Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)
Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)A:--
F: --
 Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)
U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)
U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
 U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)
U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)
U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)
China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Oct)
Japan Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)
Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)
Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate
Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate--
F: --
P: --
 RBA Rate Statement
RBA Rate Statement RBA Press Conference
RBA Press Conference Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)
U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)
Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)
U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook
EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)
South Korea Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Reuters Tankan Non-Manufacturers Index (Dec)
Japan Reuters Tankan Non-Manufacturers Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Reuters Tankan Manufacturers Index (Dec)
Japan Reuters Tankan Manufacturers Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index MoM (Nov)
Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index YoY (Nov)
Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland PPI YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland PPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
After years of mounting concern over deflation and the bruising price wars that have plagued much of China’s economy, President Xi Jinping’s government is showing signs of finally taking action.
After years of mounting concern over deflation and the bruising price wars that have plagued much of China’s economy, President Xi Jinping’s government is showing signs of finally taking action.
Beijing’s messaging has noticeably shifted in recent weeks, with Xi and other top officials offering their bluntest assessment yet of the cutthroat competition that’s been dragging down prices and profits across industries, from steel and solar panels to electric vehicles. This pivot comes after nearly three years of factory-gate deflation and growing pressure from US tariffs and trade tensions.
Finding a solution would be welcome news for much of the world. A successful effort to rein in industrial overcapacity, long a source of friction with trading partners, stands to ease trade tensions and restore confidence in the globe’s second-biggest economy.
But the path forward is far from clear. Xi’s government must curb excess supply without stalling growth or putting jobs at risk, especially as external demand slows and a lasting trade deal with the US remains elusive.
“If executed right, it could be helpful to global trade, in terms of easing tensions coming from China’s overcapacity, output spilling into the global markets,” Wendy Liu, chief Asia and China equity strategist at JPMorgan Chase & Co., told Bloomberg Television on Wednesday. “But short term, it’s not GDP-friendly or employment-friendly, so it’s a balancing act.”
China reported this week that factory deflation persisted into a 33rd month in June, with the producer price index falling 3.6% from a year earlier. The decline was the most since July 2023 and sharper than any economists had forecast, underscoring the urgency of the problem.
While no formal plan has been announced, optimism is building that a more coordinated policy response is on the way. A meeting this month of the top Communist Party body in charge of economic policy acknowledged the underlying causes of the problem, ranging from local governments’ drive to promote investment to a tax system that favors output over efficiency.
Though it doesn’t directly reference deflation, until recently a taboo topic in Beijing, the assessment “represents the strongest signal yet that Chinese policymakers are intending to tackle disorderly competition and the price wars in sectors like autos,” said Duncan Wrigley, chief China economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics.
It omitted a mention of industry associations — whose efforts at self-regulation have largely failed at limiting production — in what Pantheon said could indicate a new approach “with greater top-down determination.”
Industry groups and official media have echoed the shift in tone, calling for efforts to end the price wars. Some companies in sectors ranging from steel to glassmaking are reportedly planning to cut output. The cost of reinforcing bars, a key steel product used in construction, has fallen to the lowest since 2017, while glass prices are hovering near a nine-year low.
The People’s Bank of China expressed similar concerns, naming “prices running at a low level continuously” as a key challenge of the economy for the first time in recent years. In May, the central bank offered another detailed analysis of downward pressure on prices, which highlighted the limits of relying on monetary easing to reflate the economy under a growth model that’s tilted toward investment and supply.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, or MIIT, met with solar companies, while a group of almost three dozen construction firms signed on to an “anti-involution” initiative, a term used in China to describe intense competition sparked by excess capacity. The government also launched a platform to handle supplier complaints over late payments, part of a broader push to clean up unfair business practices.
For now, the lack of concrete policy measures is tempering expectations. If officials follow through, as they did after a similar meeting early 2024 that led to a consumer goods trade-in program — many economists expect them to reprise a playbook used between 2015 and 2017.
That supply-side reform largely consisted of aggressive cuts of heavy industry capacity including steel and coal, as well as a shantytown redevelopment program that encouraged residents to buy new homes. The effort helped revive commodity prices and home sales. Eventually, it contributed to a recovery in industrial profits and stabilized economic growth.
But the challenge now is more complex. Domestic demand remains weak, export prospects are deteriorating, and many of the sectors engaged in the most intense price wars — like EVs — are dominated by private firms, limiting the government’s ability to impose capacity cuts. Local officials, wary of unemployment, may resist moves that threaten jobs, even if it means keeping unprofitable firms alive.
