Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)
U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)
U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Dec)
U.S. UMich 5-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim YoY (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)
U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Current Economic Conditions Index Prelim (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Consumer Sentiment Index Prelim (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich 1-Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations Prelim (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Dec)
U.S. UMich Consumer Expectations Index Prelim (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Unit Labor Cost Prelim (SA) (Q3)
U.S. Unit Labor Cost Prelim (SA) (Q3)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)
China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Wages MoM (Oct)
Japan Wages MoM (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Oct)
Japan Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)
Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Oct)
Japan Trade Balance (Customs Data) (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan GDP Annualized QoQ Revised (Q3)
Japan GDP Annualized QoQ Revised (Q3)A:--
F: --
 China, Mainland Exports YoY (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports YoY (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)
Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Leading Index MoM (Nov)
Canada Leading Index MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Dallas Fed PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Dallas Fed PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (USD) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield
U.S. 3-Year Note Auction Yield--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate
Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate--
F: --
P: --
 RBA Rate Statement
RBA Rate Statement RBA Press Conference
RBA Press Conference Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)
U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)
Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico CPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)
U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook
EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield
U.S. 10-Year Note Auction Avg. Yield--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
China is rapidly narrowing the biotech gap with the U.S., driven by state-led strategies, faster regulation, and growing talent, raising concerns in Washington over losing global leadership in critical technologies.
Federal Reserve Governor Adriana Kugler on Thursday said she supports keeping short-term U.S. borrowing costs at their current "moderately restrictive" level as long as tariffs continue to threaten to lift inflation.
"Disinflation has slowed, and we are already seeing the effects of higher tariffs, which I expect will continue to raise inflation over 2025," Kugler said in remarks prepared for delivery to the Economic Club of New York. "I see greater upside risks to inflation at this juncture and potential downside risks to employment and output growth down the road, and this leads me to continue to support maintaining the FOMC’s policy rate at its current setting if upside risks to inflation remain."
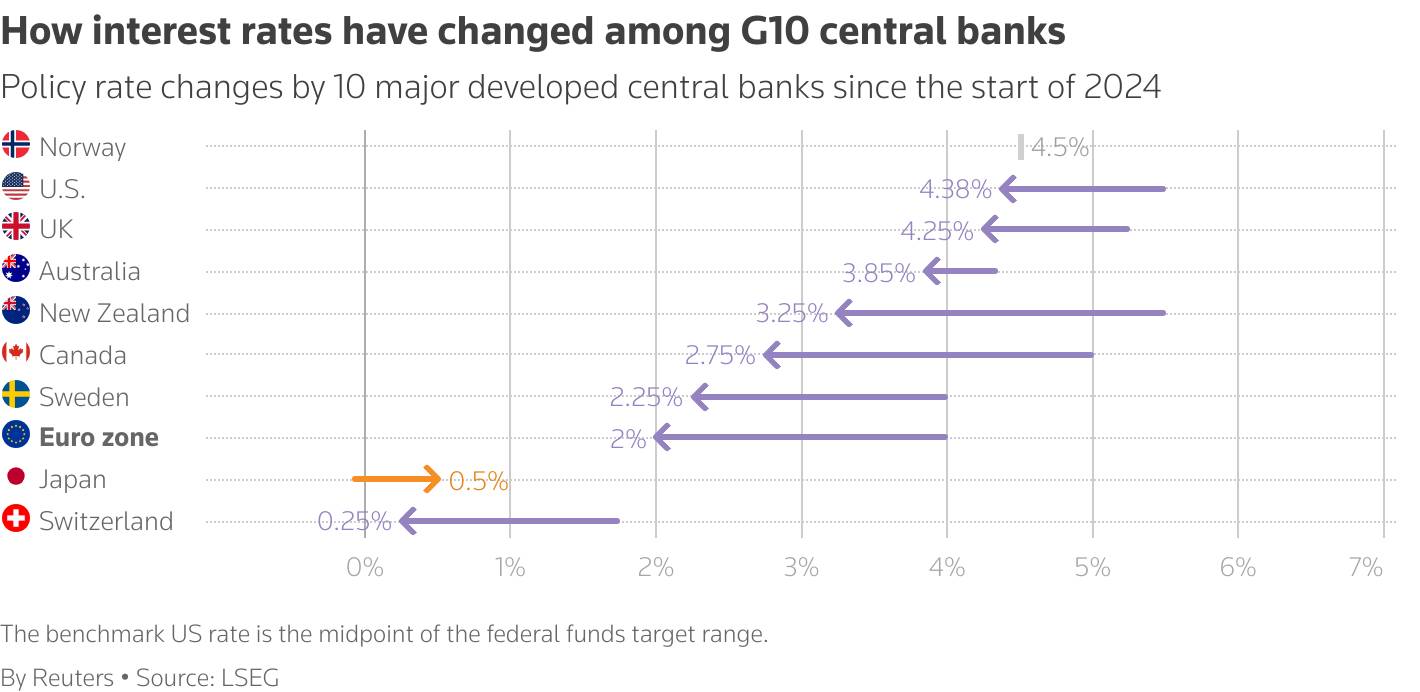
Kugler's remarks, among the last of public comments from Fed policymakers ahead of their June 17-18 meeting, indicate that she sees inflation as the more pressing worry for the Fed. The central bank is widely expected to leave the policy rate in its current 4.25%-4.50% range for the next couple of meetings.
