Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil StocksA:--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Unemployment Rate (Not SA) (Nov)
Mexico Unemployment Rate (Not SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoW
U.S. MBA Mortgage Application Activity Index WoWA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Continued Jobless Claims (SA)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)
U.S. Weekly Initial Jobless Claims (SA)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)
U.S. Initial Jobless Claims 4-Week Avg. (SA)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Construction Orders YoY (Nov)
Japan Construction Orders YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan New Housing Starts YoY (Nov)
Japan New Housing Starts YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Capacity Utilization (Dec)
Turkey Capacity Utilization (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tokyo CPI YoY (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)
Japan Tokyo CPI YoY (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Unemployment Rate (Nov)
Japan Unemployment Rate (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tokyo Core CPI YoY (Dec)
Japan Tokyo Core CPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tokyo CPI YoY (Dec)
Japan Tokyo CPI YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Jobs to Applicants Ratio (Nov)
Japan Jobs to Applicants Ratio (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tokyo CPI MoM (Dec)
Japan Tokyo CPI MoM (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Tokyo CPI MoM (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)
Japan Tokyo CPI MoM (Excl. Food & Energy) (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Industrial Inventory MoM (Nov)
Japan Industrial Inventory MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Retail Sales (Nov)
Japan Retail Sales (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Industrial Output Prelim MoM (Nov)
Japan Industrial Output Prelim MoM (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Large-Scale Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Japan Large-Scale Retail Sales YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Industrial Output Prelim YoY (Nov)
Japan Industrial Output Prelim YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Retail Sales MoM (SA) (Nov)
Japan Retail Sales MoM (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Japan Retail Sales YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
Russia Retail Sales YoY (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Russia Unemployment Rate (Nov)
Russia Unemployment Rate (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Argentina Retail Sales YoY (Oct)
Argentina Retail Sales YoY (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central Banks
U.S. Weekly Treasuries Held by Foreign Central Banks--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Industrial Profit YoY (YTD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 India Industrial Production Index YoY (Nov)
India Industrial Production Index YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 India Manufacturing Output MoM (Nov)
India Manufacturing Output MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Dec)
Russia IHS Markit Manufacturing PMI (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 India Manufacturing Output MoM (Nov)
India Manufacturing Output MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 India Industrial Production Index YoY (Nov)
India Industrial Production Index YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 France Unemployment Class-A (Nov)
France Unemployment Class-A (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)
Euro Zone Total Reserve Assets (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Pending Home Sales Index (Nov)
U.S. Pending Home Sales Index (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Pending Home Sales Index MoM (SA) (Nov)
U.S. Pending Home Sales Index MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Pending Home Sales Index YoY (Nov)
U.S. Pending Home Sales Index YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Oil Imports Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Cushing, Oklahoma Crude Oil Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Demand Projected by Production--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Gasoline Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Dallas Fed General Business Activity Index (Dec)
U.S. Dallas Fed General Business Activity Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes
U.S. EIA Weekly Heating Oil Stock Changes--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Crude Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Dec)
U.S. Dallas Fed New Orders Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia CPI YoY (Dec)
Russia CPI YoY (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks Change
U.S. EIA Weekly Natural Gas Stocks Change--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil CAGED Net Payroll Jobs (Nov)
Brazil CAGED Net Payroll Jobs (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Nov)
South Korea Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Retail Sales MoM (Nov)
South Korea Retail Sales MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Services Output MoM (Nov)
South Korea Services Output MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Russia IHS Markit Services PMI (Dec)
Russia IHS Markit Services PMI (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Dec)
Turkey Economic Sentiment Indicator (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Brazil Unemployment Rate (Nov)
Brazil Unemployment Rate (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Oct)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index YoY (Not SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Oct)
U.S. S&P/CS 20-City Home Price Index MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Oct)
U.S. FHFA House Price Index MoM (Oct)--
F: --
P: --





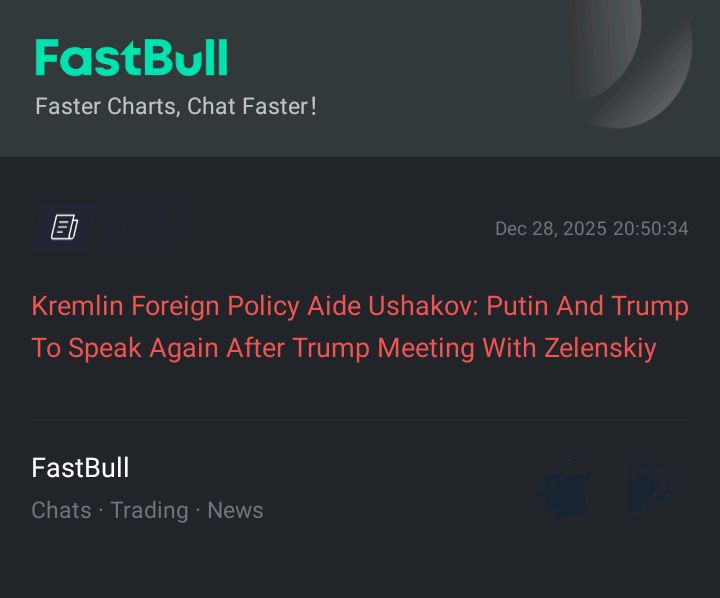

















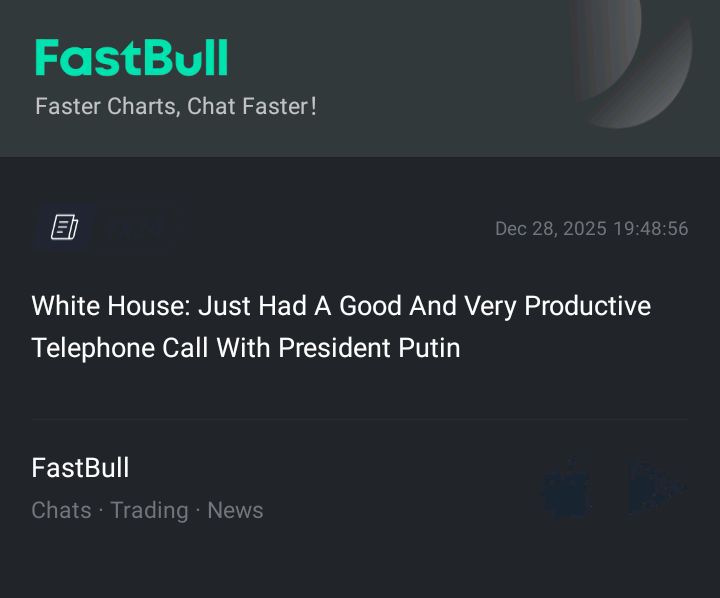
























No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
In the first 11 months of 2025, Vietnam–China cross-border railway freight volume reached nearly 1.072 million tonnes up 29% year-on-year signaling a renewed momentum for trade between the two countries through improved logistics efficiency and border cooperation...
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up