And while China is eager to defuse the pressure on prices, it’s equally determined to increase its manufacturing might in the face of President Donald Trump’s push to bring more factories back to the US. Beijing is considering a new version of its “Made in 2025” campaign to boost production of high-end technological goods, Bloomberg News previously reported.
For Citigroup Inc., upcoming measures could include capacity cuts in sectors dominated by big state-owned enterprises, such as coal, steel and cement, as well as stricter enforcement of environmental, labor and quality standards in private-dominated industries.
Authorities could also reduce subsidies for industries, including those motivated by local favoritism, or cut export tax rebate, according to a Citi report last week. The latter already happened for products including aluminum, copper and batteries in late 2024.
Officials may also move to rein in bad business practices, such as exploiting suppliers to win lower prices or delaying payments. In March, new rules required firms to pay suppliers within 60 days, and several automakers have since pledged to comply.
Analysts at HSBC Holdings Plc argue that demand-side measures will be equally important, with steps such as improving the social safety net as well as stabilizing employment and the property market.
But longer-term change will require deeper reforms to the China’s growth model, one which relies on investment and production. That could mean adjusting how local officials are evaluated, shifting from pure economic expansion targets to metrics like consumption and income growth, according to Morgan Stanley.
For now, the shift in tone is notable, but the follow-through remains uncertain. “The tone is sharper, the intent more coherent,” Morgan Stanley economists led by Robin Xing wrote in a report. “But no timeline has been laid out, and no mechanism for enforcement has been introduced,” they said, adding that “the gap between diagnosis and delivery remains wide.”
Opec has raised its forecast for world energy demand for the medium and long term as global economies expand and population growth boosts requirements for oil.
Overall energy demand in the long term is expected to increase by 23 per cent to reach 378 million barrels of oil equivalent per day by 2050, the supergroup of oil producers said on Thursday in its World Oil Outlook 2050 report.
In the medium term, global oil demand is projected to increase by 9 per cent to reach 113.3 million barrels per day by 2030, from 103.7 million bpd in 2024, while in the long term, it is forecast to surge by 18.5 per cent to reach 123 million bpd by 2050, Opec said.
This will be driven by “expanding economic growth, rising populations, increasing urbanisation, new energy-intensive industries like artificial intelligence, and the need to bring energy to the billions without it”, Haitham Al Ghais, secretary general of Opec, said.
The global population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, from 8.2 billion in 2024, with the working age population set to increase by 800 million over the same period to reach about 6.1 billion.
The global urbanisation rate is also expected to rise to 68 per cent from 58 per cent during the period, resulting in about 1.9 billion people moving to cities by 2050, Opec said.
The world economy, meanwhile, is set to more than double in size to $358 trillion by 2050, with global average income expected to rise during the period, according to Opec.
Countries outside the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), including India, Africa and Middle East states, are projected to lead the oil demand growth for both medium and long-term forecast periods.
The non-OECD oil demand during the long term is projected to increase by almost 28 million bpd, while OECD oil demand is set to witness a decline of 8.5 million bpd.
Combined demand in India, other Asia, the Middle East and Africa is set to increase by 22.4 million bpd between 2024 and 2050, with India alone adding 8.2 million bpd, the report said. China’s oil demand is projected to increase by less than 2 million bpd over the same period.
Road transport, petrochemicals and aviation are expected to play a key role in boosting demand for oil. The transportation sector accounted for more than 57 per cent of global oil demand in 2024 and is projected to retain this share over the entire forecast period. A significant demand increase of 4.7 million bpd is also projected in the petrochemicals sector.
“Oil underpins the global economy and is central to our daily lives,” Mr Al Ghais said. “There is no peak oil demand on the horizon.”
Opec+ countries have been boosting production since April in anticipation of higher demand after curtaining production for several years.
The group will boost production by 548,000 bpd for August, it said last week, after increasing output by 411,000 bpd for each of May, June and July. The group also approved an increase of 138,000 bpd in April.
"You can see that even with the increases for several months, we haven’t seen a major build-up in inventories, which means the market needed those barrels," Suhail Al Mazrouei, the UAE’s Minister of Energy and Infrastructure, said in Vienna on Wednesday.
"What we want is stability and you cannot be short-sighted just by looking at the price. We need the price to be right for investments to happen," he said, adding that countries with big oil reserves were still not investing enough.