While trade and other policy changes from the Trump administration may increase the jobless rate from its current 4.2% level, she said, so far the labor market looks stable. April spending data and many surveys -- including the Fed's own Beige Book, published on Wednesday -- show a softening in economic activity, she said, but "not yet a significant slowdown."
The inflationary effects of tariffs, on the other hand, are already evident in a reversal of core goods inflation, and research shows not only that tariffs have already added to overall price increases but are likely to continue to do so, and relatively quickly. Meanwhile short-term inflation expectations have increased, and though most readings of long-term inflation expectations have remained stable, she said she is closely monitoring the jump in the University of Michigan survey.
"I view our current stance of monetary policy as well-positioned for any changes in the macroeconomic environment," she said.
The European Union has changed its team locked in trade talks with the Trump administration, bringing in a close aide to European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen to deal more swiftly with political questions arising from the technical negotiations, three sources familiar with the talks said.
The move follows frequent outbursts of frustration by U.S. President Donald Trump at what the White House perceives as slow progress in talks with the EU. Late in May he recommended a 50% tariff on most European goods from June, before backtracking.
The move to bring more political decision-making to the EU team reflects challenges confronting the bloc as it negotiates a trading relationship with a U.S. president who has said repeatedly the EU was established to screw the United States.
It also reflects the difficulties negotiating trade terms in isolation when Trump has sought to fold non-tariff barriers such as digital services taxes and food standards into the talks.
"If you are a trade negotiator you need to be sure you have full political backing, so if the top level is there you feel stronger," one of the sources said.
The expanded team, which apart from the von der Leyen aide now also includes a cabinet member of Trade Commissioner Maros Sefcovic, was dispatched to Washington this week after a call between Trump and von der Leyen in which they agreed to fast-track negotiations.
Following that call Trump agreed to allow more time for talks between Washington and the 27-nation bloc to produce a deal by July 9.
"It was a merger of Commission layers to reinforce and act fast," a second of the sources said of the team's expansion, adding the team's shape could change again as talks continue.
U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer said a meeting with Sefcovic in Paris on Wednesday had been constructive and that he was pleased negotiations were advancing quickly. He noted "a willingness by the EU to work with us to find a concrete way forward to achieve reciprocal trade".
Sefcovic told reporters that both sides had concluded talks were "advancing in the right direction, at pace," and that high-level contacts would follow shortly. He and Greer had agreed how to "restructure" the focus of negotiations with the United States, he added.
Washington was focused on four areas in its negotiations with other countries: tariffs, non-tariff barriers, purchases and economic security, one of the sources said.
Trump has already hit Europe with a 50% tariff on steel and aluminium as well as a heightened levy on car imports. The EU is racing to secure a deal before July 9 when "reciprocal" tariffs on most other goods could surge from 10% to as high as 50%.
