Markets
News
Analysis
User
24/7
Economic Calendar
Education
Data
- Names
- Latest
- Prev













Signal Accounts for Members
All Signal Accounts
All Contests



 France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
France Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)
France Trade Balance (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)
Euro Zone Employment YoY (SA) (Q3)A:--
F: --
 Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Part-Time Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
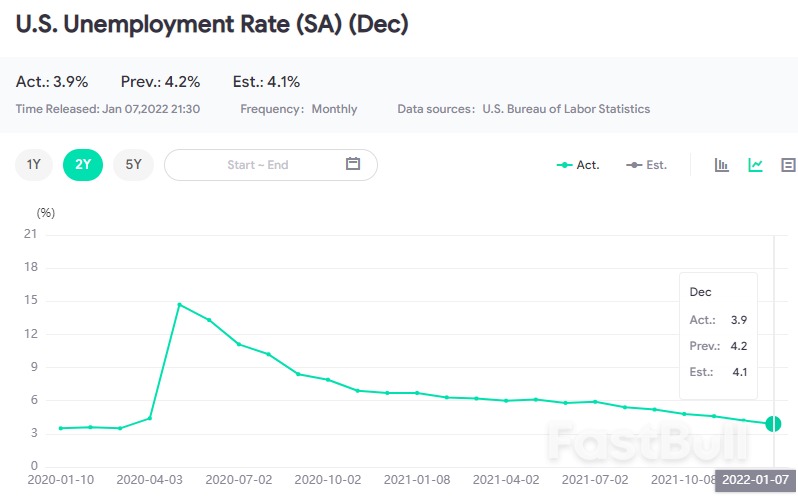
 Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Full-time Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)
Canada Labor Force Participation Rate (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)
Canada Employment (SA) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
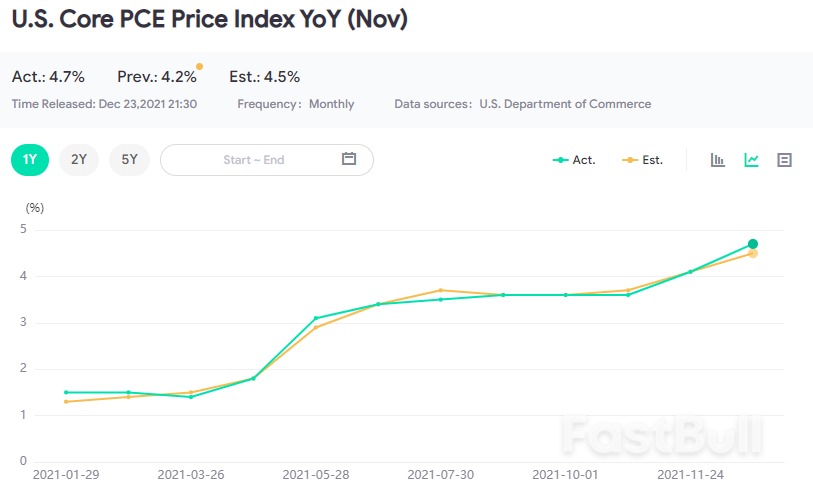
 U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)
U.S. Personal Income MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)
U.S. PCE Price Index YoY (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)
U.S. Core PCE Price Index YoY (Sept)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)
U.S. Personal Outlays MoM (SA) (Sept)A:--
F: --
 U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)
U.S. 5-10 Year-Ahead Inflation Expectations (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)
U.S. Real Personal Consumption Expenditures MoM (Sept)A:--
F: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig Count
U.S. Weekly Total Oil Rig CountA:--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)
U.S. Consumer Credit (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)
China, Mainland Foreign Exchange Reserves (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Trade Balance (Oct)
Japan Trade Balance (Oct)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)
Japan Nominal GDP Revised QoQ (Q3)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)
China, Mainland Trade Balance (CNH) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Exports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)
China, Mainland Imports YoY (USD) (Nov)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Industrial Output MoM (SA) (Oct)A:--
F: --
 Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)
Euro Zone Sentix Investor Confidence Index (Dec)A:--
F: --
P: --
 Canada National Economic Confidence Index
Canada National Economic Confidence Index--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Like-For-Like Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)
U.K. BRC Overall Retail Sales YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate
Australia Overnight (Borrowing) Key Rate--
F: --
P: --
 RBA Rate Statement
RBA Rate Statement RBA Press Conference
RBA Press Conference Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)
Germany Exports MoM (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)
U.S. NFIB Small Business Optimism Index (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)
Mexico 12-Month Inflation (CPI) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico Core CPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)
Mexico PPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY
U.S. Weekly Redbook Index YoY--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)
U.S. JOLTS Job Openings (SA) (Oct)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M1 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M0 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland M2 Money Supply YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Natural Gas Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)
U.S. EIA Short-Term Crude Production Forecast For The Next Year (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook
EIA Monthly Short-Term Energy Outlook U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Gasoline Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Cushing Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Crude Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks
U.S. API Weekly Refined Oil Stocks--
F: --
P: --
 South Korea Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)
South Korea Unemployment Rate (SA) (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Reuters Tankan Non-Manufacturers Index (Dec)
Japan Reuters Tankan Non-Manufacturers Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Reuters Tankan Manufacturers Index (Dec)
Japan Reuters Tankan Manufacturers Index (Dec)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index MoM (Nov)
Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index YoY (Nov)
Japan Domestic Enterprise Commodity Price Index YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland PPI YoY (Nov)
China, Mainland PPI YoY (Nov)--
F: --
P: --
 China, Mainland CPI MoM (Nov)
China, Mainland CPI MoM (Nov)--
F: --
P: --