Mr Al Ghais also underscored the importance of boosting investments in the oil sector, with investment requirements of $18.2 trillion until 2050.
“It is vital that these investments are made for consumers and producers everywhere, as well as for the effective functioning of the global economy at large,” Mr Al Ghais said.
Oil markets remained volatile this year amid US President Donald Trump’s tariff plans and the Israel-Iran conflict.
Crude prices started the year strongly. The closing price of Brent, the benchmark for two-thirds of the world's oil, peaked at more than $82 a barrel on January 15, while West Texas Intermediate, the gauge that tracks US crude, hit almost $79 per barrel on that day.
However, demand concerns, a slowing global economy and less-than-stellar growth in China, the world's biggest crude importer, have weighed on crude prices this year.
Mr Trump’s push to impose hefty tariffs on trade partners has been the biggest driver of declining oil prices.
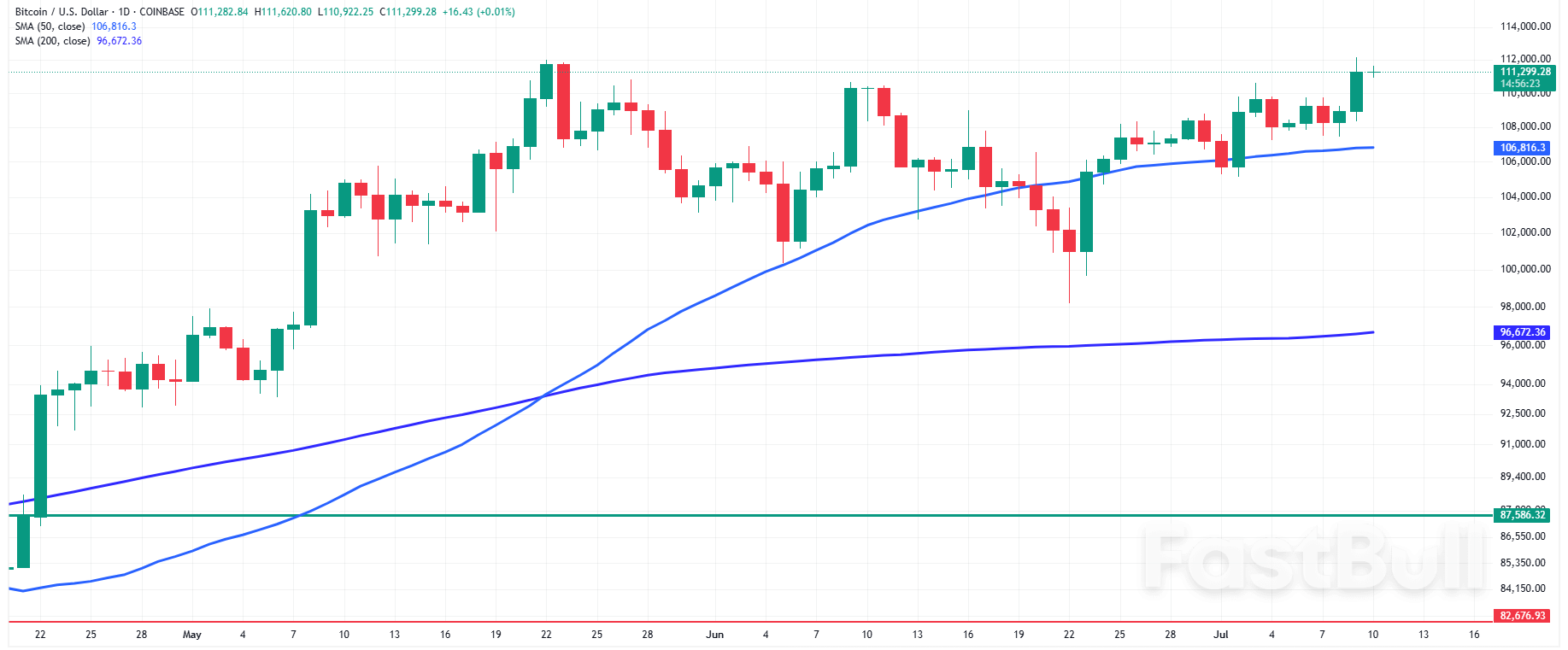 Daily Bitcoin (BTCUSD)
Daily Bitcoin (BTCUSD)
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up