Unlike Britain, the first major economy to reach a narrow trade agreement with the Trump administration, the EU is pushing for a comprehensive deal, with a baseline tariff rate below the 10% now in force.
Two of the three sources said additional technical expertise had also been added to the negotiating team, but there had been no changes to the team's leadership.
"I think it suits everyone to have the political cover," the first source said.
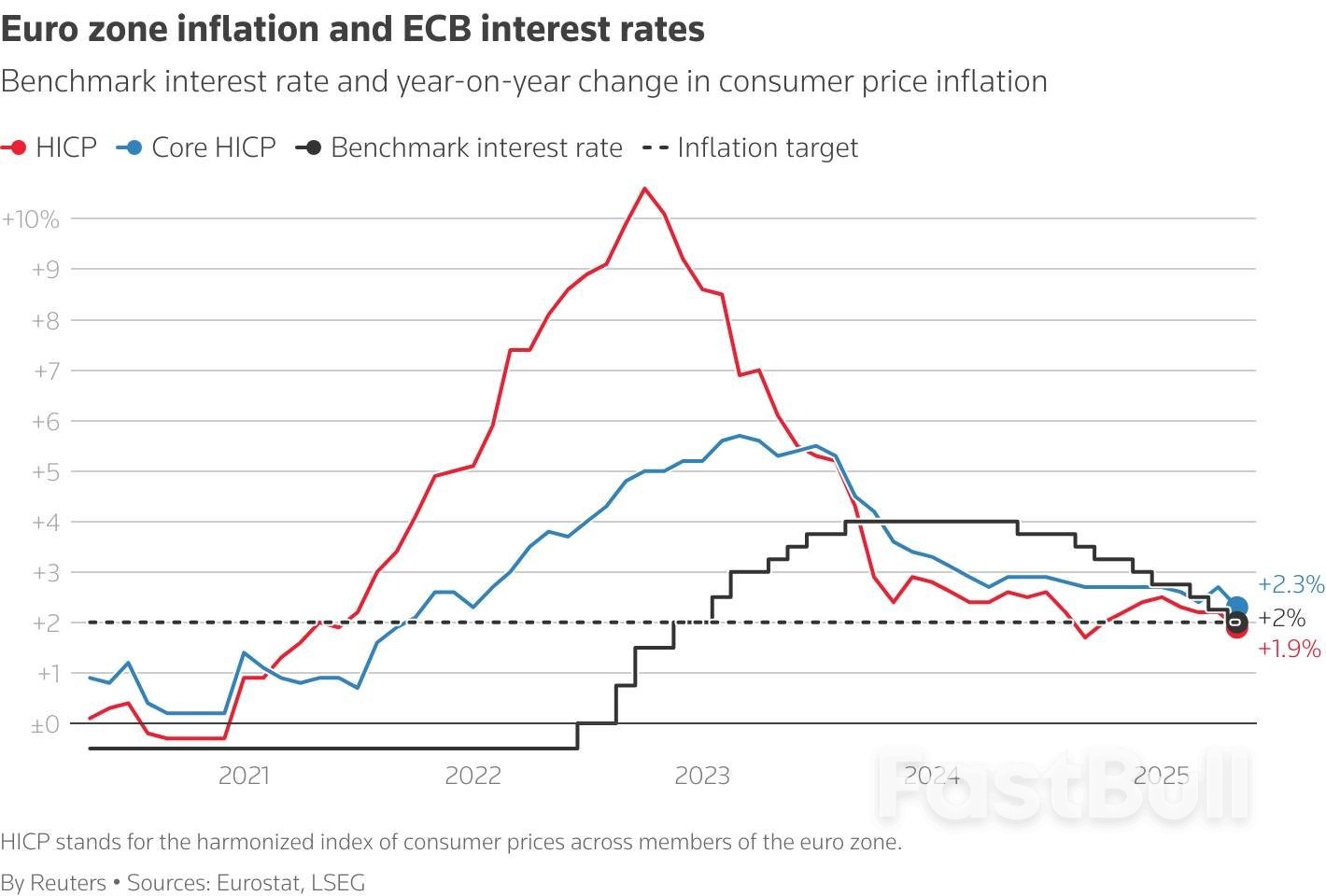
The European Central Bank cut interest rates as expected on Thursday but hinted at a pause in its year-long easing cycle after inflation finally returned to its 2% target.