No matching data
Latest Views
Latest Views
Trending Topics
Top Columnists
Latest Update
White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Affiliate Program
View All

No data
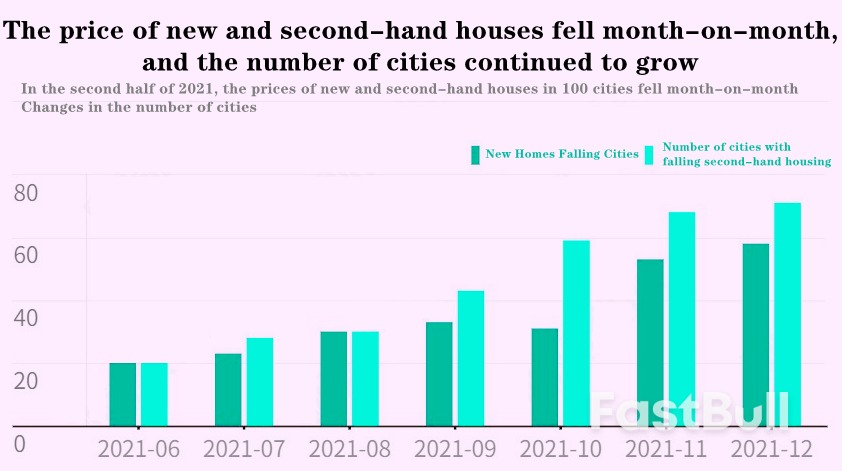
To prevent the economy from recession as a whole, the Fed will still probably choose to raise interest rates, which may be late to cater for the market.

White Label
Data API
Web Plug-ins
Poster Maker
Affiliate Program
The risk of loss in trading financial instruments such as stocks, FX, commodities, futures, bonds, ETFs and crypto can be substantial. You may sustain a total loss of the funds that you deposit with your broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your circumstances and financial resources.
No decision to invest should be made without thoroughly conducting due diligence by yourself or consulting with your financial advisors. Our web content might not suit you since we don't know your financial conditions and investment needs. Our financial information might have latency or contain inaccuracy, so you should be fully responsible for any of your trading and investment decisions. The company will not be responsible for your capital loss.
Without getting permission from the website, you are not allowed to copy the website's graphics, texts, or trademarks. Intellectual property rights in the content or data incorporated into this website belong to its providers and exchange merchants.
Not Logged In
Log in to access more features

FastBull Membership
Not yet
Purchase


Log In
Sign Up