock.
“Several participants emphasized that inflation had exceeded 2% for an extended period and that this experience increased the risk of longer-term inflation expectations becoming unanchored in the event of drawn-out effects of higher tariffs on inflation,” the minutes said.
Many officials also noted that it could take some time for the full effects of tariffs to be felt in consumer goods and services prices.
The minutes arrived two days before Powell will deliver a closely-watched speech in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, a stage he has previously used to steer investor expectations on interest rates.
Recent economic data has supported the cautious view on inflation, but undermined confidence on employment.
The biggest spike in wholesale inflation in three years provided the latest sign that companies have begun to raise prices to offset rising input costs. Some Fed officials have voiced concerns that the levies will influence prices well into next year.
But large downward revisions to payroll gains revealed weakness in the labor market in the three months through July. Hiring hit its slowest pace since the pandemic and unemployment ticked up to 4.2%.
Even before the release of those numbers, signs of weakness in the jobs market had prompted Governors Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman to dissent at the July meeting in favor of a quarter-point rate cut.
Policymakers will receive another jobs report and more inflation data before they meet again in mid-September.
The minutes also come after President Trump called for the resignation of Fed Governor Lisa Cook after an administration official accused her of mortgage fraud.
Trump has repeatedly called for the Fed to lower interest rates, echoed by his top officials and a growing list of candidates in consideration to succeed Powell when his term as chair ends in May. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent argued last week in favor of a half-point cut by September.
The minutes showed officials held a discussion over financial stability, with several pointing to “concerns about elevated asset valuation pressures.”
In 2024, Kazuo Ueda delivered Japan's first interest rate hike in 17 years, a bold shift for a central bank once dominated by advocates of ultra-loose monetary settings - now, the Bank of Japan head is among the policy board's least hawkish members.
The 73-year-old governor will attend the Federal Reserve's Jackson Hole annual symposium this week, where Chair Jerome Powell's assessment of the American economy and hints on the next U.S. rate cut will be factors in Japan's own deliberations.
Ueda has become one of the more cautious members of the BOJ's nine-member board in recent months and his concerns about the economic impact of U.S. tariffs are likely to provide some restraint among his fellow policymakers who are calling for more rate hikes, analysts and sources say.
An analysis in the BOJ's recent outlook report in part underscores his caution over the expected hit to Japan's economy from tariffs that could complicate its decision around the timing of the next rate hike.
"Japan's trade deal with the U.S. reduced, but did not eliminate, uncertainty over tariffs," said a source familiar with the central bank's thinking, a view echoed by another source. "It's too early for the BOJ to be optimistic on Japan's economy."
Ueda has faced growing calls from within his board to pay more attention to mounting inflationary pressure in Japan's once deflation-prone economy.
A U.S. rate cut could push up the yen against the dollar, which may ease concern about the inflationary impact of a weak yen - but could hurt exporters' profits depending on the pace.
Stubbornly high food inflation has led some BOJ board members to warn of second-round price effects that could warrant another rate hike, a summary of the bank's July meeting showed.
The hawkish signals contrast with Ueda's post-meeting comments justifying going slow on rate hikes on the view underlying inflation, which focuses on domestic demand and wages, remains below the BOJ's target.
"Governor Ueda appears to pay particularly close attention to the U.S. economy," said former BOJ board member Takahide Kiuchi. "If he becomes more convinced that the U.S. economy will stabilise, the BOJ could eye a rate hike this year."
On the surface, the hawks appear to be gaining an upper hand.
Among current board members, three - Naoki Tamura, Hajime Takata and Junko Koeda - are seen by markets as hawks due in part to their recent comments warning that rising food prices could risk leading to broader-based, sustained inflation.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features


Log In
Sign Up