The ECB has lowered borrowing costs eight times, or by 2 percentage points, since last June, seeking to prop up a euro zone economy that was struggling even before erratic U.S. economic and trade policies dealt it further blows.
With inflation now just below 2%, ECB President Christine Lagarde said the central bank for the 20 countries that share the euro was in a "good position", which investors took as signalling a break in cuts, if not an end to policy easing.
"We are well-positioned after that 25 basis point rate cut and with the rate path as it is," Lagarde told a press conference. "With today's cut, at the current level of interest rates, we believe we are in a good position."
The interest rate path implied by markets sees a pause in July and anticipates just one more cut in the deposit rate toward the end of the year, possibly in December.
"I think we are getting to the end of a monetary policy cycle that was responding to compounded shocks, including COVID, including the war in Ukraine, the illegitimate war in Ukraine, and the energy crisis," Lagarde said.
Economists also saw her words as a clear indication of a pause and some even bet that the ECB's most aggressive easing cycle since the global financial crisis of 2008-2009 might be at a close.
"We think the ECB is done cutting rates now, but this view is contingent on no major negative surprises surfacing and economic outlook to gradually become more robust in line with the ECB's forecasts," Nordea said in a note to clients.
Lagarde said the decision on Thursday was virtually unanimous, with only one policymaker objecting to a cut.
"Our central view is that today's cut is likely the last for some time," HSBC said in a note.
Lagarde also said the euro zone appeared to be attracting more foreign investment, a sign of growing investor confidence and part of the reason why the euro has firmed so much since the U.S. administration embarked on its global trade war.
But there is exceptional uncertainty in the outlook.

European Central Bank (ECB) President Christine Lagarde speaks to the media following the Governing Council's monthly monetary policy meeting in Frankfurt, Germany, March 6, 2025. REUTERS/Jana Rodenbusch/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights, opens new tab
Falling energy prices and a stronger euro could put further downward pressure on inflation, said Lagarde, adding that effect could be reinforced if higher tariffs led to lower demand for euro exports and re-routing of overcapacity to Europe.
Depending on the outcome of the trade war with the United States, inflation and growth could significantly differ from projections, the ECB said, as it took the unusual step of releasing alternative scenarios to its forecasts.
The case for a pause rests on the premise that the short- and medium-term prospects for the currency bloc differ greatly and may require different policy responses.
Inflation is set to dip in the short term and undershoot the ECB's target next year, but increased government spending and higher trade barriers will add to price pressures later.
The added complication is that monetary policy impacts the economy with a 12-to-18 month lag, so support approved now could be giving help to a bloc that no longer needs it.
"In our baseline, we expect the ECB to pause at the July meeting and deliver a final rate cut in September," PIMCO portfolio manager Konstantin Veit said. "A more recessionary configuration will likely be needed for the ECB to go faster and further in this cutting cycle."
A line chart comparing inflation metrics over the past five years.
Acknowledging near-term weakness, the ECB cut its inflation projection for next year.
U.S. President Donald Trump's tariffs are already damaging activity and will have a lasting impact even if an amicable resolution is found, given the hit to confidence and investment.
Most economists think inflation could fall below the ECB's 2% target next year, triggering memories of the pre-pandemic decade when price growth persistently undershot 2%, even if projections show it back at target in 2027.
Further ahead, the outlook changes significantly.
The European Union is likely to retaliate against any permanent U.S. tariffs, raising the cost of trade. Firms could relocate some activity to avoid trade barriers but changes to corporate value chains are also likely to raise costs.
Higher European defence spending, particularly by Germany, and the cost of the green transition could add to inflation while a shrinking workforce due to an ageing population will keep wage pressures elevated.
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up